Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
CVE-2024-31333Privilege Escalation affecting Google Android - Privilege Escalation affecting Google Android - This vulnerability allows a local app on an Android device to gain elevated system privileges. This issue stems from a flaw in the PowerVR-GPU, where user input is not properly validated. As a result, a malicious app can execute code with higher privileges than it should have.
PoC for High-Severity SSRF Vulnerability Affecting Apache HTTP (CVE-2024-38472) - On August 4, 2024, security researcher OneArch released a test script for a vulnerability affecting Apache HTTP Server on Windows systems. This vulnerability allows attackers to trick the server into sending sensitive NTLM password hashes to a malicious server. If attackers capture these hashes, they can use them to gain unauthorised access to secure information.
CVE-2024-42219 - Exfiltration of Sensitive Data in 1Password for Mac - This vulnerability allows a malicious process running locally on a Mac to bypass security protections in 1Password, letting an attacker steal sensitive vault items such as passwords and account keys.
Potential Threats
Threat Actors Exploit Google and WhatsApp in a New Phishing Campaign - A phishing campaign uses fake Amazon login pages within trusted apps like Google Drawings and WhatsApp to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
Ongoing Malware Campaign Targets Chrome and Edge Users- A malware campaign has been observed installing rogue Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge extensions via a trojan distributed via fake websites masquerading as popular software.
Microsoft Warns of OpenVPN Vulnerabilities, Potential for Exploit Chains - Microsoft disclosed at the Black Hat conference that OpenVPN vulnerabilities could enable hackers to create exploit chains for remote code execution attacks.
General News
Windows Update Flaws Enable Undetectable Downgrade Attacks - At the Black Hat conference, Alon Leviev revealed critical flaws in Windows Update that allow attackers to downgrade systems and exploit older vulnerabilities. Microsoft is developing security updates, with interim guidance available to mitigate risks.
CISA Warns of Cisco Vulnerabilities - CISA has issued a warning about attackers exploiting misconfigured Cisco devices and weak passwords, including the outdated Smart Install feature, to access system configuration files. The Shadowserver Foundation identified over 6,000 exposed IPs.
New Windows Vulnerability Triggers Blue Screen of Death Security researcher Alex Ionescu has discovered a flaw in Windows that could cause millions of devices to repeatedly crash with the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), risking major disruptions and data loss. The vulnerability affects multiple Windows versions; however, an attacker would need local access to exploit it.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
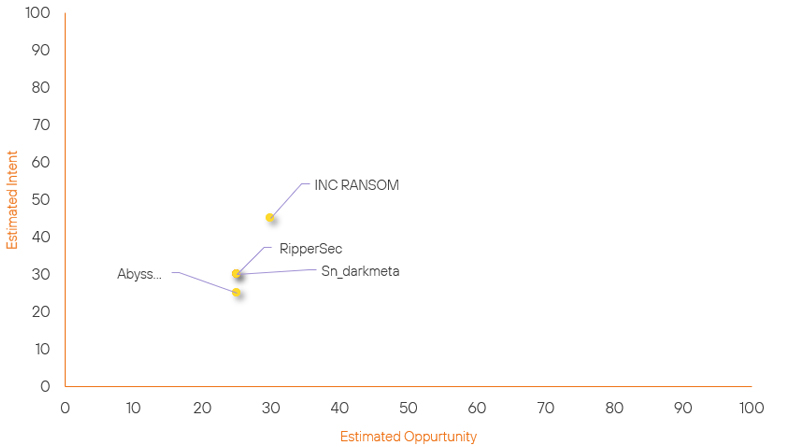
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RipperSec | New | → | Basic | (25) | → 0 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
| Sn_darkmeta | Basic | → | Basic | (25) | → 0 | (30) | ↑ 5 |
| INC RANSOM | Basic | → | Basic | (30) | ↓ 10 | (45) | → 0 |
| Abyss Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (25) | ↓ 10 | (25) | → 0 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iranian Hackers | ▲ | Rhysida | ▲ | CVE-2023-31315 | ▲ | Elon Musk | ▲ |
| ROBERT | ▲ | Cobalt Strike | ▲ | CVE-2024-38077 | ▲ | The New York Times | ▲ |
| WeRedEvilsOG | ▲ | ShadowPad | ▲ | 0.0.0.0 day | ▲ | Apollo Asset Management | ▲ |
| TAG-67 | ▲ | GrewApacha | ▲ | CVE-2024-20419 | ▲ | ADT Security Services | ▲ |
| Chinese Hackers | ▲ | PlugY | ▲ | CVE-2024-38200 | ▲ | Central Bank | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Active Malware Campaign Targeting Chrome and Edge Users
Source: Insikt Group, ReasonLabs | Vulnerability Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA1: b57022344af1b4cf15ead0bb15deacc6acb6ff18
IOC: SHA1: 02eb1f019d41924299d71007a4c7fd28d009563a
IOC: SHA1: 06941262e1361c380acb6f04608ed5ae7d1c9d32
IOC: SHA1: 3bd71a7db286e4d73dd6a3b8ce5245b982cad327
On August 6, 2024, ReasonLabs highlighted an ongoing malware campaign targeting Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge users. Active since 2021, this campaign employs trojan malware distributed through fake software installers and malicious browser extensions.
The malware aims to hijack search queries, steal browsing history, disable browser updates, and maintain control over infected systems while evading antivirus detection.
Victims are tricked into downloading the malware, which is disguised as popular software tools such as Roblox FPS Unlocker, TikTok Video Downloader, or YouTube Downloader. These deceptive installers are promoted through ads in search results on Chrome and Edge. Once downloaded and executed, the malware establishes a scheduled task to ensure its persistence.
This task runs a PowerShell script that retrieves and executes additional malicious payloads from a remote server. It also modifies the Windows Registry to keep the malicious extensions active, even if the user tries to disable them.
The malicious extensions alter browser settings by redirecting homepages and search queries to the attackers' command-and-control (C2) servers. They steal login credentials, monitor online activity, and execute commands from the C2 server. Additionally, the PowerShell payloads disable browser updates, helping the malware maintain control over the compromised system and evade detection and removal efforts.
Apache, CVE-2024-38472.
Source: Insikt Group, GitHub | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-38472 | CVVS Score: 7.5 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Medium – 43
On August 4, 2024, a security researcher OneArch published a proof-of-concept (PoC) script for CVE-2024-38472 found in Apache HTTP Server on Windows, affecting versions 2.4.0 to 2.4.59. This vulnerability is classified as a high-severity server-side request forgery (SSRF) flaw.
It allows attackers to steal NTLM hashes, which are used for authentication in Windows, by tricking the server into sending these hashes to a malicious server. If attackers obtain these NTLM hashes, they could potentially gain unauthorised access to systems.
The problem arises because Apache HTTP Server does not properly handle Universal Naming Convention (UNC) paths, which attackers can exploit to gain access to sensitive information like NTLM hashes.
The proof-of-concept (PoC) developed by OneArch demonstrates how this vulnerability can be exploited. To use the PoC, an attacker would need several details: the target server's IP address, the port it's listening on, the path to the vulnerable application, the UNC path to a malicious server, the URL of an internal service for remote code execution (RCE), and a command to execute. The PoC then verifies if the Apache server is vulnerable, creates an SSRF attack payload, and sends it to the target server.
If the attack is successful, the internal service processes the payload and executes the command, effectively bypassing security measures. A response code of 200 indicates the attack was successful; otherwise, an error message is shown.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned above be fully patched and updated. We want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches should they apply:
- Android CVE-2024-31333 - Install the security updates and patches provided by the vendor.
- Apache POC CVE-2024-38472 - Update Apache HTTP Server to a version newer than 2.4.61
- 1Password CVE-2024-42219 – Update to the versions 8.10.36 and above of 1Password 8 for Mac.
We also recommend proactively checking your environment for the software versions mentioned above and hunting for any known IOCs related to them.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing the searching and hunting activities within your environment.
