Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
CVE-2024-28000- LiteSpeed Cache plugin for WordPress - This vulnerability can be exploited remotely over the network, requiring no user interaction or special privileges. It allows unauthenticated attackers to gain administrative access and control over WordPress sites. With a CVSS score of 9.8, it affects LiteSpeed Cache versions from 1.9 through 6.3.0.1.
CVE-2024-7971 - Critical Type Confusion Vulnerability in Chrome's V8 Engine – This vulnerability can be exploited remotely through crafted HTML pages, requiring no user interaction or special privileges. It allows attackers to corrupt heap memory, leading to arbitrary code execution. With a CVSS score of 8.8, it affects versions before 128.0.6613.84.
CVE-2024-38193 - Critical Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability in Windows AFD.sys - This vulnerability can be exploited locally due to improper handling of operations in AFD.sys, leading to a "Use After Free" condition, which attackers can exploit. With a CVSS score of 7.8, it affects several Windows operating systems such as Windows 10 version 1607 and Windows 11 version 21H2.
Potential Threats
Linux Malware "sedexp" Evades Detection - On August 19, 2024, Stroz Friedberg identified "sedexp," a Linux malware active since 2022. It uses evasion techniques to avoid detection and executes malicious scripts via udev rules when new devices connect. It targets financial data and disguises itself as a legitimate process.
Qilin Ransomware Targets Chrome with New Credential Stealer - On August 22, 2024, Sophos reported that the Qilin Ransomware Group has adopted a new multi-stage attack. It starts with a custom stealer to harvest credentials from Google Chrome, followed by deploying Qilin ransomware to compromise the network further.
New NGate Malware Targets NFC Data on Android Device - On August 25, 2024, The Hacker News reported that a new Android malware strain named Ngate has emerged. This malware utilises NFC (Near Field Communication) technology to steal sensitive information from affected devices.
General News
Microsoft to Host Cybersecurity Summit in Response to Recent IT Outage - Microsoft will host a cybersecurity summit on September 10, 2024, in Washington, D.C., in response to a recent IT outage linked to a vulnerability found by CrowdStrike. The event will gather experts and leaders to discuss security advancements and strategies.
Halliburton Confirms Cyberattack – A cyber-attack targeting Halliburton caused a major systems shutdown at its Houston campus and disrupted global connectivity. Halliburton has confirmed the attack and is working with cybersecurity experts to address the situation.
WhatsApp Verification Code Phishing Scam - The National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) of Ireland has issued a warning about a rise in WhatsApp verification code scams. These attacks are compromising personal accounts and stealing payments and sensitive information. Users should be cautious and protect their verification codes.
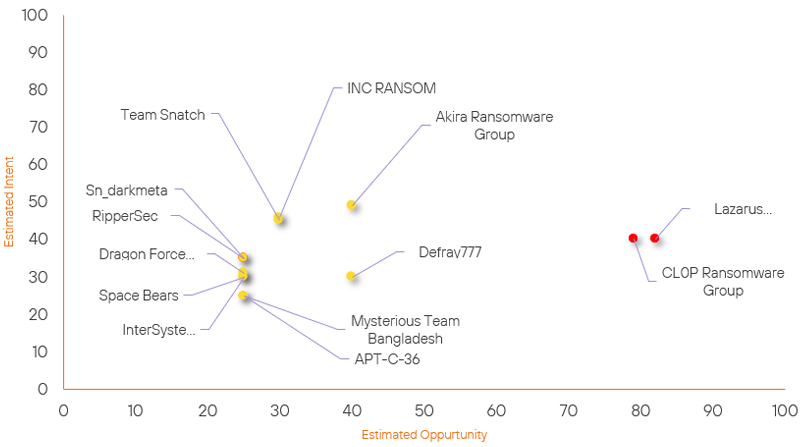
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defray777 | New | → | Basic | (40) | ↑ 40 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
| Space Bears | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 |
(30) | ↑ 30 |
| InterSystems | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
| APT-C-36 | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (25) | ↑ 25 |
| Sn_darkmeta | Basic | → | Basic | (25) | → 0 | (35) | ↑ 5 |
| Dragon Force Group | Basic | → | Basic | (25) | → 0 | (31) | ↑ 5 |
| RipperSec | Basic | → | Basic | (25) | → 0 | (35) | ↑ 5 |
| INC RANSOM | Basic | → | Basic | (30) | → 0 | (46) | ↑ 1 |
| Lazarus Group | High | → | High | (82) | ↑ 1 | (40) | → 0 |
| Team Snatch | Basic | → | Basic | (30) | → 0 | (45) | ↓ 1 |
| Mysterious Team Bangladesh | Basic | → | Basic | (25) | → 0 | (25) | ↓ 5 |
| CL0P Ransomware Group | High | → | High | (79) | → 0 | (40) | ↓ 5 |
| Akira Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (40) | ↓ 5 | (49) | → 0 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iranian Hackers | ▲ | Zero Day Exploit | ▲ | CVE-2024-20399 | ▲ | Transportation | ▲ |
| APT42 | ▲ | RansomHub Ransomware | ▲ | CVE-2024-39717 | ▲ | ▲ | |
| HUNT3R | ▲ | Backdoor | ▲ | CVE-2021-44228 | ▲ | Uber | ▲ |
| Killnet | ▲ | UULoader | ▲ | CVE-2023-42793 | ▲ | French Government | ▲ |
| Kaddu | ▲ | Msupedge | ▲ | CVE-2024-4577 | ▲ | Adobe | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Qilin Ransomware Targets Chrome with New Credential Stealer.
Source: Insikt Group, SOPHOS NEWS | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256: 37546b811e369547c8bd631fa4399730d3bdaff635e744d83632b74f44f56cf6
IOC: SHA256: e4a319f7afafbbd710ff2dbe8d0883ef332afcb0363efd4e919ed3c3faba0342
IOC: SHA256: a996ccd0d58125bf299e89f4c03ff37afdab33fc
IOC: SHA256: 117fc30c25b1f28cd923b530ab9f91a0a818925b0b89b8bc9a7f820a9e630464
On August 22, 2024, Sophos reported that the Qilin Ransomware Group has recently adopted a new tactic that involves targeting credentials stored in Google Chrome browsers.
The attack begins with the exploitation of compromised VPN portal credentials, allowing the actors to gain initial access to the network.
After gaining access, the Qilin group deploys a custom credential stealer specifically designed to harvest account credentials saved in Google Chrome. This process involves running scripts that extract and exfiltrate sensitive data, which is a significant escalation in their attack methods.
Following the credential theft, the ransomware is deployed to encrypt the systems, leaving behind a ransom note demanding payment for decryption.
This two-pronged approach not only compromises data security but also increases the likelihood of successful ransom payments. The shift in tactics by Qilin signals a troubling trend in ransomware attacks, where credential theft is prioritised to facilitate further exploitation.
Organisations are urged to implement stronger security measures, including browser security, regular credential audits, and the enforcement of MFA.
CVE-2024-7971 - Critical Type Confusion Vulnerability in Chrome's V8 Engine
Source: Insikt Group, Bleeping Computer | Vulnerability Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-7971 | CVVS Score: 8.8 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Very Critical – 99
CVE-2024-7971 is a high-severity vulnerability, identified in the V8 JavaScript engine of Google Chrome prior to version 128.0.6613.84.
The vulnerability is categorised as a type confusion issue, which allows a remote attacker to exploit heap corruption by crafting a malicious HTML page. This flaw has been recognised as having significant impacts on confidentiality, integrity, and availability, with a CVSS base score of 8.8.
Current reports indicate that this vulnerability is actively being exploited in the wild.
Google has acknowledged the existence of exploits targeting CVE-2024-7971, confirming that threat actors are utilising this vulnerability to compromise systems.
A public proof of concept (PoC) has been validated, highlighting the vulnerability's potential for exploitation.
Affected versions of Google Chrome include several older releases, such as:
Google Chrome 24.0.1312.56
Google Chrome 54.0.2840.59
Google Chrome 40.0.2214.85
Google Chrome 79.0.3945.79
Google Chrome 33.0.1750.146
To mitigate the risk, users are strongly advised to update to the latest version of Chrome (128.0.6613.84 or higher).
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned above be fully patched and updated. We want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches should they apply:
- CVE-2024-28000 - Update the LiteSpeed Cache plugin to version 6.4 or later.
- CVE-2024-7971 – Update to the latest version of Chrome (128.0.6613.84 or higher).
- CVE-2024-38193 – Update to the latest patched versions available from Microsoft.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing the searching and hunting activities within your environment.
