Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
NachoVPN, PoC Tool to Exploit RCE Vulnerabilities Affecting SonicWall NetExtender and Palo Alto GlobalProtect - On November 26, 2024, cybersecurity firm AmberWolf published multiple write-ups detailing CVE-2024-29014, CVE-2024-5921, and a proof-of-concept (PoC) tool called NachoVPN designed to exploit these vulnerabilities.
Zero Day Vulnerability Affecting Windows Server 2012; No CVE Identifier - On November 28, 2024, 0patch researchers published findings regarding a zero-day vulnerability in Windows Server 2012 and 2012 R2 that bypasses Mark of the Web (MotW) security checks.
VMWare Patches Five Vulnerabilities Affecting VMware Aria Operations - On November 26, 2024, VMware patched five high-severity vulnerabilities affecting VMware Aria Operations version 8.x and VMware Cloud Foundation versions 4.x and 5.x running on Aria Operations.
Potential Threats
Salt Typhoon Employs New GHOSTSPIDER Backdoor - On November 25, 2024, cybersecurity firm Trend Micro published their analysis detailing GHOSTSPIDER, a new backdoor employed by Salt Typhoon, a China-linked advanced persistent threat (APT) group. According to their analysis, Salt Typhoon targeted and compromised various sectors, including telecommunications, government, technology, consulting firms, and non-governmental organisations (NGOs), with operations spanning Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and North America.
Russia-Linked Threat Group RomCom Exploits Firefox and Windows Zero-Days - On November 26, 2024, ESET reported that RomCom, a Russia-nexus group also tracked as Storm-0978, Tropical Scorpius, and UNC2596, exploited two zero-day vulnerabilities affecting Mozilla and Windows software in a chained attack to execute arbitrary code without requiring any user interaction.
PowerSCP Stealer: Ensuring Valid Credential Exfiltration and System Compromise - PowerSCP Stealer, a PowerShell-based credential stealer targeting Windows systems, has been identified by Insikt Group during an investigation of command-and-control (C2) activity linked to the IP address 185.255.178[.]85 (Intelligence Card). This stealer uses SCP (Secure Copy Protocol) for data exfiltration and employs a password input prompt to lure their targets to enter their Windows login password.
General News
Interpol Arrested 1,006 Individuals and Took Down 134,089 Malicious Infrastructures in Operation Serengeti - On November 26, 2024, the International Criminal Police Organization (INTERPOL) announced the arrest of 1,006 individuals and the shutdown of 134,089 malicious infrastructures in nineteen countries across Africa during an operation dubbed Operation Serengeti.
Bank of Uganda Confirms Cyberattack - On November 29, 2024, the Bank of Uganda confirmed a cyberattack that caused significant financial loss. Multiple media sources reported that a Southeast Asia-based threat actor using the alias "Waste" was responsible. The threat actor gained unauthorised access to the bank's IT systems and purportedly transferred 62 billion Ugandan shillings (approximately USD 16.8 million) to accounts in Japan and the United Kingdom.
T-Mobile rebuffed breach attempts by hackers likely connected to China’s Salt Typhoon - T-Mobile recently detected attempts to infiltrate its systems by hackers believed to be linked to the China-backed Salt Typhoon hacking campaign. In a blog post and in comments to Recorded Future News, the company explained that the intrusion attempts “originated from a wireline provider’s network” connected to T-Mobile.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
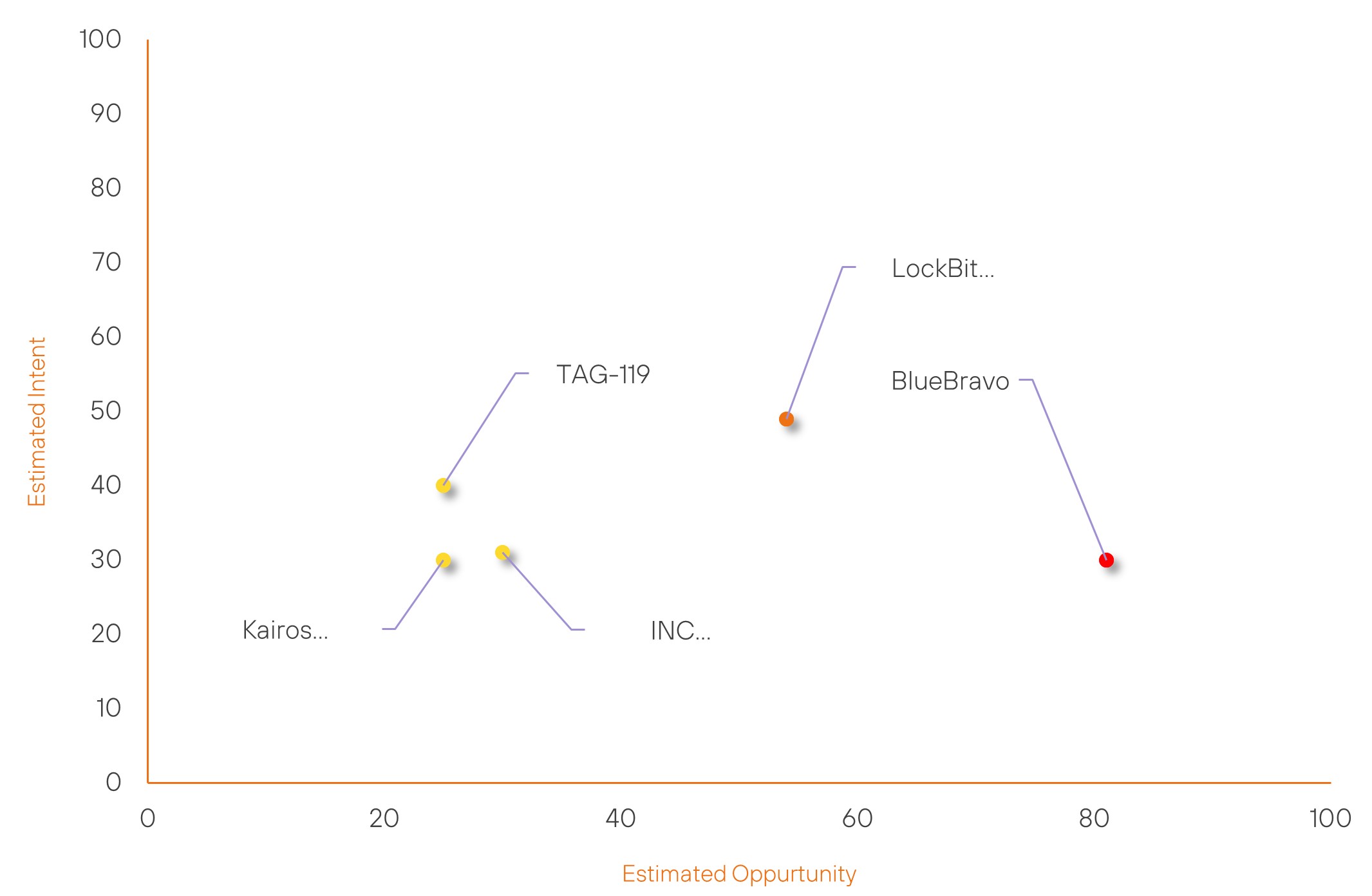
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LockBit Gang | Basic | → | Moderate | (54) | ↑ 19 | (49) | → 0 |
| BlueBravo | High | → | High | (81) | → 0 | (30) | ↑ 5 |
| TAG-119 | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (40) | ↑ 40 |
| Kairos Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
| INC RANSOM | Basic | → | Basic | (30) | → 0 | (31) | ↑ 26 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APT-C-60 | ▲ | SpyLoan | ▲ | CVE-2024-44308 | ▲ | Hyogo | ▲ |
| OsipVoid | ▲ | Network Intrusion | ▲ | BrakTooth | ▲ | Agencia Tributaria | ▲ |
| Eagle Cyber Crew | ▲ | Adware | ▲ | CWE-693 | ▲ | Bologna FC | ▲ |
| Volt Typhoon | ▲ | SmokeLoader | ▲ | LogoFAIL | ▲ | Panasonic Corporation | ▲ |
| Space Bears | ▲ | XWorm | ▲ | CVE-2024-38178 | ▲ | Uganda | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Russia-Linked Threat Group RomCom Exploits Firefox and Windows Zero-Days (CVE-2024-9680 and CVE-2024-49039) to Deploy RomCom Backdoor.
Source: Insikt Group, Mozilla | Vulnerability Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: CVE-2024-9680 | CVVS Score: 6.9 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Medium – 30
IOC: CVE-2024-49039 | CVVS Score: 5.3 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Medium – 26
IOC: SHA256 - a9d445b77f6f4e90c29e385264d4b1b95947add5
IOC: IP – 62[.]60[.]237[.]38
IOC: Domain - journalctd[.]live
IOC: Domain - correctiv[.]sbs
IOC: Domain - cwise[.]store
On November 26, 2024, ESET reported that RomCom, a Russia-nexus group also tracked as Storm-0978, Tropical Scorpius, and UNC2596, exploited two zero-day vulnerabilities affecting Mozilla and Windows software in a chained attack to execute arbitrary code without requiring any user interaction.
The vulnerabilities were CVE-2024-9680, a use-after-free flaw in the animation timeline feature of Firefox, Thunderbird, and Tor Browser, and CVE-2024-49039, a privilege escalation flaw in Windows Task Scheduler. By chaining the vulnerabilities, RomCom was able to execute code within sandboxed environments of target browsers and break out of browser sandboxes, achieving privilege escalation on victims’ systems and deploying the RomCom backdoor without any user interaction. Mozilla patched CVE-2024-9680 on October 9, 2024, and Microsoft addressed CVE-2024-49039 on November 12, 2024.
The campaign, tracked by ESET from October 10, 2024 to November 4, 2024, and mostly targeted entities in Europe and North America, affecting up to 250 victims per country.
The infection chain began with fake websites designed to redirect victims to malicious servers hosting the exploit for CVE-2024-9680. When a victim visited the malicious websites using vulnerable versions of Firefox, Thunderbird, or Tor Browser, the exploit triggered, executing shellcode within the sandboxed browser environment. The shellcode, in turn, ran in two stages: first, it loaded additional code and prepared the environment for further execution; second, it triggered the exploit for CVE-2024-49039 to bypass browser sandboxes and execute arbitrary code with elevated privileges. Following the sandbox escape, the shellcode downloaded and installed the RomCom backdoor from the group’s command-and-control (C2) server.
Salt Typhoon Employs New GHOSTSPIDER Backdoor for Stealthy Espionage Campaigns.
Source: Insikt Group, Trend Micro | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256: 3f9806f7ff5e502081204d98b528e9307eb57aa98ee6f74882c7a9245a90f4e5
IOC: SHA256: 238de794aa3c6a41339aa9cba25fc8e37ec7b8a973d3d74217ff6d175918041b
IOC: Domain: billing.clothworls.com
IOC: Domain: helpdesk.stnekpro.com
IOC: Domain: jasmine.lhousewares.com
IOC: Domain: private.royalnas.com
IOC: Domain: telcom.grishamarkovgf8936.workers.dev
On November 25, 2024, cybersecurity firm Trend Micro published their analysis detailing GHOSTSPIDER, a new backdoor employed by Salt Typhoon, a China-linked advanced persistent threat (APT) group. According to their analysis, Salt Typhoon targeted and compromised various sectors, including telecommunications, government, technology, consulting firms, and non-governmental organisations (NGOs), with operations spanning Asia-Pacific, the Middle East, and North America. GHOSTSPIDER is a multi-modular backdoor capable of secure communication, flexible payload execution, and long-term control over compromised systems.
Salt Typhoon exploits public-facing server vulnerabilities to gain initial access to a target system. These vulnerabilities include authentication bypass and command execution vulnerabilities in Ivanti Connect Secure VPN (CVE-2023-46805, CVE-2024-21887), a SQL injection vulnerability in Fortinet's FortiClient EMS (CVE-2023-48788), a code injection vulnerability in Sophos Firewall's User Portal and WebAdmin (CVE-2022-3236), and chained ProxyLogon vulnerabilities in Microsoft Exchange servers (CVE-2021-26855, CVE-2021-26857, CVE-2021-26858, CVE-2021-27065)
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-29014 – Update to NetExtender Windows version 10.2.341 and higher.
- CVE-2024-5921 – Update to GlobalProtect app 6.2.6 and all later GlobalProtect app 6.2 versions on Windows. Additional fixes are under development for macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
