Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Google Fixes High-Severity Chrome Vulnerability - On December 3, 2024, Google addressed CVE-2024-12053, a high-severity type confusion vulnerability in Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine. This flaw could enable arbitrary code execution and compromise security. Affected versions include Chrome below 131.0.6778.108/.109 on Windows/Mac and 131.0.6778.108 on Linux. Google recommends updating immediately via the “About Google Chrome” menu.
CISA Warns of Active Exploitation of Flaws in Zyxel, ProjectSend, and CyberPanel - On December 4, 2024, CISA added CVE-2024-51378, a critical command injection vulnerability in CyberPanel, to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalogue. The flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary commands, compromising systems. Affected versions include CyberPanel 2.3.5 to 2.3.7. CISA advises updating to the latest version to mitigate risks, as the vulnerability is actively exploited and linked to ransomware campaigns like PSAUX and Helldown.
Cisco Warns of Exploitation of Decade-Old ASA WebVPN Vulnerability - On December 2, 2024, Cisco warned of the active exploitation of CVE-2014-2120, a decade-old cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the WebVPN login page of its Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA). This flaw allows unauthenticated attackers to execute XSS attacks by tricking users into clicking malicious links. Cisco urged users to update to patched versions.
Potential Threats
New Android RAT Called DroidBot - On December 4, 2024, Cleafy LABS reported on DroidBot, an Android RAT targeting the banking and cryptocurrency sectors. It uses Android’s Accessibility services for actions like keylogging and bypassing 2FA. DroidBot operates within a malware-as-a-service model, using encrypted MQTT for C2 communication and allowing affiliates to customise campaigns.
New Tool Lets Red Teamers Execute Commands via Microsoft Teams - On December 9, 2024, CybersecurityNews reported on a red team tool that exploits Microsoft Teams to remotely execute commands. The tool targets businesses by leveraging Teams as a vector for command execution, demonstrating a potential security risk for enterprise communication platforms. It highlights the need for organisations to enhance defences against such attacks.
New QR Code-Based C2 Attack Lets Hackers Bypass All Types of Browser Isolation Security - On December 9, 2024, CybersecurityNews reported on a QR-code-based C2 attack that bypasses browser isolation security. The attack leverages QR codes to enable remote control of compromised devices by bypassing traditional browser isolation mechanisms.
General News
Metadata stolen by Chinese hackers - On December 4, 2024, Reuters reported that Chinese hackers stole Americans' metadata in a cyberespionage campaign targeting U.S. telecom networks. The breach, attributed to the "Salt Typhoon," compromised call records and raised national security concerns. Affected companies are enhancing defences as investigations continue
Microsoft Challenged AI Hackers To Break LLM Email Service - On December 7, 2024, CybersecurityNews reported Microsoft’s challenge inviting hackers and security researchers to uncover vulnerabilities in an AI-powered email service using large language models (LLMs). The competition aimed to identify issues like data leaks or unauthorised access, offering rewards of up to $100,000 for impactful discoveries. Microsoft plans to use these insights to strengthen the security of its AI-based technologies
A New Phone Scanner That Detects Spyware - On December 8, 2024, Wired reported on a mobile tool designed to detect spyware like Pegasus. It helps users identify potential device compromises and offers security recommendations.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
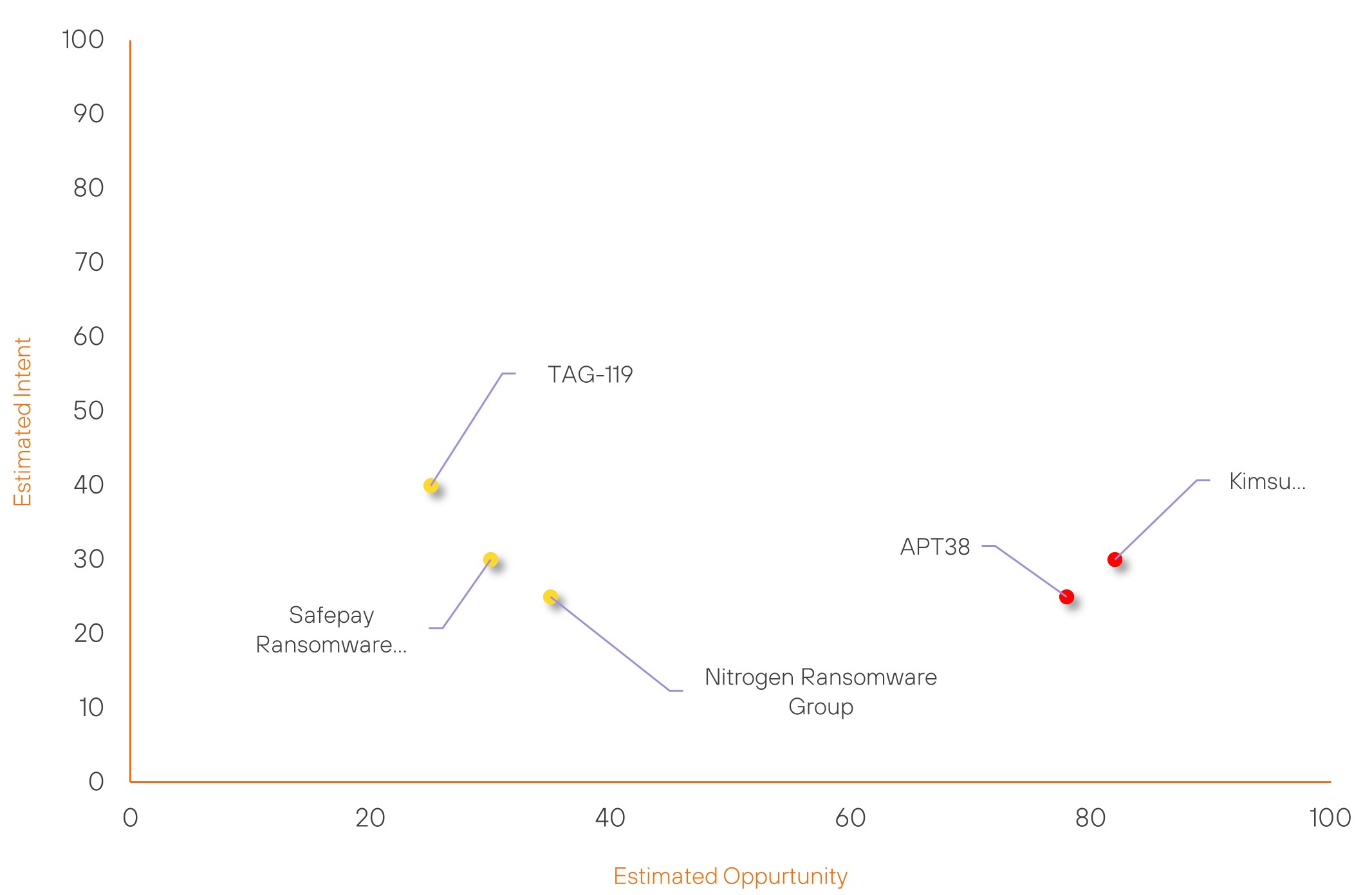
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APT38 | High | → | High | (78) | ↓ 1 | (25) | ↓ 5 |
| Kimsuky | High | → | High | (82) | ↑ 1 | (30) | → 0 |
| TAG-119 | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (40) | ↑ 40 |
| Safepay Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (30) | ↑ 30 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
| Nitrogen Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (35) | ↑ 35 | (25) | ↑ 25 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anonymous | ▲ | Network Intrusion | ▲ | BrakTooth | ▲ | Cardano Foundation | ▲ |
| Brain Cipher Ransomware Group | ▲ | Command Injection | ▲ | CVE-2024-38193 | ▲ | Ultralytics, Inc | ▲ |
| Akira Ransomware Group | ▲ | Supply Chain Attack | ▲ | CVE-2023-46604 | ▲ | Panasonic Corporation | ▲ |
| Termite Ransomware Group | ▲ | XWorm | ▲ | CVE-2024-38178 | ▲ | Communication | ▲ |
| 8Base Ransomware Group | ▲ | C&C Server | ▲ | CVE-2024-0012 | ▲ | Telegram | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Cisco Warns of Exploitation of Decade-Old ASA WebVPN Vulnerability
Source: Insikt Group, The Hacker News | Vulnerability Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: CVE-2014-2120 | CVVS Score: 6.1 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Very Critical – 99
IOC: SHA256 - 22b1fdcd8a40dacc2fc4907a3cd9e25fcbd8a8466ccfd9de0242a6bde5b8e181
IOC: SHA256 - fbe8234329cfc678ca2b51f78b3c6f7886d658b74274bc97c06bffa20cd6b2c7
IOC: SHA256 - 0669b7eaff043cbb9b3e0e590adc14783c4bd4a9fbb054fb810b1d4d9e13363d
IOC: IP - 45.202.35.24
IOC: IP - 154.216.17.31
IOC: Domain - api.next.eventsrealm.com
On December 2, 2024, Cisco disclosed the active exploitation of CVE-2014-2120, a decade-old cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability in the WebVPN login page of its Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA). This vulnerability allows unauthenticated remote attackers to perform XSS attacks by tricking users into clicking malicious links. Cisco urged users of affected software versions to upgrade to patched releases.
On November 6, 2024, cybersecurity firm CloudSEK reported that the AndroxGh0st botnet was exploiting CVE-2014-2120 to expand its operations. Recently, AndroxGh0st integrated payloads and tactics from the Mozi botnet, improving its ability to target Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
However, it remains unclear whether the attacks disclosed by Cisco are directly linked to the AndroxGh0st activity reported by CloudSEK.
On November 12, 2024, CVE-2014-2120 was added to the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency's (CISA) Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalogue.
New Android RAT Called DroidBot
Source: Insikt Group, Cleafy | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256: cc9a45540262aaa9b733384e218512eb596092ef698ba12beb9d239f98e8bbf6
IOC: Domain: k358a192.ala.dedicated.aws.emqxcloud.com
IOC: URL: https://dr0id.best/GETM5662
IPC: URL: https://dr0id.best/errorhandle
On December 4, 2024, Cleafy LABS published a detailed report on DroidBot, an advanced Android remote access trojan (RAT) operating within a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) framework.
DroidBot is notable for combining banking malware techniques, such as overlay attacks and hidden virtual network computing (hVNC), with spyware features like keylogging and full device control via Android Accessibility services. Targeting banking and cryptocurrency sectors across the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Spain, Turkey, and Portugal, DroidBot poses a growing threat, with potential expansion into Latin America based on its language similarities.
The malware disguises itself as legitimate applications, such as banking tools or Google services, to trick users into installation. Once active, it exploits Android Accessibility services to intercept credentials, bypass multi-factor authentication by capturing transaction authentication numbers (TANs) and simulate user actions. Communication with its command-and-control (C2) infrastructure is handled using encrypted protocols like MQTT and HTTPS, enabling it to exfiltrate data and deliver commands efficiently.
As part of its MaaS framework, DroidBot offers a management panel for affiliates to customise and control botnets, harvest credentials, and execute fraud campaigns. Its modular design and widespread capabilities make it a potent tool for cybercriminals, elevating its threat level to individuals and institutions alike. Cleafy LABS emphasises the need for stronger defences to mitigate the risks posed by this evolving malware.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-12053 - Google recommends updating immediately by going to the "About Google Chrome" section in settings, where the browser will automatically check for and install the latest version.
- CVE-2024-51378 - CISA advises updating to the latest version immediately to mitigate risks.
- CVE-2014-2120 - Cisco urges users to update to the latest patched versions.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
