Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Microsoft Patches Actively Exploited CLFS Zero-Day Vulnerability - On December 12, 2024, Microsoft patched CVE-2024-49138, a zero-day vulnerability in the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) driver. Exploited in the wild, this flaw allows attackers to escalate privileges and gain SYSTEM access through a heapbased buffer overflow. The vulnerability affects all supported versions of Windows, including 10, 11, and Server. Microsoft urges users to apply the update immediately to protect against potential attacks, including ransomware campaigns exploiting this vulnerability.
Attackers Exploit Cleo File Transfer Vulnerability - According to TechTarget, a critical vulnerability, CVE2024-50623, is being actively exploited in Cleo’s managed file transfer (MFT) products, including Harmony, VLTrader, and LexiCom. This flaw allows remote code execution through unrestricted file uploads and downloads. Organisations are advised to secure internet-facing systems behind firewalls until a patch is released.
Dell Patched Critical Dell Power Manager Vulnerability - On December 6, 2024, Dell patched a critical vulnerability affecting its Dell Power Manager versions 3.16 and earlier, tracked as CVE-2024-49600. Dell Power Manager is an application designed to optimise system battery life by configuring maintenance settings.
Potential Threats
Latest Zloader Employs DNS Tunneling for C2 Communication - On December 10, 2024, Zscaler ThreatLabz published a write-up detailing the latest Zloader version. Zloader is a modular trojan that originated from Zeus source code. The new Zloader version implements new features, including enhanced anti-analysis techniques, an interactive shell for remote operations, and domain name system (DNS) tunnelling for commandand-control (C2) communications.
Fake SSA Campaign Delivers Trojanised ScreenConnect Software - On December 11, 2024, cybersecurity firm SpiderLabs shared information detailing a campaign that uses fake Social Security Administration (SSA) notifications to deliver a trojanised version of ScreenConnect. Threat actors abuse the inherent remote desktop features of ScreenConnect to take control of a victim’s system.
Insikt Group Detecting TrustFiles Ransomware with YARA and Sigma - Insikt Group recently identified a sample of TrustFiles ransomware, a ransomware family that targets Windows environments. We have found that the sample we observed was submitted to multiple sandboxes beginning in July 2024, and that submission continued through September 2024.
General News
Krispy Kreme Discloses Cyberattack Disrupting US Online Orders - On December 10, 2024, doughnut chain Krispy Kreme reported to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) that unauthorized activity detected on November 29, 2024, had disrupted online ordering across parts of the United States. Although the incident disrupted online services, all physical stores remain open and operational.
Joint Law Enforcement Operation, Operation PowerOFF, Dismantles 27 DDoS-for-Hire Platforms - On December 11, 2024, the European Union Agency for Law Enforcement Cooperation (Europol) announced the shutdown of 27 Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS)-for-hire platforms, the arrest of three administrators, and the identification of 300 threat actors across 15 countries during an operation dubbed Operation PowerOFF.
US sanctions Chinese cyber firm for compromising ‘thousands’ of firewalls in 2020 - Sichuan Silence Information Technology Company and one of its employees, Guan Tianfeng, were the targets of the sanctions, and the Justice Department indicted Guan for his role in the attacks. The State Department also issued a $10 million reward for additional information on the company or Guan.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
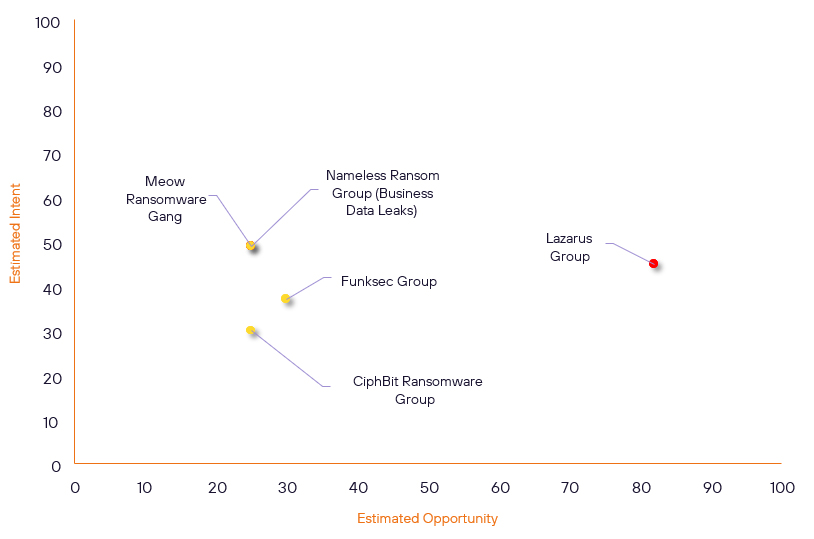
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lazarus Group | High | → | High | (82) | ↓ 1 | (45) | → 0 |
| Nameless Ransom Group (Business Data Leaks) | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (49) | ↑ 49 |
| Meow Ransomware Gang | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (49) | ↑ 49 |
| Funksec Group | New | → | Basic | (30) | ↑ 30 | (37) | ↑ 37 |
| CiphBit Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @Hillzthethird | ▲ | Brain Cipher | ▲ | BrakTooth | ▲ | Deloitte LLP | ▲ |
| Brain Cipher Ransomware Group | ▲ | Malware-as-aService | ▲ | CVE-2024-49848 | ▲ | United States | ▲ |
| miyako | ▲ | Network Intrusion | ▲ | CVE-2024-51378 | ▲ | Telecom Namibia | ▲ |
| APT-C-60 | ▲ | XWorm | ▲ | CVE-2024-48990 | ▲ | Telecom Namibia | ▲ |
| CL0P Ransomware Group (FANCYCAT) | ▲ | Zero Day Exploit | ▲ | CVE-2024-50623 | ▲ | Web Application Technology | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Fake SSA Campaign Delivers Trojanised ScreenConnect Software to Take Over Target Systems
Source: Insikt Group, Polyswarm | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256 - 7fc6d695f877a4f8bfb4c679eae94d5715ab06b9655bf5123c1a3e9d6a85b279
IOC: SHA256 - d23eebf10e0241161cda8ecd880ff0695c6849e3647fb7f776aa2c5be19c5c43
IOC: SHA256 - 936c4a050bce8cbe67cfb5ac6cf8babafdf1d887914423fecc05abf0e40e7525d IOC: IP - 191.96.207.97
IOC: Domain – lucaria[.]site
IOC: URL - hxxps://statement-certification.com/View/re
IOC: URL - hxxps://statement-certification.com/view?token
IOC: URL - hxxps://bitbucket.org/megan12/thankyou/downloads
On December 11, 2024, cybersecurity firm SpiderLabs shared information detailing a campaign that uses fake Social Security Administration (SSA) notifications to deliver a trojanised version of ScreenConnect. ScreenConnect is a legitimate remote desktop and support tool within the ConnectWise suite. ConnectWise is a suite of IT management and remote support tools designed to monitor, manage, and secure systems and networks.
At the time of writing, the C2 servers return error messages while the URLs remain active.
Insikt Group obtained an SSA notification sample shared by SpiderLabs from PolySwarm and Recorded Future Malware Intelligence. Sandbox analysis detected the SSA notification sample as malicious due to the sample exhibiting discovery capabilities. Once executed, the SSA notification sample performs the following actions on a victim’s machine:
- Drops the files “ScreenConnect.ClientService.exe” and “setup.msi” inside the %temp% directory
- Executes setup.msi using msiexec.exe
- Enumerates physical and hard drives connected to the machine
- Retrieves the system language and machine’s geolocation using the Windows registry
- Enables the SeDebugPrivilege security token using the AdjustTokenPrivileges API function to perform actions with elevated privileges
Latest Zloader Version 2.9.4.0 Employs DNS Tunneling for C2 Communication
Source: Insikt Group, Zscaler | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256: a9f2c4bc268765fc6d72d8e00363d2440cf1dcbd1ef7ee08978959fc118922c9
IOC: SHA256: d212042504f851253347754c3d3624628e7ebf7c0bbd8160220bf6edcff24f16
IOC: Domain: bigdealcenter.world
IOC: Domain: ns1.brownswer.com
IOC: URL: https://bigdealcenter.world/
On December 10, 2024, Zscaler ThreatLabz published a write-up detailing the latest Zloader version 2.9.4.0. Zloader is a modular trojan that originated from Zeus source code. According to ThreatLabz, the new Zloader version implements new features, including enhanced anti-analysis techniques, an interactive shell for remote operations, and domain name system (DNS) tunnelling for command-and-control (C2) communications.
Based on ThreatLabz’s write-up, threat actors use social engineering techniques to lure victims into Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) sessions via tools like AnyDesk, TeamViewer, or Microsoft Quick Assist. After establishing access, the threat actors drop an initial payload, such as GhostSocks, which then loads Zloader.
Upon installation, Zloader performs anti-analysis checks, including validating its bot ID by hashing systemspecific values like computer name, username, and installation date. It then modifies its executable header and creates a secondary version of itself to evade detection.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-49138 – Install the latest security updates and monthly rollups provided by Microsoft.
- CVE-2024-50623 - Cleo strongly advises all customers to immediately upgrade instances of Harmony, VLTrader, and LexiCom to the latest released patch (version 5.8.0.21)
- CVE-2024-49600 – Update Dell Power Manager to versions 3.17 or later
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
