Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Fortinet FortiClient EMS Vulnerability CVE-2023-48788 Exploited to Deploy AnyDesk or ScreenConnect - On December 19, 2024, Kaspersky reported that unidentified threat actors exploited CVE2023-48788, an already patched critical vulnerability in Fortinet FortiClient Enterprise Management Server (EMS), to infiltrate the network of an unnamed company. In October 2024, uses these remote access tools (RAT) to deliver additional payloads, steal credentials, and enable lateral movement within networks.
Sophos Patches Critical Vulnerabilities in Firewall Products - Sophos has addressed three critical security vulnerabilities affecting its Firewall products that could allow remote code execution and privileged system access. According to Sophos’s advisory on December 19, 2024, CVE-2024-12727 and CVE-2024-12728, are rated as critical with a CVSS score of 9.8, while CVE-2024-12729 is rated as high severity with a CVSS score of 8.8.
Over 430,000 SonicWall SSL-VPN Exposed on the Internet - Researchers discover over 430,000 SonicWall SSL-VPN devices vulnerable to critical security flaws, with many operating outdated or unsupported firmware. According to a report by Bishop Fox on December 13, 2024, out of 430,363 SonicWall firewalls exposed on the public internet, 119,503 devices remain vulnerable to high or critical severity issues.
Potential Threats
Consistent Scanning for FortiOS SSL VPN Endpoints Linked to Russian VPNs - Insikt Group has identified scanning activity associated with FortiOS SSL VPN endpoints originating from Russian geolocated IP addresses. This request is associated with Fortinet SSL VPN products denoting a login endpoint for deployments of the VPN. Previous reporting has demonstrated that this request may be indicative of threat actors attempting to scan for FortiOS SSL VPN appliances vulnerable to CVE-2022-42475, a heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability that allows adversaries to perform remote code execution (RCE) in victim environments.
Phishing Campaign Targeting European Organizations Aims to Steal Credentials - Since June 2024, the financially motivated threat actor Muddled Libra has targeted over 20,000 European automotive, chemical, and industrial manufacturing organisations in a smishing campaign. Muddled Libra exploited SMS-based authentication to compromise Microsoft Azure cloud infrastructure.
DarkGate Malware Deployment via Microsoft Teams Vishing Attack - On December 13, 2024, Trend Micro reported that an unidentified threat actor launched a Vishing attack via Microsoft Teams call to deploy DarkGate malware. DarkGate malware is multi-functional malware known for its capabilities in data theft, remote access, and facilitating additional malware payloads.
General News
Pirelli Reports Data Breach Affecting Customer Information - On December 19, 2024, Italian tire manufacturer Pirelli Tire LLC notified approximately 332 customers that a data breach suffered between September 18 and September 19, 2024, compromised their sensitive personal information. The compromised data included names and Social Security numbers.
Judge rules NSO Group is liable for spyware hacks targeting 1,400 WhatsApp user devices - The developer of the powerful Pegasus spyware was found liable on Friday for its role in the infection of devices belonging to 1,400 WhatsApp users. The precedent-setting ruling from a Northern California federal judge could lead to massive damages against NSO Group, whose notorious spyware has been reportedly used, and often abused, by a roster of anonymous government clients worldwide.
US seeks extradition of alleged LockBit ransomware developer from Israel - The United States is attempting to extradite an Israeli citizen, Rostislav Panev, who is charged with working as a software developer for the LockBit ransomware group.Panev is accused of assisting LockBit between 2019 and 2024.
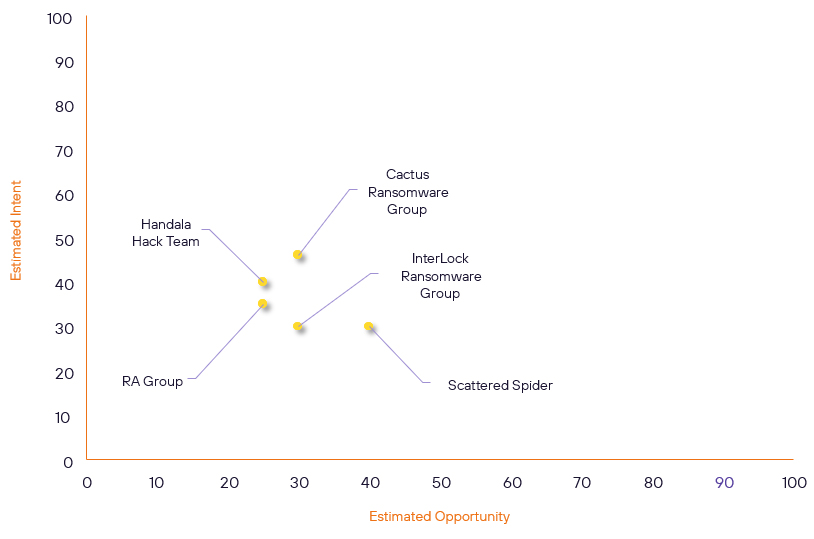
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handala Hack Team | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↓ 1 | (40) | → 0 |
| InterLock Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (30) | ↑ 30 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
| RA Group | Basic | → | Basic | (25) | ↓ 5 | (35) | ↓ 5 |
| Cactus Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (30) | → 0 | (46) | ↑ 5 |
| Scattered Spider | Basic | → | Basic | (40) | ↓ 5 | (30) | → 0 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @Hillzthethird | ▲ | Malware-as-aService | ▲ | BrakTooth | ▲ | Deloitte LLP | ▲ |
| APT-C-60 | ▲ | Network Intrusion | ▲ | CVE-2024-56145 | ▲ | ▲ | |
| Lazarus Group (Cyber Warfare Guidance Unit, Diamond Sleet) | ▲ | XWorm | ▲ | CVE-2023-48788 | ▲ | Palo Alto Networks Firewall | ▲ |
| Mysterious Team Bangladesh | ▲ | Pegasus | ▲ | CVE-2024-53376 | ▲ | Saint-Petersburg State University | ▲ |
| miyako | ▲ | Mirai | ▲ | CVE-2024-51378 | ▲ | National Bureau of Statistics | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
DarkGate Malware Deployment via Microsoft Teams Vishing Attack
Source: Insikt Group, TrendMicro | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256 - 4e291266399bd8db27da0f0913c041134657f3b1cf45f340263444c050ed3ee1
IOC: SHA256 - bb56354cdb241de0051b7bcc7e68099e19cc2f26256af66fad69e3d2bc8a8922
IOC: SHA256 – 1cbda9a3f202e7aacc57bcf3d43ec7b1ca42564a947d6b5a778df90cddef079a
IOC: SHA256 - faa54f7152775fa6ccaecc2fe4a6696e5b984dfa41db9a622e4d3e0f59c82d8b
IOC: SHA256 - e4d13af4bfc3effe4f515c2530b1b182e18ad0c0a3dacac4dd80d6edcf0b007a IOC: IP – 179[.]60[.]149[.]194
On December 13, 2024, Trend Micro reported that an unidentified threat actor launched a Vishing attack via Microsoft Teams call to deploy DarkGate malware. DarkGate malware is multi-functional malware known for its capabilities in data theft, remote access, and facilitating additional malware payloads. Trend Micro confirmed that no activities related to exfiltration occurred, and the attack was prevented before the threat actors achieved their goal.
The DarkGate infection chain begins with social engineering tactics via a Microsoft Teams vishing call. The threat impersonated a victim's client and tricked them into downloading AnyDesk after failing to install a Microsoft Remote Support application. Once the victim provides credentials to AnyDesk, the threat actors gain remote access to the system.
After gaining access, the threat actor deployed malicious files, including a DLL file, SafeStored.dll, executed via DLL sideloading techniques. The DLL file enabled the execution of commands such as systeminfo, route print, and ipconfig /all to gather system and network information. Subsequently, the threat actor deployed DarkGate malware named”SystemCert.exe“ which created an AutoIt script, script.a3x, and its interpreter, AutoIt3.exe. The AutoIt script executed as shellcode and injected itself into legitimate processes, including MicrosoftEdgeUpdateCore.exe.
The injected process is connected to the threat actors’ command-and-control (C2) server, 179[.]60[.]149[.]194, allowing the deployment of additional payloads. To maintain persistence, the threat actors created redundant copies of files, such as AutoIt3.exe and bbbckdb.a3x, across multiple directories, and added a registry entry at HKCU\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run to ensure execution on startup.
Phishing Campaign Targeting European Organizations Aims to Steal Credentials, Taking Over Microsoft Azure Cloud Infrastructure.
Source: Insikt Group, Palo Alto | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256: b2ca9c6859598255cd92700de1c217a595adb93093a43995c8bb7af94974f067
IOC: SHA256: f3f0bf362f7313d87fcfefcd6a80ab0f18bc6c5517d047be186f7b81a979ff91
IOC: SHA256: deff0a6fbf88428ddef2ee3c4d857697d341c35110e4c1208717d9cce1897a21
IOC: URL: hxxps://share-eu1.hsforms[.]com/1P_6IFHnbRriC_DG56YzVhw2dz72l
IOC: URL: hxxps://share-eu1.hsforms[.]com/1UgPJ18suRU-NEpmYkEwteg2ec0io
IOC: URL: hxxps://share-eu1.hsforms[.]com/12-j0Y4sfQh-4pEV6VKVOeg2dzmbq IOC: IP: 167[.]114[.]27[.]228
Since June 2024, the financially motivated threat actor Muddled Libra has targeted over 20,000 European automotive, chemical, and industrial manufacturing organisations in a smishing campaign. Muddled Libra exploited SMS-based authentication to compromise Microsoft Azure cloud infrastructure. According to a December 18, 2024 report by Palo Alto, Muddled Libra specifically targeted customer support accounts, searching for financial data and other sensitive information. The phishing campaign was still active as of September 2024.
The attack began with Muddled Libra using fake messages impersonating a single sign-on (SSO) provider that contained malicious content, including DocuSign-enabled PDF files and embedded HTML links. Accessing these links redirected victims to a fake HubSpot Free Form Builder login page designed to steal Microsoft Azure cloud credentials and multi-factor authentication (MFA) tokens.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2023-48788 – Upgrade to FortiClientEMS version 7.0.11 or above or 7.2.3 or above
- CVE-2024-12727, CVE-2024-12728, CVE-2024-12729 – Apply the provided Hotfixes by Sophos as soon as possible
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
