Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
PoC Exploit for CVE-2024-53677 - On December 11, 2024, Apache disclosed a critical vulnerability in Apache Struts 2, an open-source web application framework used for building Java-based web applications. The path traversal vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-53677, allows attackers to conduct unauthorised file uploads through the framework’s file upload mechanism under some circumstances, which can lead to remote code execution (RCE).
State-Sponsored Threat Group Exploit CVE-2024-9474 - On December 24, 2024, Northwave reported that an unidentified state-sponsored threat group exploited CVE-2024-9474, a recently patched privilege escalation vulnerability affecting Palo Alto Networks Firewall. This exploitation led to the deployment of a backdoor named LITTLELAMB.WOOLTEA that enabled persistent access and control over compromised devices.
CVE-2024-41713 and New CVE-2024-55550 Affecting Mitel MiCollab VoIP Platform - On December 5, 2024, cybersecurity firm watchTowr Labs detailed multiple vulnerabilities in Mitel's MiCollab Voice over IP (VoIP) platform. The vulnerabilities include a critical SQL injection vulnerability (CVE-2024-35286) in version 9.8.0.33 and earlier, a critical path traversal vulnerability (CVE-2024-41713) in version 9.8.1.201 and earlier, and a newly identified medium severity arbitrary file read vulnerability (CVE-2024-55550) in version 9.8 and earlier.
Potential Threats
Threat Actors Exploit IoT Devices to Deploy New Mirai-based Variant - Threat actors are exploiting vulnerabilities in network video recorders (NVRs), routers, and digital video recorders (DVRs) to deploy a Miraibased malware variant dubbed “Hail Cock Botnet”. Recent findings by Akamai on December 19, 2024, reveal that the malware has been active since at least September 2024, although the overall campaign is part of a disparate Mirai campaign that began in October 2024.
Malicious Cyberhaven Chrome Extension Published after Phishing Cyberattack - On December 24, 2024, Cyberhaven revealed that threat actors gained access to Cyberhaven Chrome Web Store credentials and used these compromised credentials to push a malicious Cyberhaven Chrome extension update. Threat actors gained access to the credentials by successfully phishing a Cyberhaven employee.
APT Group Cloud Atlas Employs New VBCloud Backdoor - On December 23, 2024, Kaspersky’s Securelist published a write-up detailing new TTPs employed by the advanced persistent threat (APT) group Cloud Atlas. Cloud Atlas, active since 2014, uses phishing emails with malicious RTF attachments to deploy malware. Per SecureList, they observed Cloud Atlas’s recent campaign using a new backdoor called VBCloud, replacing previous DLL-based malware loaders.
General News
ZAGG iPhone Case Maker Hit by Third-Party Breach - On December 26, 2024, consumer electronics Zagg Incorporated notified individuals about a data breach involving a third-party application managed by their e-commerce provider, BigCommerce. An unknown threat actor injected malicious code into the FreshClicks application, hosted on BigCommerce’s app marketplace.
Blue Yonder says November ransomware attack not connected to Cleo vulnerability - Blue Yonder, the supply chain management giant that was hit by a ransomware attack last month that caused ripples throughout the retail sector, said it is investigating claims of data theft made by a ransomware gang on Christmas Eve. The Clop ransomware operation said it stole information from Blue Yonder and dozens of other companies through a recently discovered zero-day vulnerability in file-sharing software from Cleo.
White House Names Ninth Victim of Salt Typhoon Telecommunications Cyberattacks - This announcement follows disclosures of Salt Typhoon’s previous attacks on telecommunications companies TMobile, AT&T, Lumen Technologies, Verizon, and other US telecommunications and internet service providers.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
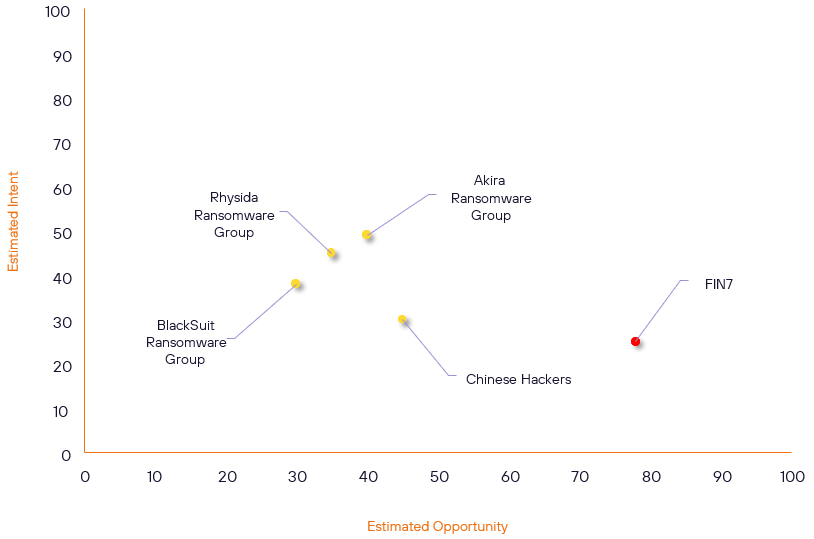
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akira Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (40) | → 0 | (49) | ↑ 5 |
| Rhysida Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (35) | ↓ 5 | (45) | ↓ 1 |
| BlackSuit Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (30) | → 0 | (38) | ↓ 5 |
| FIN7 | High | → | High | (78) | ↓ 8 | (25) | → 0 |
| Chinese Hackers | Basic | → | Basic | (45) | → 0 | (30) | ↑ 5 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salt Typhoon (FamousSparrow, GhostEmperor, UNC2286) | ▲ | Cyber espionage | ▲ | BrakTooth | ▲ | Alphabet Inc. | ▲ |
| APT-C-60 | ▲ | Malware-as-aService | ▲ | CVE-2019-0708 (BlueKeep) | ▲ | Chrome Extensions | ▲ |
| NoName057(16) | ▲ | Network Intrusion | ▲ | CVE-2024-45387 | ▲ | Volkswagen AG | ▲ |
| CL0P Ransomware Group (FANCYCAT) | ▲ | XMRig Miner | ▲ | CVE-2023-4147 | ▲ | Cyberhaven | ▲ |
| miyako | ▲ | 2FA Bypass | ▲ | CVE-2024-50623 | ▲ | Italy | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
APT Group Cloud Atlas Employs New VBCloud Backdoor.
Source: Insikt Group, Securelist | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256 - b2769bc8a25ee6b65e58b6f2795316d67771c54b9a423bf02c3779d63b08bc4a
IOC: Domain – kim[.]nl[.]tab[.]digital
IOC: Domain – webdav[.]mydrive[.]ch
IOC: URL - hxxps://webdav.yandex.ru/kzknvcqjseub/zmfaufpyegu.txt
IOC: URL - hxxps://webdav.yandex.ru/cdyoqavfufbc/
On December 23, 2024, Kaspersky’s Securelist published a write-up detailing new TTPs employed by the advanced persistent threat (APT) group Cloud Atlas. Cloud Atlas, active since 2014, uses phishing emails with malicious RTF attachments to deploy malware, primarily targeting Eastern Europe and Central Asia. Per SecureList, they observed Cloud Atlas’s recent campaign using a new backdoor called VBCloud, replacing previous DLL-based malware loaders.
Based on Securelist’s write-up, the campaign uses a phishing email with a malicious document attachment. When opened, the document downloads a malicious RTF template from a remote server controlled by Cloud
Atlas. The malicious RTF template exploits CVE-2018-0802, a remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in Microsoft Office’s Equation Editor, to download an HTA file from Cloud Atlas’s server. Once executed, the HTA file uses New Technology File System (NTFS) Alternate Data Streams (ADS) to stealthily extract and write files that make up the VBShower backdoor. The VBShower backdoor consists of a launcher, a cleaner, an encrypted payload, and additional scripts. The HTA file also adds a Windows registry Run key named “dmwappushservice” to execute the VBShower launcher when a user logs in.
The VBShower launcher decrypts the encrypted backdoor payload and executes it. The decrypted VBShower payload performs the following actions on a victim’s machine:
- Checks whether the Windows registry Run key named “dmwappushservice” exists and restores it if missing
- Downloads encrypted VB scripts from a command-and-control (C2) server and runs them in memory; if the downloaded scripts weigh more than 1 MB, VBShower stores them in ADS and executes them via “wscript”
- Checks whether the ADS contains a TMP file and sends it to the C2 server
Threat Actors Exploit Multiple Vulnerabilities in IoT Devices to Deploy New Miraibased Variant “Hail Cock Botnet” in Ongoing Campaign.
Source: Insikt Group, Akamai | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256: 3c0eb5de2946c558159a6b6a656d463febee037c17a1f605330e601cfcd39615
IOC: SHA256: 0d8c3289a2b21abb0d414e2c730d46081e9334a97b5e0b52b9a2f248c59a59ad
IOC: SHA256: b32390e3ed03b99419c736b2eb707886b9966f731e629f23e3af63ea7a91a7af
IOC: IP: 5[.]39[.]254[.]71
IOC: IP: 149[.]50[.]106[.]25
IOC: IP: 45[.]202[.]35[.]24
Threat actors are exploiting vulnerabilities in network video recorders (NVRs), routers, and digital video recorders (DVRs) to deploy a Mirai-based malware variant dubbed “Hail Cock Botnet”. Recent findings by Akamai on December 19, 2024, reveal that the malware has been active since at least September 2024, although the overall campaign is a part of a disparate Mirai campaign that began in October 2024.
One of the vulnerabilities exploited in this campaign is an unspecified remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in DigiEver DS-2105 Pro DVR. This vulnerability was identified by Ta-Lun Yen, a researcher from TXOne, during an analysis of exposed DVR devices presented at the DefCamp security conference in 2023. Additional vulnerabilities exploited in this campaign include CVE-2023-1389 in TP-Link routers and CVE2018-17532 in Teltonika RUT900, RUT950, and RUT955 routers.
The infection chain begins with threat actors scanning for publicly-exposed DVR instances. After identifying vulnerable devices, they exploit the aforementioned RCE vulnerability by sending HTTP POST requests that inject malicious commands. This allows the threat actors to download and execute the Hail Cock Botnet from a command-and-control (C2) server, adding the compromised devices to a botnet.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-53677 – Upgrade at least to Struts version 6.4.0 and migrate to the new file upload mechanism.
- CVE-2024-9474 – Update to the latest version of PAN-OS.
- CVE-2024-35286, CVE-2024-41713, CVE-2024-55550 – Update to the latest version of MiCollab
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
