Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Dell Patches XSS Vulnerability CVE-2025-22402 Affecting Dell UMP - Dell patched a cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability affecting Dell Update Manager Plugin (UMP) versions 1.5.0 to 1.6.0, tracked as CVE-2025-22402. Dell UMP is designed to manage repositories of update packages for PowerEdge devices managed within Dell OpenManage Enterprise.
Over 12,000 Kerio Control Firewalls Vulnerable to RCE Flaw, CVE-2024-52875 - On February 10, 2025, the Shadow Server Foundation reported that over 12,000 GFI Software Kerio Control firewall instances remain vulnerable to a critical remote code execution (RCE) flaw, CVE-2024-52875, even though it was patched on December 19, 2024.
Fortinet Patches FortiOS Privilege Escalation Vulnerability, CVE-2024-40591 - On February 11, 2025, Fortinet patched CVE-2024-40591, a high-severity privilege escalation vulnerability affecting its FortiOS Security Fabric. CVE-2024-40591 allows an authenticated administrator with Security Fabric permissions to escalate their privileges to the super-admin level due to improper privilege management. FortiOS versions 7.6.0, 7.4.0 through 7.4.4, 7.2.0 through 7.2.9, 7.0.0 through 7.0.15, and all versions of 6.4 are impacted.
Potential Threats
Phishing Campaign Uses CAPTCHA to Steal Financial Data via Fraudulent PDFs - On February 12, 2025, Netskope Threat Labs reported an ongoing phishing campaign that abuses Webflow's content delivery network (CDN) to host malicious PDFs containing CAPTCHA images embedded with phishing links. The campaign ultimately seeks to steal financial and personal data.
Threat Actors Distribute NetSupport RAT via Fake Cisco AnyConnect Installer in Malvertising Campaign - On February 5, 2025, Malwarebytes reported a malvertising campaign distributing NetSupport RAT via a fake Cisco AnyConnect installer. Threat actors behind the campaign used Google ads and impersonated Technische Universität Dresden’s website to evade detection. According to Malwarebytes, the infection chain begins with a Google advertisement when victims search for Cisco AnyConnect on Google. After clicking the ad, victims are redirected to the threat actors’ malicious website, where the fake Cisco AnyConnect installer is embedded and signed with a valid certificate.
Flesh Stealer Malware Targets Browsers and Messaging Apps to Steal Credentials - On February 4, 2025, Cyfirma reported Flesh Stealer, a . NET-based malware written in C# that targets web browsers and messaging applications to steal credentials, cookies, browsing history, and chat logs. The targeted browsers include Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Opera, while the targeted messaging applications include Signal and Telegram. According to Cyfirma, Flesh Stealer first appeared in August 2024 and continues to receive updates, with the latest version supporting Chrome version 131.
General News
Cybercrime evolving into national security threat: Google - Cybercrime continues to expand and evolve and has become a national security-level threat that is enabling more attacks by state-backed groups, Google warned in a new report. Released ahead of the Munich Security Conference, the Google Threat Intelligence Group and Mandiant research covers their investigations throughout 2024 and observations from the last four years.
Apple fixes security flaw allowing third-party access to locked devices - Apple on Monday announced it has fixed its mobile operating systems in response to a newly uncovered vulnerability that the company said may have been used in an “extremely sophisticated attack against specifically targeted individuals.”
Russian bulletproof hosting service Zservers sanctioned by US for LockBit coordination - A Russian service used to facilitate ransomware attacks by LockBit hackers has been sanctioned by U.S. authorities. The company, Zservers, offers bulletproof hosting — which allows cybercriminals to avoid law enforcement while renting IP addresses, servers and domains used for disseminating malware, forming botnet armies and carrying out other tasks related to fraud and cyberattacks.
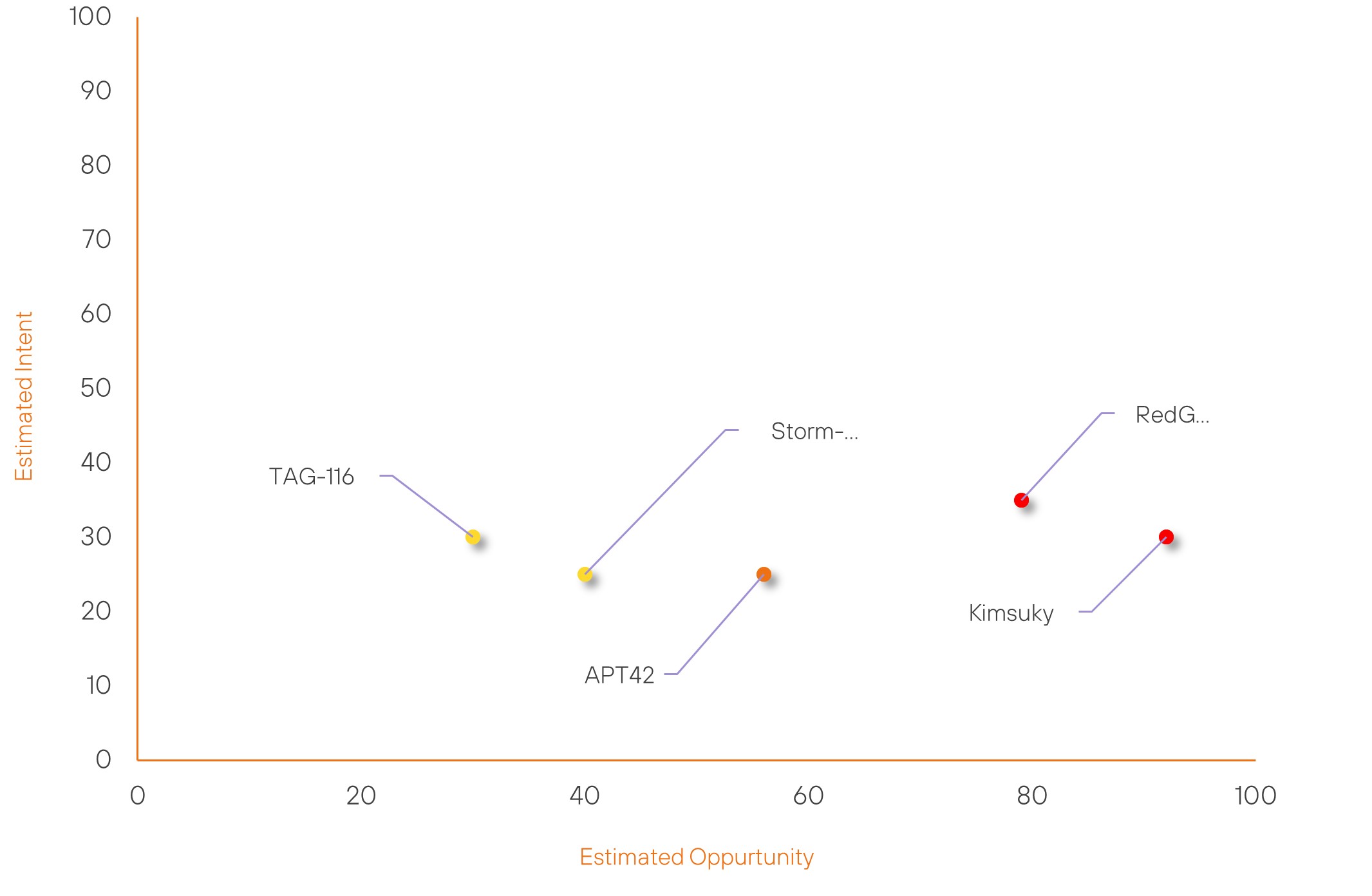
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kimsuky | High | → | High | (91) | ↑ 1 | (30) | → 0 |
| RedGolf | High | → | High | (79) | ↑ 1 | (35) | → 0 |
| APT42 | Moderate | → | Moderate | (56) | ↓ 1 | (25) | → 0 |
| Storm-2372 | New | → | Basic | (40) | ↑ 40 | (25) | ↑ 25 |
| TAG-116 | New | → | Basic | (30) | ↑ 30 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NoName057(16) | ▲ | DDoS | ▲ | CVE-2025-1094 | ▲ | Saudi Arabia | ▲ |
| Russian Hackers | ▲ | Spear Phishing | ▲ | CVE-2025-0108 | ▲ | DOGE | ▲ |
| Medusa Ransomware Group (Frozen Spider, Transforming Scorpius) | ▲ | Stealware | ▲ | CVE-2022-31631 | ▲ | Rockstar Games | ▲ |
| Indian Hackers (Ghost057-5P3C706) | ▲ | WellMess | ▲ | CVE-2025-24200 | ▲ | TechRadar | ▲ |
| RedMike (Earth Estries, FamousSparrow, GhostEmperor, Salt Typhoon, UNC2286) | ▲ | Adware | ▲ | CVE-2024-12356 | ▲ | Zacks Investment | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Threat Actors Distribute NetSupport RAT via Fake Cisco AnyConnect Installer in Malvertising Campaign.
Source: Insikt Group, MalwareBytes | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256 - 78e1e350aa5525669f85e6972150b679d489a3787b6522f278ab40ea978dd65d
IOC: Domain - anyconnect-secure-client[.]com
IOC: Domain - cisco-secure-client[.]com[.]vissnatech[.]com
IOC: Domain – monagpt[.]com
IOC: Domain – mtsalesfunnel[.]com
IOC: IP - 91.222.173[.]67
IOC: IP - 199.188.200[.]195
On February 5, 2025, Malwarebytes reported a malvertising campaign distributing NetSupport RAT via a fake Cisco AnyConnect installer. Threat actors behind the campaign used Google ads and impersonated Technische Universität Dresden’s website to evade detection.
According to Malwarebytes, the infection chain begins with a Google advertisement when victims search for Cisco AnyConnect on Google. After clicking the ad, victims are redirected to the threat actors’ malicious website, where the fake Cisco AnyConnect installer is embedded and signed with a valid certificate.
When executed, the installer extracts a malicious executable named client32.exe, a known NetSupport RAT component that connects to the threat actors’ command-and-control (C2) servers, granting them remote access to infected machines.
At the time of writing, the identity of the threat actor remains undisclosed.
Flesh Stealer Malware Targets Browsers and Messaging Apps to Steal Credentials.
Source: Insikt Group, Cyfirma | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256 - d96e63fb18eb2e587f33e100501f66cc83225b8f19a374ad5817bc7c1ec07896
IOC: SHA256 - b388d2b53453add11982a0e5b86ee01bbaf318ee77483300731d2202ce906146
IOC: Domain – Utka[.]xyz
On February 4, 2025, Cyfirma reported Flesh Stealer, a. NET-based malware written in C# that targets web browsers and messaging applications to steal credentials, cookies, browsing history, and chat logs. The targeted browsers include Chrome, Edge, Firefox, and Opera, while the targeted messaging applications include Signal and Telegram.
The malware avoids execution on systems in Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries by checking installed languages, indicating that the developers are likely Russian-speaking individuals.
According to Cyfirma, Flesh Stealer first appeared in August 2024 and continues to receive updates, with the latest version supporting Chrome version 131.
To evade detection, flesh Stealer uses anti-debugging and anti-virtual machine (VM) techniques, scans for debugging tools, checks system memory, and identifies virtualisation software.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2025-22402 – Update Dell Update Manager Plugin to version 1.7.0 and above
- CVE-2024-52875 – Update to version 9.4.5 Patch 2 for KerioControl
- CVE-2024-40591 – For FortiOS 7.6, update to 7.6.1 or above; for 7.4 (versions 7.4.0 – 7.4.4), upgrade to 7.4.5 or above; for 7.2 (versions 7.2.0 – 7.2.9), update to 7.2.10 or above; and for 7.0 (versions 7.0.0 – 7.0.15), upgrade to 7.0.16 or above. FortiOS 6.4 users should migrate to a fixed release.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
