Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
PoC Exploit for CVE-2024-49113 - SafeBreach released a PoC for CVE-2024-49113, a critical DoS vulnerability in Windows LDAP. The flaw, part of LDAPNightmare, allows attackers to crash LSASS, disrupting authentication on unpatched servers. Exploitable via the DsrGetDcNameEx2 RPC function and a malicious LDAP server, it affects Windows Servers and domain controllers. Though patched by Microsoft in December 2024, unpatched systems remain vulnerable.
Botnets Ficora and Capsaicin Exploit Old D-Link Routers for DDoS Attacks - BleepingComputer reported that in October and November 2024, the Ficora (Mirai variant) and Capsaicin (Kaiten variant) botnets exploited vulnerabilities in outdated D-Link routers (CVE-2015-2051, CVE-2024-33112) via the HNAP interface. This allowed remote access for DDoS attacks, malware distribution, and data exfiltration. Ficora targeted multiple regions, while Capsaicin primarily affected Japan and Taiwan.
SSRF Flaw CVE-2024-53353 in Invoice Ninja - Pretera disclosed a critical SSRF vulnerability (CVE-2024-53353) in Invoice Ninja's PDF generation feature. It arises from improper input handling, allowing attackers with administrative or limited client access to inject malicious code. This can expose sensitive database credentials or enable unauthorized file access, revealing critical system files. No active exploitation has been reported at the time.
Potential Threats
Hackers target dozens of VPN and AI extensions for Google Chrome to compromise data - ExtensionTotal reported that hackers compromised 36 Chrome extensions, mostly AI tools and VPNs, affecting around 2.6 million users. The attack was carried out via malicious updates pushed to these extensions through phishing attacks on developers. Researchers warn that browser extensions, due to their deep access to sensitive data, should be carefully scrutinised and only trusted versions used to avoid exploitation.
Malicious npm Packages Attacking Developers To Steal Sensitive Data - Socket reported that threat actors hijacked npm packages targeting Ethereum developers. The malicious packages posed as Hardhat plugins, stealing private keys and mnemonic phrases. Over 20 such packages were identified, with some reaching over 1,000 downloads. These packages used Ethereum smart contracts to track command-and-control servers, making takedowns more difficult.
FireScam Android Malware Masquerades as Telegram Premium - The Hacker News reported that FireScam, an Android malware, is disguising itself as a premium version of Telegram. Distributed through a phishing site mimicking RuStore, the malware steals sensitive data and maintains remote control over compromised devices. It blocks legitimate app updates and exfiltrates information through Firebase Cloud Messaging and a command-and-control server. The malware also monitors notifications, calls, and messages.
General News
Apple to pay $95 million to settle Siri privacy lawsuit - Apple agreed to settle a lawsuit over privacy violations involving Siri. The company will pay up to $95 million to U.S. users who experienced accidental Siri activations between 2014 and 2024, violating their privacy. Affected users can claim $20 per device for eligible Siri-enabled products, such as iPhones, iPads, and Macs.
BCM One Suffers Data Breach - BCM One, Inc., a US-based telecommunications and IT services company, notified several customers of a data breach that compromised their personal information. Details about the compromised data, the identity of the threat actors, and their method of initial access remain undisclosed.
Atos Denies Data Theft Claims by Ransomware Group - Atos responded to ransomware group Space Bears' claims of stealing its data, denying the breach. Atos stated there was no evidence of compromise to its systems. It acknowledged that the group may have obtained some data related to Atos, but clarified that the data was public or technical, containing no sensitive information.
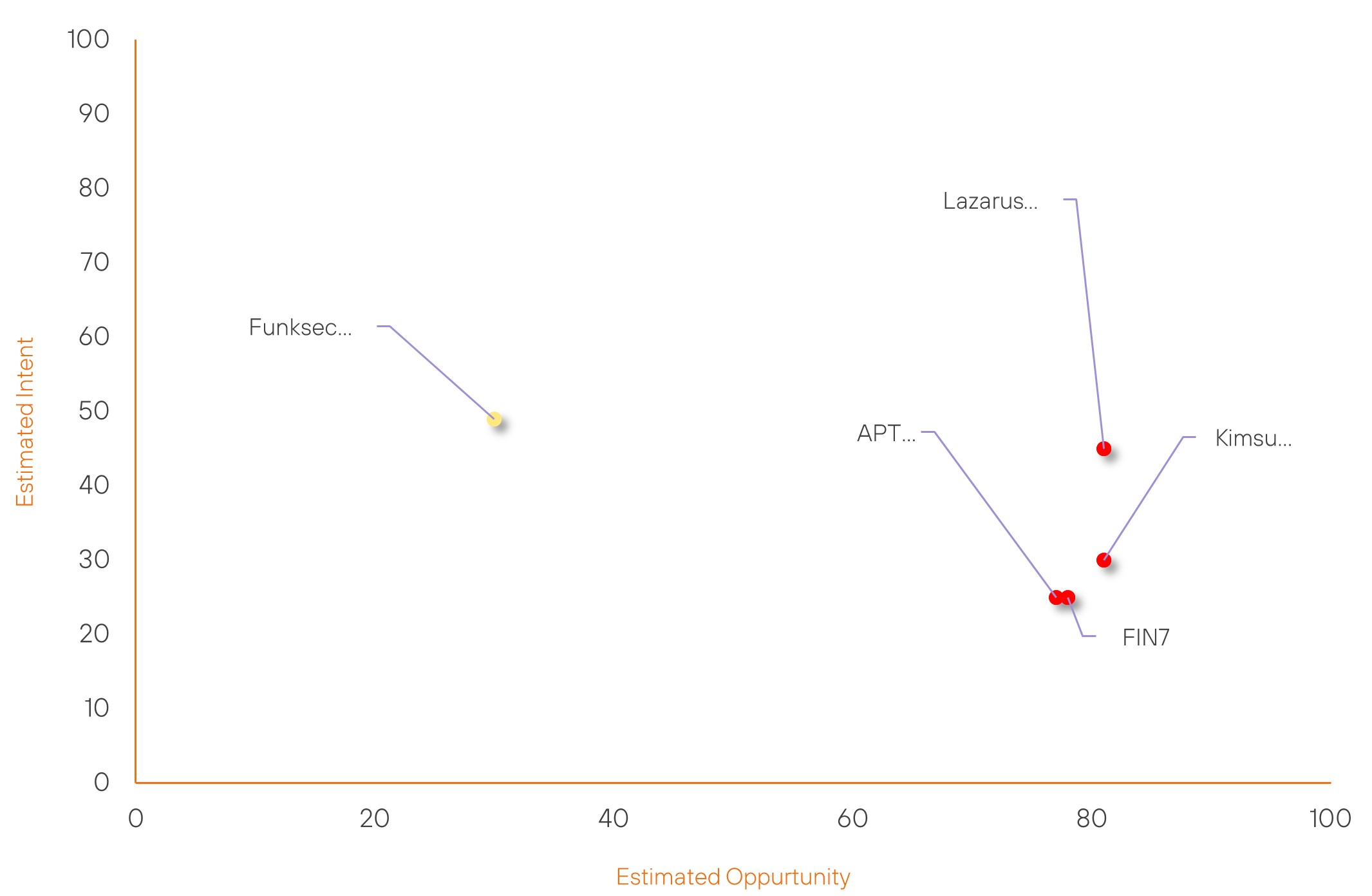
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIN7 | High | → | High | (78) | ↓ 8 | (25) | → 0 |
| Lazarus Group | High | → | High | (81) | ↓ 2 | (45) | → 0 |
| Kimsuky | High | → | High | (81) | ↓ 1 | (30) | → 0 |
| APT38 | High | → | High | (77) | ↓ 1 | (25) | → 0 |
| Funksec Group | New | → | Basic | (30) | ↑ 30 | (49) | ↑ 49 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volt Typhoon | ▲ | Malware-as-a-Service | ▲ | BrakTooth | ▲ | Deloitte LLP | ▲ |
| A Brain Cipher Ransomware Group | ▲ | Network Intrusion | ▲ | CVE-2024-49112 (LDAPNightmare) | ▲ | Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Corp. | ▲ |
| Lazarus Group | ▲ | XMRig Miner | ▲ | CVE-2024-43452 | ▲ | Twitch | ▲ |
| APT-C-60 | ▲ | Malicious code | ▲ | CVE-2023-49113 | ▲ | Germany | ▲ |
| miyako | ▲ | XWorm | ▲ | CVE-2024-43641 | ▲ | Alibaba | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Botnets Ficora and Capsaicin Exploit Old D-Link Routers for DDoS Attacks
Source: Insikt Group, BleepingCpmputer | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256 - 18c92006951f93a77df14eca6430f32389080838d97c9e47364bf82f6c21a907
IOC: SHA256 - f71dc58cc969e79cb0fdfe5163fbb9ed4fee5e13cc9407a11d231601ee4c6e23
IOC: Domain – pirati[.]abuser[.]eu
IOC: Domain – www[.]codingdrunk[.]in
IOC: CVE-2024-33112
IOC: CVE-2015-2051
IOC: IP Address: 45[.]86[.]86[.]60
IOC: IP Address: 194[.]110[.]247[.]46
BleepingComputer reported that in October and November 2024, attackers exploited outdated D-Link routers using Ficora (Mirai variant) and Capsaicin (Kaiten variant) botnets. These botnets targeted vulnerabilities like CVE-2015-2051 and CVE-2024-33112, exploiting the HNAP protocol to enable DDoS attacks, data theft, and malware distribution.
Ficora launched widespread DDoS attacks in North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia. Capsaicin focused on Japan and Taiwan, disabling rival payloads, exfiltrating data, and executing advanced DDoS techniques.
To mitigate risks, it is advised to update devices to the latest firmware, replace unsupported models, use strong passwords, and disable unnecessary remote access. These measures significantly enhance security.
Malicious npm Packages Attacking Developers To Steal Sensitive Data
Source: Insikt Group, Socket | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: URL: hxxps://projects[.]metabest[.]tech/api
IOC: URL: hxxps://cryptoshiny[.]com/api
IOC: URL: hxxps://pastebin[.]com/api/api_post[.]php
IOC: Ethereum Address: 0xC02aaA39b223FE8D0A0e5C4F27eAD9083C756Cc2
IOC: Ethereum Address: 0xbb4CdB9CBd36B01bD1cBaEBF2De08d9173bc095c
On January 2, 2025, Socket reported a targeted attack involving hijacked npm packages aimed specifically at Ethereum developers. The attackers disguised the malicious packages as legitimate Hardhat plugins, a crucial tool for Ethereum development.
These rogue packages were designed to stealthily exfiltrate private keys and mnemonic phrases—critical credentials for Ethereum wallets—posing significant security risks to developers using them. More than 20 compromised packages were identified in total, some of which had been downloaded over 1,000 times.
The malicious actors employed a particularly sophisticated tactic by using Ethereum smart contracts to store and dynamically update the command-and-control (C2) server addresses. This made it extremely difficult for security teams to shut down the attack and neutralise the infrastructure, as the C2 servers could change in real time.
This tactic, leveraging the immutable and decentralised nature of the Ethereum blockchain, underscores a significant shift in attack strategies, demonstrating the increasing complexity of supply chain attacks within the blockchain development ecosystem.
This campaign highlights the need for greater vigilance when using open-source tools, and it serves as a cautionary reminder of the critical importance of verifying dependencies in development environments.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-49113 – To mitigate the risks, it is advised to apply the security updates provided by Microsoft.
- CVE-2015-2051 and CVE-2024-33112 – To mitigate risks, it is advised to update devices to the latest firmware, replace unsupported models, use strong passwords, and disable unnecessary remote access.
- CVE-2024-53353 – To address this vulnerability, it is recommended to update Invoice Ninja to its latest version.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
