Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Ivanti Addresses Zero-Day and High-Severity Vulnerabilities - Ivanti disclosed two vulnerabilities affecting Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and ZTA Gateways. CVE-2025-0282, a critical stack-based buffer overflow, allows remote code execution and has been exploited in zero-day attacks to install malware. Ivanti has patched Connect Secure and plans to release patches for Policy Secure and ZTA Gateways by January 21, 2025. CVE-2025-0283, also a buffer overflow, enables local privilege escalation but has not been actively exploited.
Palo Alto Networks Patches Vulnerabilities in Expedition Tool - These include CVE-2025-0103, a high-severity SQL injection allowing database manipulation; CVE-2025-0104, a medium-severity XSS flaw enabling script execution in authenticated users' browsers; CVE-2025-0105, which allows unauthorised file deletion affecting www-data files; CVE-2025-0106, which lets unauthorised users list files; and CVE-2025-0107, a command injection flaw allowing authenticated users to execute commands as www-data. No active exploitation has been reported.
CISA Warns of Exploited Vulnerabilities in Mitel MiCollab - CVE-2024-41713 and CVE-2024-55550 are path traversal issues affecting versions 9.8 SP1 FP2 (9.8.1.201) and earlier. CVE-2024-41713 allows remote threat actors to read arbitrary files on the server, potentially leading to unauthorised access and data breaches. CVE-2024-55550 lets attackers with administrative credentials exploit insufficient input validation to access sensitive files. Both vulnerabilities are actively targeted.
Potential Threats
Threat Actors Impersonate CrowdStrike with Job Offer Emails to Target Developers with Crypto Miners - CrowdStrike reported a phishing campaign targeting developers with fake job offers to distribute XMRig cryptocurrency mining malware. The emails impersonated CrowdStrike recruitment and led victims to download a fake "employee CRM application." The app bypassed security checks, installed the XMRig miner, and used up to 10% of the CPU. It ensured persistence through startup scripts and registry keys. CrowdStrike advises candidates to verify the authenticity of recruitment emails.
Information Stealer Masquerades as LDAPNightmare - Trend Micro reported that a fake CVE-2024-49113 (LDAPNightmare) proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit is being used to deliver a PowerShell-based information stealer. The exploit, masquerading as a Python project, is hosted on GitHub under the user "YoonJae-rep" and contains an executable named "poc.exe." Despite the exploit’s critical nature, the GitHub repository remains active, distributing the malware. Upon execution, the malware gathers system and network information, performs API hooking, DLL injection, and uploads sensitive data to a remote FTP server.
PayPal Phishing Campaign Employs Genuine Links to Take Over Accounts - Fortinet reported a phishing campaign targeting PayPal users, leveraging a Microsoft 365 feature that uses a free test domain to bypass security checks like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. The emails, disguised as PayPal payment requests, steal users' credentials when clicked, giving attackers control over their accounts. Fortinet advises employing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) systems to flag distribution list emails and conducting security awareness training to help users recognise phishing attempts.
General News
E.U. Commission Fined for Transferring User Data to Meta - The European General Court has fined the European Commission and ordered it to pay €400 ($412) in compensation to an individual whose personal data was transferred to Meta without adequate safeguards.
New OT Product Security Guide Published to Strengthen Industrial Cybersecurity - A new guide released by CISA aims to improve the security of Operational Technology (OT) products by providing essential strategies and best practices to protect critical industrial systems from evolving cyber threats.
Location Tracking Firm Unacast Reports Data Breach - Unacast notified Norwegian authorities about a data breach that may have compromised user information. The company is investigating the incident but has not disclosed further details.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
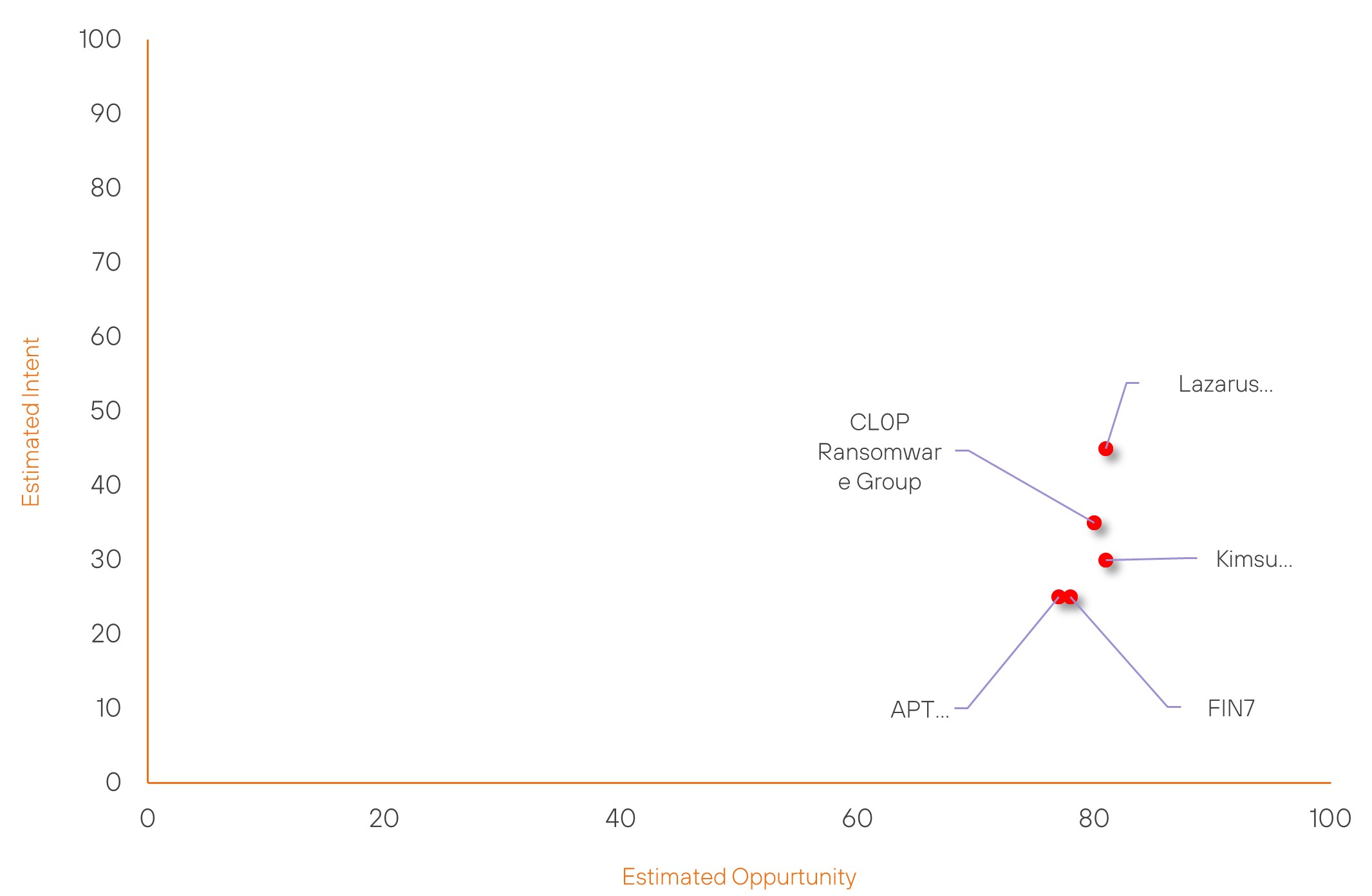
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIN7 | High | → | High | (78) | ↓ 8 | (25) | → 0 |
| Lazarus Group | High | → | High | (81) | ↓ 1 | (45) | → 0 |
| CL0P Ransomware Group | High | → | High | (80) | ↑ 1 | (35) | → 0 |
| Kimsuky | High | → | High | (81) | ↓ 1 | (30) | → 0 |
| APT38 | High | → | High | (77) | ↓ 1 | (25) | → 0 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| @Hillzthethird (Obi Cubanaa) | ▲ | DDoS | ▲ | CVE-2024-49112 (LDAPNightmare) | ▲ | Financial Technology | ▲ |
| UNC5337 | ▲ | Adware | ▲ | CVE-2024-54498 | ▲ | Gravy Analytics | ▲ |
| RansomHouse Group | ▲ | Malware-as-a-Service | ▲ | BrakTooth | ▲ | Deloitte LLP | ▲ |
| NoName057(16) | ▲ | Zero Day Exploit | ▲ | CVE-2023-21894 | ▲ | Litecoin | ▲ |
| Everest Ransomware Group | ▲ | XMRig Miner | ▲ | CVE-2024-49113 | ▲ | Italy | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Threat Actors Impersonate CrowdStrike with Job Offer Emails to Target Developers with Crypto Miners
Source: Insikt Group, BleepingCpmputer | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256 - 62f3a21db99bcd45371ca4845c7296af81ce3ff6f0adcaee3f1698317dd4898b
IOC: SHA256 -96558bd6be9bcd8d25aed03b996db893ed7563cf10304dffe6423905772bbfa1
IOC: Domain – cscrm-hiring[.]com
IOC: IP Address: 93[.]115[.]172[.]41
IOC: URL: hxxps://cscrm-hiring.com/cs-applicant-crm-installer.zip
BleepingComputer reported that a phishing campaign impersonating CrowdStrike's recruitment process targeted developers with XMRig cryptocurrency mining malware. The attackers used fake job offer emails to lure victims into downloading a fraudulent "employee CRM application" from a counterfeit website, cscrm-hiring[.]com.
The malicious app conducted security checks to evade detection, verifying debugging tools, CPU cores, and active processes. After passing these checks, it downloaded and executed the XMRig miner, designed to use no more than 10% of the victim's CPU. To ensure persistence, the malware added a batch script to the startup folder and created a registry autostart key.
This incident highlights the sophistication of phishing campaigns and the critical importance of verifying recruitment communications. CrowdStrike advises job candidates to confirm the legitimacy of recruitment emails via official channels.
Information Stealer Masquerades as LDAPNightmare
Source: Insikt Group, TrendMicro | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: CVE-2024-49113 | CVVS Score: 8.7 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Very Critical - 99
IOC: SHA256 - 0d610a6e7cbafe1d18a51a06cb154a95d40278e3ac01a7440bff1886e73ed93a
IOC: URL: hxxps://Pastebin[.]com/raw/9TxS7Ldc
IOC: Username: YoonJae-rep
Trend Micro reported a malicious campaign distributing an information stealer disguised as a fake proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2024-49113, a critical DoS vulnerability in Microsoft's Windows LDAP service, known as LDAPNightmare.
The fake PoC was published on GitHub by a user named "YoonJae-rep" within a Python project, which included a malicious executable, "poc.exe." Sandbox analysis flagged it due to the use of the UPX packer and its malicious actions such as API hooking, DLL injection, and reflective PE injection.
Upon execution, the "poc.exe" file:
- Drops and executes a PowerShell script
- Gathers system information like language, geolocation, and storage devices
- Downloads and runs a secondary PowerShell script from Pastebin
The secondary script collects sensitive system data, such as IP addresses, processes, installed applications, and user folder contents, compresses it into a ZIP file, and uploads it to a remote FTP server using hardcoded credentials. It also creates a scheduled task to ensure the script runs every 30 minutes for persistent exfiltration.
This campaign highlights the dangers of downloading unverified PoC exploits and emphasizes the importance of scrutinising open-source repositories to prevent malware infections.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2025-0282 – Ivanti recommends that administrators of Connect Secure (affected versions up to 22.7R2.4) perform both internal and external scans to detect any signs of compromise. If no issues are found, a factory reset should be performed before upgrading to version 22.7R2.5. If a compromise is detected, the factory reset should be conducted to remove the malware, after which the upgrade can proceed.
- CVE-2025-0283 – The patch for this vulnerability is scheduled to be released on January 21, 2025.
- CVE-2025-0103, CVE-2025-0104, CVE-2025-0105, CVE-2025-0106 and CVE-2025-0107 – To mitigate risks, users should apply the latest patches. However, since the tool is no longer supported, Palo Alto Networks advises limiting its use, shutting it down if it is not actively needed, and migrating to alternative solutions to maintain security and functionality.
- CVE-2024-41713 and CVE-2024-55550 - To address these vulnerabilities, it is recommended to update to MiCollab version 9.8 SP2 (9.8.2.12).
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
