Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
OpenSSH CVE-2024-6387 (regreSSHion) – This vulnerability presents a critical security risk as it allows unauthenticated remote code execution as root on glibc-based Linux systems. Over 14 million potentially vulnerable OpenSSH server instances are exposed to the Internet, with around 700,000 instances identified as vulnerable and internet-facing. This vulnerability stems from a regression of a previously patched flaw, CVE-2006-5051.
CVE-2024-5655 GitLab bug lets attackers run pipelines as any user – A critical vulnerability is affecting certain versions of GitLab Community and Enterprise Edition products, which could be exploited to run pipelines as any user. The vulnerability impacts all GitLab CE/EE versions from 15.8 through 16.11.4, 17.0.0 to 17.0.2, and 17.1.0 to 17.1.0.
PoC for Critical Out-of-Bounds Access Vulnerability Affecting Mozilla Firefox – On June 27, 2024, security researcher Jack Ren published a proof-of-concept for CVE-2024-29943. This is a critical out-of-bounds (OOB) access via Range Analysis bypass vulnerability affecting Mozilla Firefox versions before 124.0.1 which could lead to remote code execution (RCE).
Potential Threats
PoC for Critical Vulnerability Affecting Progress Software’s MOVEit Transfer - On June 25, 2024, cybersecurity firm watchTowr published a proof-of-concept (PoC) and a write-up disclosing CVE-2024-5806, a critical authentication bypass vulnerability affecting the secure file transfer protocol (SFTP) module in Progress Software’s MOVEit Transfer.
Critical D-Link DIR-859 router flaw used to steal passwords - Hackers are exploiting a critical vulnerability that affects all D-Link DIR-859 WiFi routers to collect account information from the device, including passwords. The security issue was disclosed in January and has a CVSS score of 9.8.
New Version of “WhiteSnake” Stealer Released - On June 15, 2024, the developers of WhiteSnake Stealer announced on their Telegram channel the release of v1.6.3.0. The new version has multiple new features, including Yandex browser passwords and credit card decryption, Windows credential manager data recovery, small optimisations with report compression, UAC bypass command for the remote terminal, updated C2 list and more.
General News
TeamViewer says Russia’s ‘Cozy Bear’ hackers attacked corporate IT system - Software company TeamViewer confirmed on June 28th that a prolific Russian hacking group breached its corporate IT environment earlier in the week.
US Sanctions Twelve Members of Kaspersky Leadership - On June 21, 2024, the US imposed sanctions on twelve individuals who hold leadership roles at Kaspersky Lab, a Russian cybersecurity firm. The Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) announced the sanctions, which also include the entities AO Kaspersky Lab and OOO Kaspersky Group, as well as Kaspersky Labs Limited. The individuals, who are also members of Kaspersky's board of directors, hold executive or leadership roles within the company.
Ticketmaster notifies impacted customers after recent data breach – The company has started to notify customers who were impacted by the recent data breach associated with the company’s Snowflake database.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
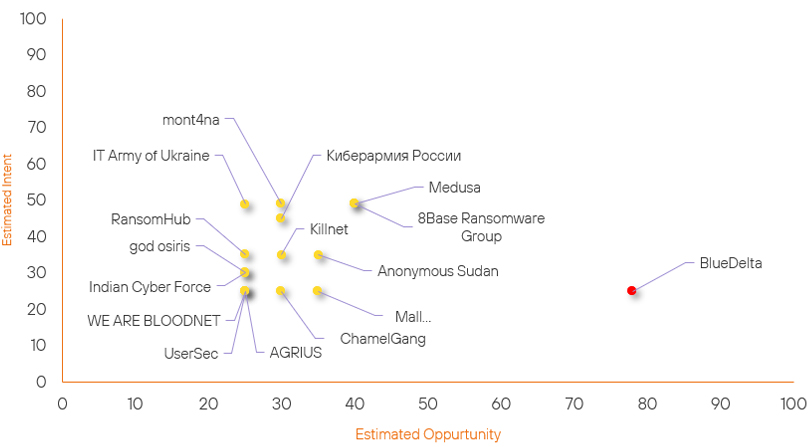
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChamelGang | New | → | Basic | ↑ 30 | (30) | ↑ 25 | (25) |
| god osiris | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 |
(25) | ↑ 30 | (30) |
| RansomHub | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (25) | ↑ 10 | (35) |
| mont4na | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (30) | ↑ 9 | (49) |
| 8Base Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | ↑ 5 | (40) | → 0 | (49) |
| Mallox | Basic | → | Basic | ↑ 5 | (35) | → 0 | (25) |
| Medusa | Basic | → | Basic | ↑ 5 | (40) | → 0 | (49) |
| Киберармия России | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (30) | ↑ 5 | (45) |
| IT Army of Ukraine | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (25) | ↑ 4 | (49) |
| BlueDelta | High | → | High | ↑ 1 | (78) | → 0 | (25) |
| Killnet | Basic | → | Basic | ↓ 5 | (30) | → 0 | (35) |
| AGRIUS | Basic | → | Basic | ↓ 5 | (25) | → 0 | (25) |
| Anonymous Sudan | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (35) | ↓ 5 | (35) |
| WE ARE BLOODNET | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (25) | ↓ 5 | (25) |
| Indian Cyber Force | Basic | → | Basic | ↓ 5 | (25) | → 0 | (30) |
| UserSec | Basic | → | Basic | ↓ 5 | (25) | ↓ 5 | (25) |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BlueBravo | ▲ | Brain Cipher | ▲ | CVE-2024-6387 | ▲ | TeamViewer | ▲ |
| LulzSec | ▲ | Remote Code Execution | ▲ | CVE-2024-0769 | ▲ | Kubota | ▲ |
| Handala | ▲ | Cross Site Scripting | ▲ | CVE-2024-5806 | ▲ | Kadokawa | ▲ |
| BlackSuit Ransomware | ▲ | Idenitty Theft | ▲ | CVE-2024-0193 | ▲ | HubSpot | ▲ |
| BlueDelta | ▲ | Merlin | ▲ | CVE-2024-3506 | ▲ | US Federal Reserve | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
TeamViewer Corporate Breach.
Source: The Record, Insikt Group, TeamViewer | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
On June 27, 2024, German software company TeamViewer disclosed a cyberattack that affected its internal corporate IT systems. In an updated statement, the company, which stated it initially observed the activity on June 26, 2024, attributed a recently announced incident to APT29, also known as Cozy Bear, BlueBravo, and Midnight Blizzard.
The group, allegedly housed within Russia’s Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR), has been implicated in several of the most consequential hacks of the last decade — including the 2020 SolarWinds hack and the 2016 attack on the Democratic National Committee.
TeamViewer explained that Wednesday’s hack was traced back to the “credentials of a standard employee account” within the company’s corporate IT environment. There is “no evidence” that APT29 was able to gain access to the company's product environment or customer data, according to the statement, which noted that the corporate IT network is segregated from other company systems.
“This means we keep all servers, networks, and accounts strictly separate to help prevent unauthorised access and lateral movement between the different environments,” the company explained.
Additional details about the nature of the attack or means of initial access have yet to be disclosed.
TeamViewer users should ensure they have enabled multi-factor authentication unless they have already done so, establish allow and block lists to restrict access to authorised individuals, and monitor any suspicious activity from network logs or TeamViewer connections.
GitLab Addresses Critical-Severity CVE-2024-5655.
Source: Insikt Group, GitLab | Vulnerability Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-5655 | CVVS Score: 8.8 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 78
GitLab released updates to address fourteen vulnerabilities affecting or its Community Edition (CE) and Enterprise Edition (EE) platforms on June 26, 2024. This patch addresses a critical severity vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-5655.
CVE-2024-5655 (critical severity) relates to a function in GitLab CE/EE that permits the operation of pipelines by any user under certain conditions.
GitLab pipelines are a feature of the Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) system that enables users to automatically run processes and tasks, either in parallel or in sequence, to build, test, or deploy code changes.
This vulnerability could allow a threat actor to perform unauthorised activities within the GitLab platform, such as impersonating another user without obtaining their permission.
No in-the-wild exploitation has been observed at this moment.
The vulnerability impacts all GitLab CE/EE versions from 15.8 through 16.11.4, 17.0.0 to 17.0.2, and 17.1.0 to 17.1.0. GitLab has addressed the vulnerability by releasing versions 17.1.1, 17.0.3, and 16.11.5, and recommends users to apply the updates as soon as possible.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned above be fully patched and updated. We want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches should they apply.
- GitLab – Update to the following versions: 17.1.1, 17.0.3, and 16.11.5
- OpenSSH:
- Apply the latest available update for the OpenSSH server (version 9.8p1), which fixes the vulnerability.
- Restrict SSH access using network-based controls.
- If the OpenSSH server cannot be updated immediately, set the 'LoginGraceTime' to 0 in the sshd configuration file, but note that this can expose the server to denial-of-service attacks.
We also recommend proactively checking your environment for the software versions mentioned above and hunting for any known IOCs related to them.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing the searching and hunting activities within your environment.
