Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
SolarWinds Patches Eight Critical Flaws in its Software - On July 17, 2024, SolarWinds addressed eight critical vulnerabilities in its Access Rights Manager (ARM) software, a crucial tool for managing and auditing access rights in enterprise environments. These vulnerabilities included six remote code execution (RCE) flaws that could allow threat actors to execute code or commands on unpatched systems, potentially with SYSTEM privileges.
Critical Path Traversal Vulnerability, CVE-2024-36991, Found in Splunk Enterprise – On July 17, 2024, the SonicWall Capture Labs threat research team identified an arbitrary file read vulnerability in Splunk Enterprise installations, tracked as CVE-2024-36991. CVE-2024-36991 is a path traversal vulnerability that allows threat actors to access files outside the restricted directory. Splunk is affected in versions below 9.2.2, 9.1.5, and 9.0.10.
PoC for VMware Vulnerability (CVE-2024-22274) Published on GitHub - On July 15, 2024, GitHub user l0n3m4n published a proof-of-concept (PoC) script for CVE-2024-22274. CVE-2024-22274 is an authenticated remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting multiple VMware products, including VMware ESXi, VMware vCenter Server, VMware Cloud Foundation, VMware Workstation, and VMware Fusion.
Potential Threats
Threat Actors Abuse Cloudflare WARP to Compromise Internet-Facing Services - On July 17, 2024, cybersecurity firm Cado Security (@CadoSecurity on X, formerly known as Twitter) published a write-up detailing how threat actors abuse Cloudflare WARP to compromise cloud services. According to Cado Security, threat actors, instead of routing traffic through Cloudflare's Content Delivery Network (CDN), can abuse Cloudflare WARP to connect to vulnerable internet-facing services directly. This method masks their IP addresses, exploiting the inherent trust organisations place in Cloudflare’s network traffic.
Telegram zero-day allowed sending malicious Android APKs as videos - A Telegram for Android zero-day vulnerability dubbed 'EvilVideo' allowed attackers to send malicious Android APK payloads disguised as video files. The EvilVideo zero-day flaw only worked on Telegram for Android. It allowed attackers to create specially crafted APK files that appear as embedded videos when sent to other users on Telegram.
Fake CrowdStrike fixes target companies - Following a disruptive software update from CrowdStrike, threat actors exploited the situation by distributing malware disguised as remedial software for the affected Windows hosts, according to a report on July 21, 2024, from BleepingComputer. These campaigns use phishing emails to promote counterfeit fixes, which include a fake CrowdStrike Hotfix update.
General News
Teenage suspect in MGM Resorts hack arrested in Britain - Police in the United Kingdom have arrested a 17-year-old for his alleged role in the cybercriminal group that brought MGM Resorts casinos to a standstill last year in a ransomware attack. Although police did not name the group the teenager was allegedly associated with, the attack on MGM Resorts was carried out by Scattered Spider.
Judge tosses out most of SEC cybersecurity case against SolarWinds - A U.S. District Court judge dismissed most of a landmark case against software company SolarWinds, throwing cold water on attempts by the federal government to punish the firm after it was hit by Russia’s Sunburst hacking campaign.
Russia-linked FIN7 hackers sell their security evasion tool to other groups – In a new report, the cybersecurity firm SentinelOne said that it observed multiple ransomware groups using updated versions of AvNeutralizer, suggesting that the customer list was no longer limited to Black Basta.
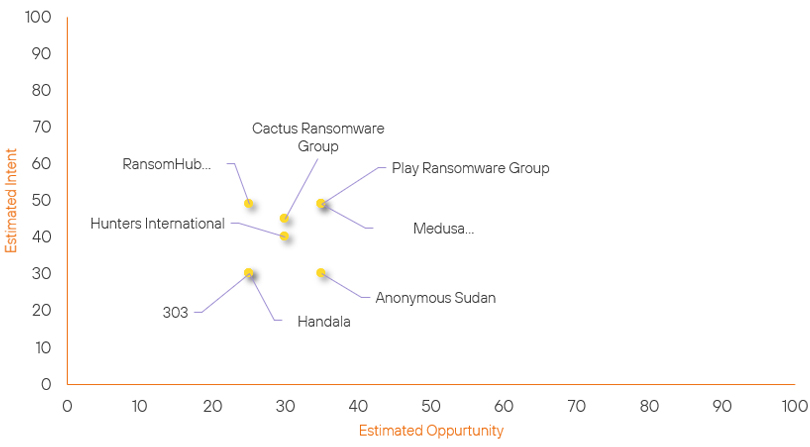
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Handala | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 | (25) | ↑ 30 | (30) |
| 303 | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 |
(25) | ↑ 30 | (30) |
| Hunters International | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (30) | ↑ 5 | (40) |
| RansomHub Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (25) | ↑ 4 | (49) |
| Cactus Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (30) | ↓ 4 | (45) |
| Medusa Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | ↓ 5 | (35) | → 0 | (49) |
| Play Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | ↓ 5 | (35) | → 0 | (49) |
| Anonymous Sudan | New | → | Basic | → 0 | (35) | ↓ 5 | (30) |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FLUXROOT | ▲ | Play Ransomware | ▲ | CVE-2024-40348 | ▲ | WazirX | ▲ |
| Brain Cipher | ▲ | REMCOS RAT | ▲ | CVE-2024-50564 | ▲ | California | ▲ |
| Scattered Spider | ▲ | Spyware | ▲ | CVE-2024-32896 | ▲ | LA County | ▲ |
| NullBulge | ▲ | Ransomware | ▲ | CVE-2024-30088 | ▲ | MediSecure | ▲ |
| RedGolf | ▲ | 9002 RAT | ▲ | CVE-2023-46944 | ▲ | Life360 | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
VMware CVE-2024-22274 POC.
Source: Insikt Group, VMware, GitHub | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-22274| CVVS Score: 7.2 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Medium – 62
On July 15, 2024, GitHub user l0n3m4n published a proof-of-concept (PoC) script for CVE-2024-22274. CVE-2024-22274 is an authenticated remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting multiple VMware products, including VMware ESXi, VMware vCenter Server, VMware Cloud Foundation, VMware Workstation, and VMware Fusion. CVE-2024-22274, when exploited, allows a threat actor with administrative privileges on the vCenter appliance to run arbitrary commands on the underlying operating system.
In May 2024, VMware released VMware vCenter Server versions 8.0 U2b and 7.0 U3q to fix CVE-2024-22274.
According to a write-up published by Matei Badanoiu, CVE-2024-22274 stems from the improper handling and validation of user-supplied input in vCenter Server’s API components, specifically “com.vmware.appliance.recovery.backup.job.create” and “com.vmware.appliance.recovery.backup.validate”.
Based on the repository, l0n3m4n’s PoC requires a target VMware vCenter Server hostname or IP address, the SSH port on the target server, a file containing a Base64-encoded payload, and a file containing SSH credentials. Once provided, the PoC attempts to connect to the target VMware vCenter Server using the provided SSH credentials. Upon establishing the SSH connection, the PoC reads and decodes the Base64-encoded payload from the specified file. The PoC then constructs a malicious command that injects and executes the decoded payload on the target server by exploiting the Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) backup mechanism. After executing the command, the PoC checks whether it achieved root access on the machine by checking for keywords in the output that signify root privileges.
Cloudflare WARP Campaign.
Source: Insikt Group, Cado Security | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-6387| CVVS Score: 8.1 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 79
On July 17, 2024, cybersecurity firm Cado Security published a write-up detailing how threat actors abuse Cloudflare WARP to compromise cloud services. According to Cado Security, threat actors, instead of routing traffic through Cloudflare's Content Delivery Network (CDN), can abuse Cloudflare WARP to directly connect to vulnerable internet-facing services.
This method masks their IP addresses, exploiting the inherent trust organizations place in Cloudflare’s network traffic. Consequently, organisation firewalls may inadvertently whitelist Cloudflare's IP ranges, allowing malicious traffic originating through Cloudflare WARP to pass undetected.
According to Cado Security, they observed two cyberattacks abusing Cloudflare WARP:
– Cryptojacking campaigns: The SSWW mining campaign — named for the script “ssww” downloaded by the campaign’s command-and-control (C2) server — specifically targeted Docker containers exposed via Cloudflare WARP. The threat actors created containers with elevated permissions to deploy a cryptojacking script. The script disables competing miners, adjusts system configurations for optimized mining, and installs a rootkit to hide its presence. The campaign used Cloudflare WARP to mask the threat actors' IP addresses, making it difficult to trace their malicious activities.
– Secure Shell (SSH) brute force attacks: Cado Security observed increased SSH brute force attacks from Cloudflare WARP addresses, abusing its “clean” IP ranges that are less likely to be blocklisted by firewalls. These attacks involved simple SSH brute forcing that surged to a few thousand per month by the end of 2023. Furthermore, Cado Security noted the potential abuse of Cloudflare WARP to exploit CVE-2024-6387, a critical unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability affecting OpenSSH's server software (sshd).
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned above be fully patched and updated. We want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches should they apply:
- SolarWinds – Update to SolarWinds Access Rights Manager (ARM) version 2024.3
- Splunk Enterprise – Update to versions 9.2.2, 9.1.5, 9.0.10
- VMware – Update to the fixed versions of products supplied in the Broadcom Security Advisory
We also recommend proactively checking your environment for the software versions mentioned above and hunting for any known IOCs related to them.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing the searching and hunting activities within your environment.
