Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Acronis CVE-2023-45249 - On July 25, 2024, Acronis patched an actively exploited vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-45249 in its Acronis Cyber Infrastructure (ACI), a platform for backup, disaster recovery, and remote endpoint management. This remote code execution (RCE) flaw arises from improper authentication handling of default credentials. Exploitation allows threat actors to gain unauthorised access and execute arbitrary code on vulnerable servers, leading to system compromise.
Critical ServiceNow RCE Actively Exploited – Threat actors are actively exploiting disclosed critical vulnerabilities in ServiceNow software. The most severe vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-4879 and CVE-2024-5217, have critical CVSSv4 scores of 9.3 and 9.2 respectively, allowing unauthenticated remote threat actors to execute arbitrary code. The third, CVE-2024-5178, with a CVSSv4 score of 6.9, enables administrative users to access sensitive files on the web application server.
Just-Patched VMware ESXi Flaw Exploited - The flaw, tagged as CVE-2024-37085 with a CVSS severity score of 6.8, has already been abused by multiple known ransomware groups to deploy data-extortion malware on enterprise networks, according to a new warning from Redmond’s threat hunting teams.
Potential Threats
PKfail Secure Boot bypass - Hundreds of UEFI products from 10 vendors are susceptible to compromise due to a critical firmware supply-chain issue known as PKfail, which allows attackers to bypass Secure Boot and install malware. As the Binarly Research Team found, affected devices use a test Secure Boot "master key"—also known as Platform Key (PK)—generated by American Megatrends International (AMI), which was tagged as "DO NOT TRUST" and that upstream vendors should've replaced with their own securely generated keys.
WhatsApp for Windows allows unknown execution - A security issue in the latest version of WhatsApp for Windows allows sending Python and PHP attachments that are executed without any warning when the recipient opens them. For the attack to be successful, Python needs to be installed, a prerequisite that may limit the targets to software developers, researchers, and power users.
Threat Actors Exploit CVE-2024-21412 to Deploy Multiple Infostealers- Fortinet identified a campaign in which threat actors exploit CVE-2024-21412, an already-patched vulnerability in Microsoft Windows SmartScreen, to distribute various infostealers. Fortinet published details about this campaign on July 23, 2024, noting that various threat actors, including Water Hydra (DarkCasino), have historically exploited CVE-2024-21412.
General News
Proofpoint settings exploited to send millions of phishing emails daily - A massive phishing campaign dubbed "EchoSpoofing" exploited now-fixed, weak permissions in Proofpoint's email protection service to dispatch millions of spoofed emails impersonating big entities like Disney, Nike, IBM, and Coca-Cola, to target Fortune 100 companies.
Threat Actors Abusing Microsoft Office Forms - A new phishing campaign abuses Microsoft Office forms to conduct sophisticated two-step phishing attacks, Perception Point reported on July 25, 2024. In this campaign, threat actors create legitimate-looking forms on Microsoft Office Forms and embed malicious links within them. These forms are then sent to targeted users via email, often masquerading as legitimate requests such as password changes or document access.
IBM: Cost of a breach reaches nearly $5 million, with healthcare being hit the hardest – Businesses that fall victim to a data breach can expect a financial hit of nearly $5 million on average — a 10% increase compared to last year — according to IBM’s annual report on cybersecurity incidents.
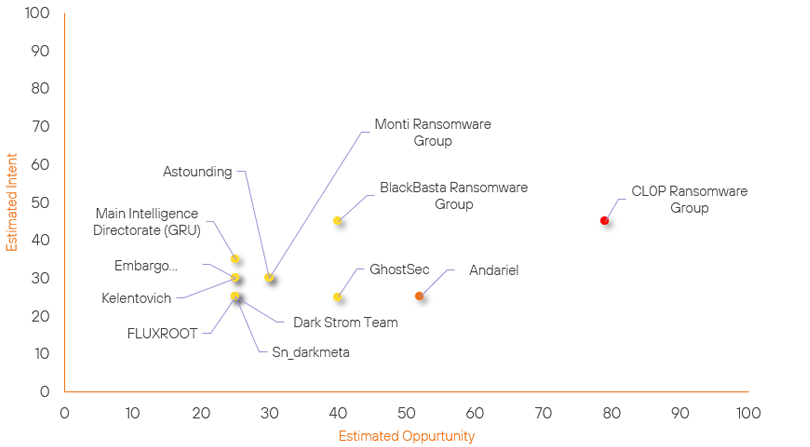
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andariel | New | → | Moderate | ↑ 52 | (52) | ↑ 25 | (25) |
| Main Intelligence Directorate | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 |
(25) | ↑ 35 | (35) |
| Astounding | New | → | Basic | ↑ 30 | (30) | ↑ 30 | (30) |
| Embargo Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 | (25) | ↑ 30 | (30) |
| Kelentovich | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 | (25) | ↑ 30 | (30) |
| Dark Strom Team | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 | (25) | ↑ 25 | (25) |
| FLUXROOT | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 | (25) | ↑ 25 | (25) |
| Sn_darkmeta | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 | (25) | ↑ 25 | (25) |
| GhostSec | Basic | → | Basic | ↑ 5 | (40) | → 0 | (25) |
| BlackBasta Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (40) | ↓ 4 | (45) |
| CL0P Ransomware Group | High | → | High | → 0 | (79) | ↓ 4 | (45) |
| Monti Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (30) | ↓ 5 | (30) |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RipperSec | ▲ | Cyber Spying | ▲ | CVE-2024-37085 | ▲ | Maritime | ▲ |
| Lazarus Group | ▲ | SQL Injection | ▲ | CVE-2024-45249 | ▲ | CrowdStrike | ▲ |
| LulzsecMuslims | ▲ | Phishing | ▲ | CVE-2024-40444 | ▲ | WazirX | ▲ |
| Mont4na | ▲ | Account Takeover | ▲ | CVE-2024-30190 | ▲ | Telesur | ▲ |
| Handala | ▲ | BianLian | ▲ | CVE-2023-34693 | ▲ | Broadcom | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Acronis CVE-2023-45249.
Source: Insikt Group, Acronis | Vulnerability Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-45249| CVVS Score: 9.8 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High - 79
On July 25, 2024, Acronis patched an actively exploited vulnerability tracked as CVE-2023-45249 in its Acronis Cyber Infrastructure (ACI), a platform for backup, disaster recovery, and remote endpoint management. This remote code execution (RCE) flaw arises from improper authentication handling of default credentials. Exploitation allows threat actors to gain unauthorised access and execute arbitrary code on vulnerable servers, leading to system compromise.
The CVE-2023-45249 flaw was patched nine months ago and impacts multiple products, including:
- Acronis Cyber Infrastructure (ACI) before build 5.0.1-61
- Acronis Cyber Infrastructure (ACI) before build 5.1.1-71
- Acronis Cyber Infrastructure (ACI) before build 5.2.1-69
- Acronis Cyber Infrastructure (ACI) before build 5.3.1-53
- Acronis Cyber Infrastructure (ACI) before build 5.4.4-132
"This update contains fixes for one critical severity security vulnerability and should be installed immediately by all users. This vulnerability is known to be exploited in the wild," Acronis said.
Acronis also confirmed in a new security advisory that the bug has been exploited in attacks and warned admins to patch their installation as soon as possible.
Critical ServiceNow RCE Actively Exploited.
Source: Insikt Group, Resecurity | Vulnerability Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-4879| CVVS Score: 9.3 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 79
CVE-2024-5217| CVVS Score: 9.2 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 79
CVE-2024-5178| CVVS Score: 6.9 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 72
Threat actors are actively exploiting disclosed critical vulnerabilities in ServiceNow software, a popular cloud-based platform for managing digital workflows. The most severe vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-4879 and CVE-2024-5217, have critical CVSSv4 scores of 9.3 and 9.2 respectively, allowing unauthenticated remote threat actors to execute arbitrary code. The third, CVE-2024-5178, with a CVSSv4 score of 6.9, enables administrative users to access sensitive files on the web application server.
On July 11, Assetnote, which reported the vulnerabilities to ServiceNow in May, published technical details on the three vulnerabilities, explaining how they can be chained together to gain full access to databases and to the MID Servers – proxy servers between cloud-hosted ServiceNow instances and enterprise networks – configured with the platform.
According to Resecurity’s July 24, 2024, report, threat actors began exploiting the vulnerabilities in ServiceNow the day after ServiceNow’s disclosure and hotfix on July 10, 2024. Threat actors chained these vulnerabilities to breach organisations and steal data, targeting government agencies, data centres, energy providers, and software development firms. As observed by Resecurity, the exploitation process started with the threat actors first using publicly available exploits to identify vulnerable instances.
Although ServiceNow released patches on July 10, 2024, Bleeping Computer reported that tens of thousands of systems may still be vulnerable.
Organisations using ServiceNow are strongly advised to apply the available security updates immediately to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned above be fully patched and updated. We want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches should they apply:
- ServiceNow – Apply the latest security patches available.
- Acronis – Ensure vulnerable versions of Acronis Cyber Infrastructure are up to date.
- VMware – Ensure deployments of ESXi and Cloud Foundation are up to date where possible.
We also recommend proactively checking your environment for the software versions mentioned above and hunting for any known IOCs related to them.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing the searching and hunting activities within your environment.
