Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Check Point Security Gateway Vulnerability CVE-2024-24919 – A newly discovered Check Point Security Gateway Vulnerability information disclosure vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-24919, could allow threat actors to access internet-connected gateways with remote access VPN or mobile access enabled.
PoC Released for Fortinet SIEM Vulnerability – Two Fortinet security information and event management (FortiSIEM) vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-23108 and CVE-2024-23109, could be exploited to enable unauthenticated remote command execution (RCE).
CVE-2024-35204 allows Incorrect Default Permissions affecting Veritas System Recovery – Found in Veritas System Recovery this CVE affects an unknown part of the component Recovery Folder. The manipulation with an unknown input leads to a permission vulnerability. Exploiting this vulnerability permits low-privileged users to conduct attacks.
Potential Threats
Phishing-as-a-Service Kit Greatness Evolves Over Time; Steals Microsoft 365 Credentials - On May 22, 2024, Trellix shared an overview of Greatness, a Phishing-as-a-Service (PaaS) tool that threat actors have been using to steal Microsoft 365 login credentials since mid-2022.
Threat Actors Use Fake Updates to Deliver BitRat and LummaStealer – A malware campaign in May 2024 used fake browser updates to distribute BitRAT and Lumma Stealer to victim's machines. The infection chain starts with users visiting a compromised webpage embedded with malicious JavaScript code.
Okta Warns of Credential-Stuffing Attacks Targeting Cross-Origin Authentication Feature - On May 28, 2024, Okta reported an increase in credential-stuffing attacks targeting the cross-origin authentication feature in their Customer Identity Cloud (CIC). These attacks began on April 15, 2024, with threat actors attempting to sign in using large lists of compromised credentials.
General News
Ticketmaster confirms massive breach - Live Nation has confirmed that Ticketmaster suffered a data breach after its data was stolen from a third-party cloud database provider, which is believed to be Snowflake.
Cooler Master Confirms Data Breach Affecting Over 500,000 Customers - Cooler Master, a computer hardware manufacturer, suffered a data breach that exposed the personal data of over 500,000 customers. On May 29, 2024, Cool Master confirmed the breach after the threat actor using the moniker “Ghostr’” claimed responsibility for compromising Cooler Master's Fanzone website on May 18, 2024.
Over 100 malware servers shut down in 'largest ever' operation against botnets - International law enforcement agencies announced Thursday that they took several of the most influential malware families offline in the “largest ever operation against botnets.” The malicious software includes droppers such as IcedID, SystemBC, Pikabot, SmokeLoader, Bumblebee and Trickbot.
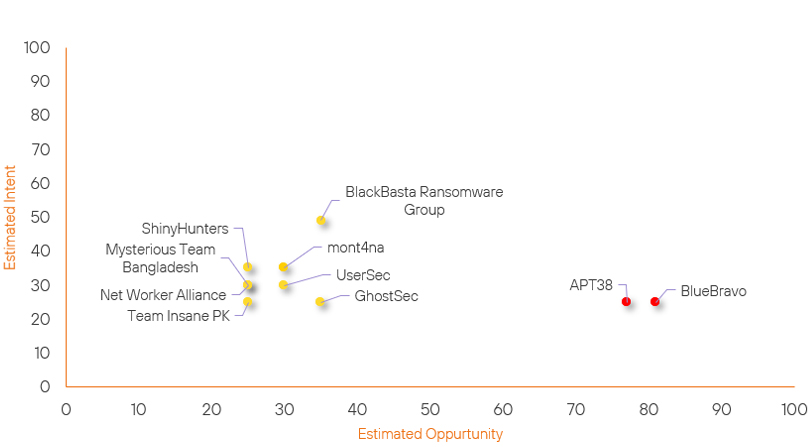
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShinyHunters | New | → | Basic | ↑ 25 | (25) | ↑ 35 | (35) |
| mont4na | Basic | → | Basic | ↑ 5 |
(30) | → 0 | (35) |
| BlueBravo | High | → | High | ↑ 1 | (81) | → 0 | (25) |
| APT38 | High | → | High | ↓ 1 | (77) | → 0 | (25) |
| UserSec | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (30) | ↓ 5 | (30) |
| Net Worker Alliance | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (25) | ↓ 5 | (30) |
| GhostSec | Basic | → | Basic | ↓ 5 | (35) | → 0 | (25) |
| Team Insane PK | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (25) | ↓ 5 | (25) |
| BlackBasta Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | ↓ 10 | (35) | → 0 | (49) |
| Mysterious Team Bangladesh | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (25) | ↓ 10 | (30) |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShinyHunters | ▲ | Credential Stuffing | ▲ | CVE-2024-24919 | ▲ | Service | ▲ |
| RansomHub Ransomware Group | ▲ | DDOS | ▲ | CVE-2024-23108 | ▲ | Live Nation Entertainment | ▲ |
| Moonstone Sleet | ▲ | Disinformation | ▲ | CVE-2024-23109 | ▲ | Retail | ▲ |
| Play Ransomware Group | ▲ | Monti Ransomware | ▲ | CVE-2024-4956 | ▲ | Ticketmaster Entertainment | ▲ |
| FortiFreaks | ▲ | Command Injection | ▲ | CVE-2023-34992 | ▲ | Software and IT Services | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
FortiSIEM CVE-2024-23108 & CVE-2024-23109.
Source: Fortinet, Insikt Group, Horizon | Vulnerability Intelligence from Insikt Group
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-23108 | CVVS Score: 9.8 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High - 79
CVE-2024-23109 | CVVS Score: 9.8 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 79
Two Fortinet security information and event management (FortiSIEM) vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-23108 and CVE-2024-23109, could be exploited to enable unauthenticated remote command execution (RCE).
On May 28, 2024, Horizon reported that the vulnerabilities allow threat actors to execute unauthorised commands via crafted API requests. Initially, Fortinet mistakenly identified these CVEs as duplicates of a previous flaw, CVE-2023-34992, but later confirmed they are distinct.
The infection chain for CVE-2024-23108 involves exploiting the FortiSIEM supervisor through improper neutralisation of special elements used in OS commands. The attack targets the datastore.py script's handling of user inputs, specifically the server_ip parameter.
By sending malicious payloads to the phMonitor service, threat actors can achieve remote code execution. Horizon3's proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit demonstrates this vulnerability, allowing unauthorised command execution on unpatched systems.
Logs from the phMonitor service in /opt/phoenix/logs/phoenix.log can reveal attempts to exploit this flaw. There are no known exploits of the vulnerabilities in the wild at the time of writing. The flaws were patched in early 2024, with proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits released in May 2024.
Fortinet recommends that these are patched immediately and have included patched versions below:
Please upgrade to FortiSIEM versions:
- 7.1.2 or above
- 7.0.3 or above
- 6.7.9 or above
- 6.6.4 or above
- 6.5.3 or above
- 7.2.0 or above
CheckPoint Security Gateway Vulnerability CVE-2024-24919.
Source: Insikt Group, CheckPoint | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-24919 | CVVS Score: 8.6 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 99
A newly discovered Check Point Security Gateway Vulnerability information disclosure vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-24919, could allow threat actors to access internet-connected gateways with remote access VPN or mobile access enabled.
Check Point released a fix for the vulnerability on May 27, 2024, and stated that the flaw affected a small number of customers who used outdated password-only authentication for old local accounts.
Check Point detected a few login attempts using old VPN local-accounts, but found no evidence of CVE-2024-24919 or any other software vulnerability being exploited.
The attempts focused on remote access scenarios involving old local accounts. The company promptly released a solution to prevent further exploitation and provided a script to discover local accounts using password-only authentication. Additionally, Check Point recommended improving VPN security by disabling unnecessary local accounts and adding layers of authentication, such as certificates.
CheckPoint has also released hotfix documentation, which can be found HERE.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we would recommend that the technologies mentioned above be fully patched and up to date. In particular, we would like to highlight and recommend applying the following patches should they apply:
- FortiSIEM – Update to the latest version or the versions listed above.
- CheckPoint Security Gateway – Apply the hotfixes provided for the specific product family provided by CheckPoint.
We would also recommend proactively checking your environment for the software versions mentioned above and hunting for any known IOCs related to them.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing these searching and hunting activities within your environment.
