Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Apache Active MQ CVE-2024-32114 – This vulnerability could allow for unauthorised access and impacts versions 6.x -6.1.1. There is currently no evidence to show exploitation in the wild. We would recommend updating to version 6.1.2, where this is patched.
WordPress Automatic Plugin CVE-2024-27956 – A proof of concept script for CVE-2024-27956 has been published. This CVE is a critical SQL injection (SQLi) vulnerability that affects all versions of the WordPress Automatic plugin.
R Programming CVE-2024-27322 – On April 29, 2024, HiddenLayer reported a new critical vulnerability CVE-2024-27322, which allows arbitrary code execution by deserialisation untrusted data. The vulnerability was addressed in the latest version of R, version 4.4.0.
Potential Threats
Threat Actors Abuse Microsoft Graph API for Covert C2 Communications - On May 2, 2024, Symantec reported an increase in the use of the Microsoft Graph API by threat actors to covert command-and-control (C2) communications via cloud services such as Microsoft OneDrive.
Goldoon Botnet – On May 1, 2024, Fortinet reported on a new botnet named Goldoon targeting D-Link routers vulnerable to CVE-2015-2051, a critical command injection flaw. This affects D-Link DIR-645 router Rev. Ax with firmware version 1.04b12 and earlier.
Scaly Wolf Phishing Campaign - Scaly Wolf Campaign Uses New Loader to Deliver WhiteSnake Stealer. The campaign uses phishing emails styled as if they were sent from a federal agency. The emails contain a legitimate document and a password-protected archive as attachments.
General News
Dropbox says hacker accessed passwords, authentication info during breach - Cloud storage company Dropbox reported that a hacker breached company systems on April 24 and gained access to sensitive information like passwords and more related to “Dropbox Sign”.
Email security loopholes are latest path for North Korean social engineering attacks - Hackers connected to North Korea are exploiting loopholes in email security systems to send spoofed messages that look legitimate. Several federal agencies published an advisory this week warning that hackers are targeting improperly configured DMARC record policies.
UK’s Ministry of Defence Targeted by Cyberattack - On May 6, 2024, it was reported that the United Kingdom’s Ministry of Defence (MoD) experienced a cyberattack, allegedly by an unidentified Chinese state-sponsored threat group. The cyberattack targeted the MoD's payroll system, compromising the personal and bank data of current and former service personnel.
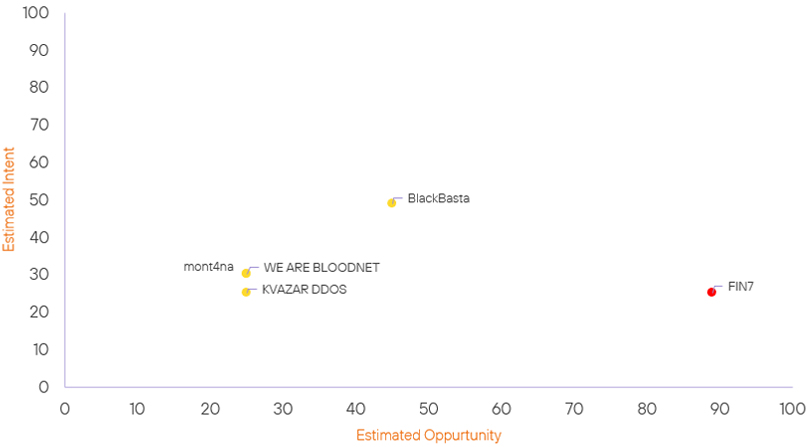
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mont4na | Basic | → | Basic | ↑ 25 | (25) | ↑ 30 | (30) |
| BlackBasta Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (45) | ↑ 4 | (49) |
| WE ARE BLOODNET | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (25) | ↓ 5 | (30) |
| KVAZAR DDOS | Basic | → | Basic | → 0 | (25) | ↓ 5 | (25) |
| FIN7 | High | → | High | → 0 | (89) | ↓ 5 | (25) |
Prominent Information Security Events
WordPress CVE-2024-27956.
Source: Insikt Group, NVD, WPScan | Global Vulnerability Risk, New Critical
or Pre NVD Vulnerabilities
Intelligence Cards: Global Vulnerability Monitoring
CVVS CNA Score: 9.9 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Critical - 89
On May 1, 2024, security researcher Diego Tellaroli (diego-tella on GitHub) published a Python-based proof-of-concept (PoC) script for CVE-2024-27956. CVE-2024-27956 is a critical SQL injection (SQLi) vulnerability that affects all versions of the WordPress Automatic plugin before 3.92.0. This CVE has been given a CVSS CNA score of 9.9 via Patchstack but is still awaiting analysis by NIST NVD.
The Automatic plugin is a popular tool for automating content imports on WordPress websites, with over 40,000 active installations. Since PatchStack disclosed the security issue, Automattic's WPScan observed more than 5.5 million attacks trying to leverage the vulnerability, most of them recorded on March 31st. WPScan reports that after obtaining admin access to the target website, attackers create backdoors and obfuscate the code to make it more difficult to find. CVE-2024-27956 allows unauthenticated threat actors to execute arbitrary SQL queries on vulnerable WordPress sites when exploited.
Administrators can check for signs that hackers took over the website by looking for the presence of an admin account starting with "xtw" and files named web.php and index.php, which are the backdoors planted in the recent campaign.
WordPress addressed CVE-2024-27956 in the Automatic plugin version 3.92.0. It is crucial that users of this plugin update immediately to the patched version.
WhiteSnake Stealer (Scaly Wolf).
Source: Insikt Group
Intelligence Cards: TTP Instance
IOC: SHA256: cbabd91fb0c1c83867f71e8df19c131ac6fb3b3f3f74765bc24924cb9d51ad41
IOC: SHA256: 93948C7FB89059E1F63AF04FEEF0A0834B65B18FFAF6610B419ADBC0E271E23D
IOC: SHA256: 10330FCC378DB73346501B2A26D2C749F51CACD962B54C62AA017DD9C1ED77C3
On May 2, 2024, cybersecurity firm BI.ZONE (@bizone_en on X, formerly known as Twitter) published a write-up detailing a new phishing campaign conducted by the threat group Scaly Wolf. The emails contain a legitimate document and a password-protected archive as attachments.
The archive file, when extracted, drops a text file (Пароль 120917.txt), a decoy document (Права и обязанности и процедура ст. 164, 170, 183 УПК РФ.rtf), and an executable file (Матералы к запросу, обязательно к ознакомлению и предоставлению информации-.exe). The text file contains the password for the archive file. The executable file was identified as a loader that delivers the WhiteSnake stealer payload. IOCs for these can be seen above.
The loader once executed, checks the system's graphics card manufacturer ID to detect virtual machine (VM) environments. If the system is identified as a VM, the loader terminates its process. Otherwise, it injects the WhiteSnake stealer payload into the "explorer.exe" process. The loader uses syscall instructions to directly access the Windows kernel instead of using traditional WinAPI calls. It also attempts to hide its activities by opening non-existent files and writing random data onto them.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we would recommend that the technologies mentioned above be fully patched and up to date. In particular, we would like to highlight and recommend applying the following patches should they apply:
- WordPress Automatic plugin – Update to version 3.92.0.
- Apache Active MQ – Update to version 6.1.2.
- R Programming – Update to version 4.4.0.
We would also recommend proactively checking your environment for the software versions mentioned above and hunting for any known IOCs related to them.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing these searching and hunting activities within your environment.
