Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
ACROS Security Releases Micropatch for Unassigned Zero-Day in Windows Themes - ACROS Security discovered a new zero-day vulnerability in Windows Themes that allows remote threat actors to steal New Technology LAN Manager (NTLM) credentials, as detailed in their October 29, 2024 report. Not yet assigned a CVE identifier, this vulnerability activates automatically when a user views a malicious theme file in Windows Explorer, requiring no further interaction.
Ransomware Groups Abuse SonicWall VPN Accounts Vulnerable to CVE-2024-40766 - Fog and Akira Ransomware Groups target devices vulnerable to CVE-2024-40766, exploiting unpatched SonicWall SSL VPNs to gain unauthorised network access. According to a report by Arctic Wolf on October 24, 2024, there have been over 30 intrusions beginning in August 2024, where these threat actors used vulnerable SonicWall devices across various industries.
PoC Published for CVE-2024-38812, Critical RCE Vulnerability in VMware's DCERPC Protocol - On October 23, 2024, SonicWall published a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) for a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, CVE-2024-38812, in VMware vCenter Server. This vulnerability explicitly affects VMware vCenter Server handling of the Distributed Computing Environment/Remote Procedure Call (DCERPC) protocol.
Potential Threats
New FakeCall Malware Variant Hijacks Bank Calls and Mimics Banking Apps to Steal Financial Data - A new variant of the voice phishing malware FakeCall is being used to redirect users' outgoing calls to attacker-controlled numbers. According to a report by Zimperium on October 30, 2024, the malware mimics legitimate banking interfaces and manipulates both incoming and outgoing calls to intercept interactions with financial institutions.
15,000 Git Cloud Account Credentials Stolen in "EmeraldWhale" Campaign - A cybercriminal operation called EMERALDWHALE targeted misconfigured Git configuration files, stealing over 15,000 cloud credentials from repositories on GitHub, GitLab, BitBucket.
BumbleBee Loader Resurgence - On October 18, 2024 Netskope Threat Labs published a blog highlighting a resurgence in BumbleBee Loader activity following a temporary disruption in May 2024 due to Europol’s Operation Endgame, which targeted malware ecosystems like BumbleBee Loader, IcedID, and Pikabot.
General News
International Law Enforcement Dismantles Redline and Meta Infostealer Infrastructure - Dutch police successfully disrupted the infrastructure of Redline and Meta Infostealers through Operation Magnus, gaining full access to their servers. According to the campaign’s page, the takedown occurred on October 28, 2024, and resulted from a coordinated effort by Dutch police, the FBI, and other international agencies.
Malware campaign expands its use of fake CAPTCHAs - To infect users with malware known as Lumma and Amadey, the hackers redirect victims to what appears to be a normal CAPTCHA. Clicking the familiar “I’m not a robot” button, however, copies malicious code to the user’s clipboard, while completing other apparently normal verification steps executes the code.
France's Second Largest Internet Service Provider, Free, Confirms Data Breach - France’s second-largest telecommunications provider, Free S.A.S., confirmed a data breach that compromised some personally identifiable information (PII) of its customers.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
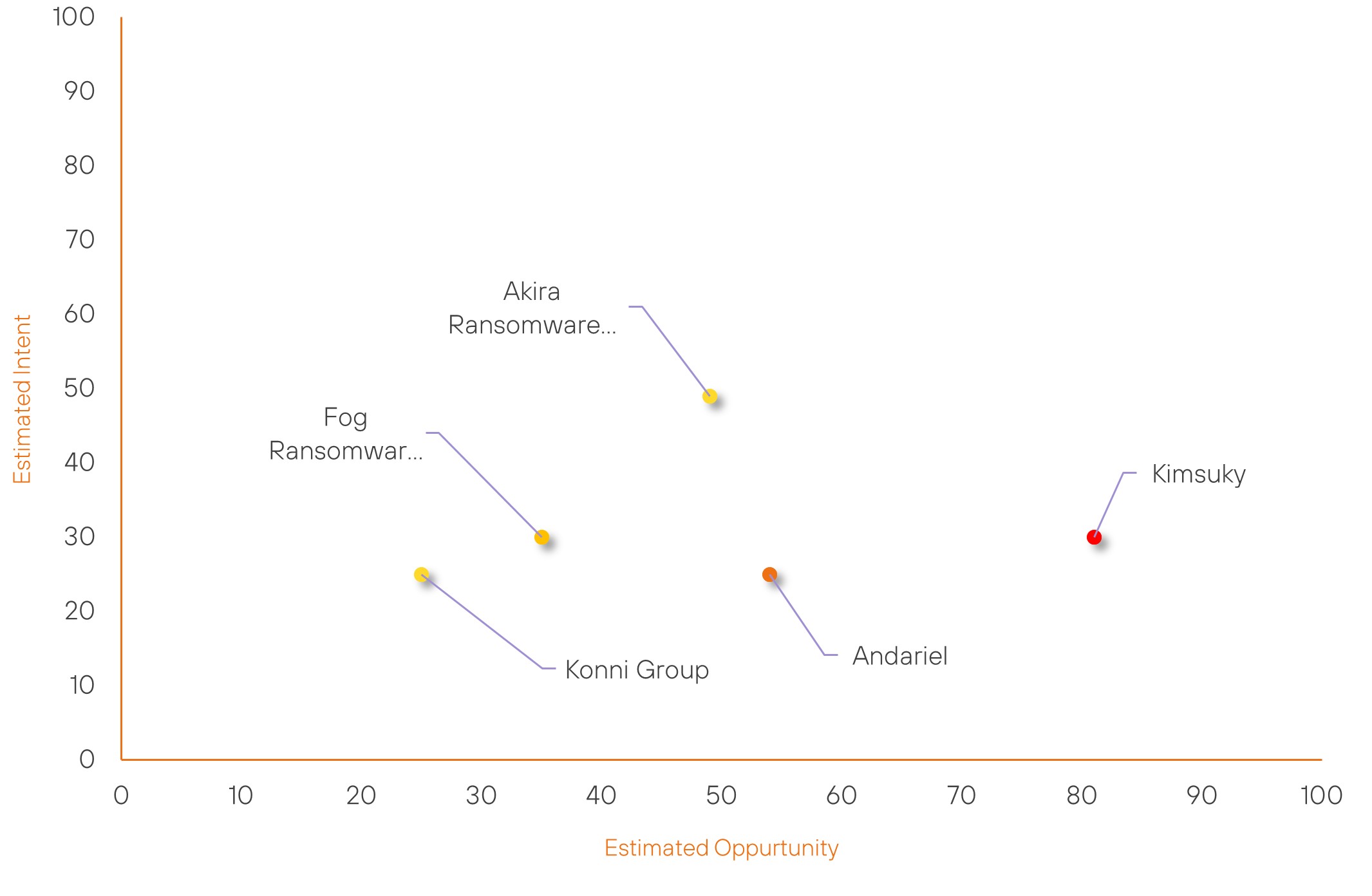
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fog Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (35) | ↑ 35 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
| Konni Group | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 30 | (25) | ↑ 25 |
| Akira Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (49) | ↑ 9 | (49) | → 0 |
| Andariel | Moderate | → | Moderate | (54) | ↑ 1 | (25) | → 0 |
| Kimsuky | High | → | High | (81) | ↑ 1 | (30) | → 0 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese Hackers | ▲ | Supply Chain Attack | ▲ | CVE-2024-47575 | ▲ | Apple Pay | ▲ |
| BlueBravo | ▲ | LummaC2 | ▲ | CVE-2024-8956 | ▲ | Moldova | ▲ |
| Cactus Ransomware Group | ▲ | Phishing | ▲ | CVE-2024-8957 | ▲ | Microsoft Azure | ▲ |
| Anonymous | ▲ | Impersonation Attack | ▲ | CVE-2024-44258 | ▲ | Kremlin | ▲ |
| Mysterious Team Bangladesh | ▲ | Rhadamanthys Stealer | ▲ | CVE-2024-38094 | ▲ | PATTI | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
BumbleBee Loader resurgence to deploy MSI files.
Source: Insikt Group, Netskope | Hunting Package
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256: 2bca5abfac168454ce4e97a10ccf8ffc068e1428fa655286210006b298de42fb
IOC: SHA256: 106c81f547cfe8332110520c968062004ca58bcfd2dbb0accd51616dd694721f
IOC: SHA256: c26344bfd07b871dd9f6bd7c71275216e18be265e91e5d0800348e8aa06543f9
IOC: SHA256: 0ab5b3e9790aa8ada1bbadd5d22908b5ba7b9f078e8f5b4e8fcc27cc0011cce7
IOC: SHA256: d3f551d1fb2c307edfceb65793e527d94d76eba1cd8ab0a5d1f86db11c9474c3
IOC: SHA256: d1cabe0d6a2f3cef5da04e35220e2431ef627470dd2801b4ed22a8ed9a918768
IOC: SHA256: 7df703625ee06db2786650b48ffefb13fa1f0dae41e521b861a16772e800c115
IOC: URL: hxxp:///193.242.145.138/mid/w1/Midjourney.msi
IOC: URL: hxxp://193.176.190.41/down1/nvinstall.msi
On October 18, 2024 Netskope Threat Labs published a blog highlighting a resurgence in BumbleBee Loader activity following a temporary disruption in May 2024 due to Europol’s Operation Endgame, which targeted malware ecosystems like BumbleBee Loader, IcedID, and Pikabot.
BumbleBee Loader was first identified in 2022 as a malware loader designed to infiltrate corporate networks and deliver additional payloads such as Cobalt Strike beacons and ransomware, leveraging fileless techniques to evade detection. The Conti Gang and Trickbot Gang are suspected of developing the malware.
Based on Netskope Threat Labs, the infection begins with a phishing email that entices the target to download a ZIP file containing a malicious LNK file, which then initiates a PowerShell command to download an MSI file. This MSI file, disguised as legitimate software (such as Nvidia or Midjourney installers), executes the BumbleBee Loader payload directly in memory without dropping it on disk, thus evading typical file-based detection methods.
Unlike previous BumbleBee Loader versions, this iteration avoids creating new processes by using a stealthy technique with the MSI SelfReg table, which calls the DLL’s DllRegisterServer function directly in memory. This approach limits detection opportunities, representing an evolved tactic to maintain persistence and covertly operate within compromised networks.
PoC Published for Critical RCE Vulnerability CVE-2024-38812 in VMware's DCERPC Protocol.
Source: Insikt Group, SonicWall, Broadcom | Vulnerability Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-38812 | CVVS Score: 9.8 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 79
On October 23, 2024, SonicWall published a Proof-of-Concept (PoC) for a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability, CVE-2024-38812, in VMware vCenter Server. This vulnerability explicitly affects VMware vCenter Server handling of the Distributed Computing Environment/Remote Procedure Call (DCERPC) protocol. VMware had previously addressed the vulnerability on October 21, 2024.
The vulnerability originates from a heap overflow flaw in the rpc_ss_ndr_contiguous_elt() function of the DCERPC protocol. This function improperly handles a range_list->lower value controlled by user input, which can be exploited through designed network packets. These packets modify the base address of p_array_addr by adding an offset derived from several parameters, including the threat actor-controlled range_list->lower value. This manipulation allows threat actors to change memory addresses and execute arbitrary code.
This flaw is present in VMware vCenter Server version 8.0U3a and VMware Cloud Foundation. Despite the publication of the PoC, there are no reports of CVE-2024-38812 being exploited in the wild.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-38812 – Update to the detailed fixed version within the Broadcom Response Matrix.
- CVE-2024-40766 – Update to the latest firmware and follow vendor-recommended mitigations.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
