Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Write-Up and Alleged PoC for Critical FortiManager Zero-Day Authentication Bypass - A critical authentication bypass vulnerability (CVE-2024-47575) in FortiManager allows remote, unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code. This flaw is actively exploited to exfiltrate sensitive data from affected devices. Fortinet issued a fix on October 30, 2024.
Critical Command Injection Vulnerability in D-Link NAS Devices - CVE-2024-10914, a critical command injection vulnerability, affects over 61,000 End-of-Life D-Link NAS devices, including models DNS-320 and DNS-340L. The flaw in the cgi_user_add command allows remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands. As of now, there have been no reports of active exploitation. D-Link recommends isolating these devices or replacing them due to a lack of support.
Critical Spoofing Vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server - CVE-2024-49040, a critical spoofing vulnerability in Microsoft Exchange Server, allows attackers to manipulate the "From" field in emails to appear legitimate. This is due to non-compliant P2 FROM headers, which affect Outlook email clients. Microsoft has issued a security update to detect malicious emails, but a patch has not yet been released. There is no known active exploitation. Administrators are advised to implement automated actions to reject suspicious emails.
Potential Threats
Fake AI Tool Spreads Lumma Stealer and AMOS Malware - On November 16, 2024, BleepingComputer reported a campaign where fake AI video generator websites distribute Lumma Stealer and AMOS malware. The sites impersonate EditProAI, tricking users into downloading malicious files that target both Windows and macOS systems. Once executed, the malware steals sensitive data, including cryptocurrency wallets and credentials, and sends it to a command-and-control server. Users should avoid these fake tools and secure their systems.
Palo Alto Networks Confirms Critical Zero-Day in Firewalls - Palo Alto Networks confirmed a critical zero-day vulnerability (CVSS 9.3) allowing unauthenticated remote command execution on exposed firewall management interfaces. The flaw is actively exploited but lacks a CVE identifier. The company is working on patches and signatures. Users should restrict access to management interfaces from trusted IPs. Prisma Access and Cloud NGFW are unaffected. The source of the vulnerability and targeted entities remain unclear.
IoT Devices Turned into Residential Proxies by Threat Actor - On November 19, SecurityWeek reported that a threat actor has hijacked thousands of IoT devices, transforming them into residential proxies. This tactic involves using compromised devices like routers and cameras to mask malicious traffic, making it difficult to trace cyberattacks. The residential proxies can be exploited for activities such as fraud, botnet control, and bypassing security measures.
General News
Microlise Confirms Cyberattack Compromised Corporate Data - The cyberattack on Microlise compromised corporate data and impacted customer systems, including British prison vans. The company confirmed no customer data was compromised, but some employee data was affected. Most systems are now back online, with some customers still verifying security.
Google Launches Shielded Email for Enhanced Privacy and Spam Protection - Google's 'Shielded Email' feature allows users to create aliases for improved privacy and spam protection. These aliases forward messages to the main inbox, preventing exposure of the primary email address.
Akira Ransomware Gang Leaks Record Data in One Day - The Akira ransomware gang leaked a record number of victims' data in a single day, with 35 new victims posted to their darknet site. Akira, active since March 2023, has reportedly earned $42 million from around 250 attacks.
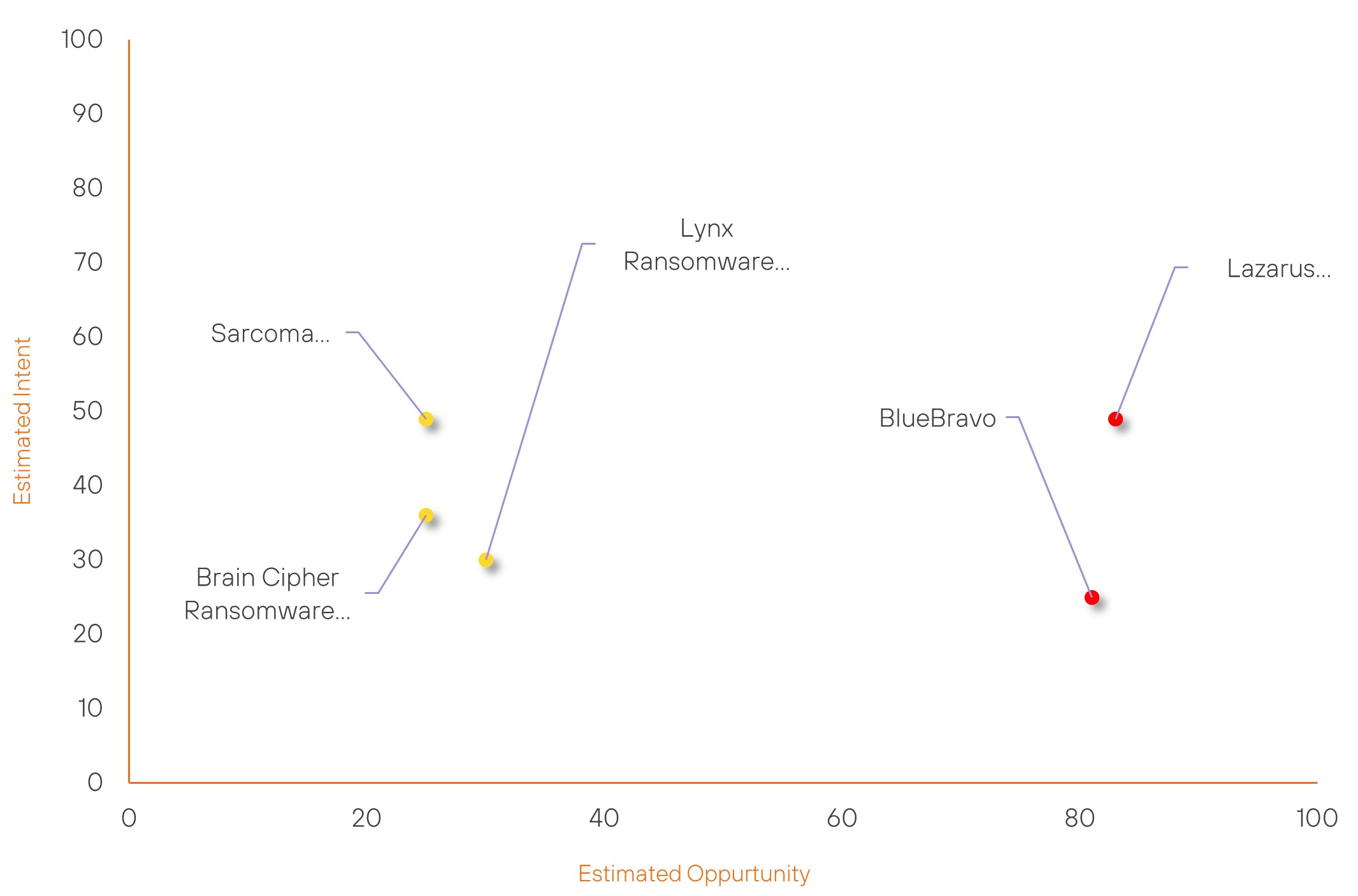
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lazarus Group | High | → | High | (83) | ↑ 3 | (49) | → 0 |
| BlueBravo | High | → | High | (81) | ↓ 1 | (25) | → 0 |
| Sarcoma Group | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (49) | ↑ 49 |
| Brain Cipher Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (36) | ↑ 36 |
| Lynx Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (30) | ↑ 30 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sarcoma Group | ▲ | Trojan | ▲ | CVE-2024-9474 | ▲ | Telegram | ▲ |
| Akira Ransomware Group | ▲ | Adware | ▲ | CVE-2024-38813 | ▲ | Electric power | ▲ |
| Origami Elephant | ▲ | Spear Phishing | ▲ | CVE-2024-0012 | ▲ | Ford Motor Company | ▲ |
| Salt Typhoon | ▲ | Cyber spying | ▲ | CVE-2024-10524 | ▲ | Eastern Europe | ▲ |
| Helldown Ransomware Group | ▲ | Phishing | ▲ | CVE-2024-38812 | ▲ | iLearningEngines, Inc. | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Write-Up and Alleged PoC for Critical FortiManager Zero-Day Authentication Bypass
Source: Insikt Group, Rapid7 | TTP Instance
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: CVE -2024-47575 | CVVS Score: 9.8 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Very Critical - 99
On November 13, 2024, Rapid7 published a detailed write-up and proof-of-concept (PoC) script for CVE-2024-47575, a critical zero-day authentication bypass vulnerability affecting Fortinet's FortiManager and FortiManager Cloud. This vulnerability impacts the following systems:
- FortiManager 7.6.0
- FortiManager 7.4.0-7.4.4
- FortiManager 7.2.0-7.2.7
- FortiManager 7.0.0-7.0.12
- FortiManager 6.4.0-6.4.14
- FortiManager 6.2.0-6.2.12
- Fortinet FortiManager Cloud 7.4.1-7.4.4
- FortiManager Cloud 7.2.1-7.2.7
- FortiManager Cloud 7.0.1-7.0.12
- FortiManager Cloud 6.4.1-6.4.7
The vulnerability is caused by a missing authentication check in the “fgfmsd” daemon, which allows unauthenticated attackers to send crafted requests and execute arbitrary code with root privileges. Exploiting this flaw enables attackers to gain remote control and exfiltrate sensitive data such as IP addresses, credentials, and system configurations.
Rapid7’s PoC demonstrates exploitation by establishing a TLS connection, registering a fake device, and executing a reverse shell. Mandiant identified over 50 affected systems and attributed the activity to UNC5820, with exploitation possibly dating back to June 2024.
Fortinet patched the vulnerability on October 30, 2024. Users are strongly advised to update their systems immediately.
Fake AI Tool Spreads Lumma Stealer and AMOS Malware
Source: Insikt Group, BleepingComputer | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: Internet Domain Name: editproai[.]org
IOC: Internet Domain Name: editproai[.]pro
IOC: Internet Domain Name: proai[.]club
IOC: SHA256: bc6f8cd01077e85c78664af75b95f6645eb611203ed2769304e23c2955fc8ca5
IOC: SHA256: a0041464eaecdb08119b38f377c919e512610307cd7f994aba11c02112fb6777
IOC: SHA256: cc5c482229f5b9d1c88f6ff68abb7461de259749f6230932654bb5aaa3fddd88
On November 16, 2024, BleepingComputer reported on a campaign where threat actors distribute Lumma Stealer and AMOS malware via fake websites masquerading as the EditProAI platform. The malware, targeting both Windows and macOS, steals sensitive data like cryptocurrency wallets, login credentials, and payment details from browsers like Firefox and Chrome.
Victims are lured through political deepfake videos, leading them to malicious download links. The malware uses stolen certificates to evade detection and exfiltrates data to a command-and-control server for further exploitation.
Users should avoid these sites and secure their systems to protect against this threat.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-47575 – Update to the latest versions available.
- CVE-2024-10914 – D-Link recommends either isolating devices with this vulnerability or replacing them.
- CVE-2024-49040 – The patches have not yet been released; therefore, administrators are advised to implement automated actions to reject suspicious emails
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
