Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
CISA Adds Ivanti EPM RCE Vulnerability, CVE-2024-29824, to Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalogue - The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added a critical-severity vulnerability affecting Ivanti Endpoint Manager (EPM) to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalogue on October 2, 2024. The vulnerability tracked as CVE-2024-29824, was initially patched by Ivanti on May 21, 2024.
CVE-2024-47555 - Allows Remote Code Execution affecting Xerox FreeFlow Core - Xerox engineering and development discovered a vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-47555, in the Xerox FreeFlow Core application. It allows attackers to perform remote code execution via user and system configuration. The vulnerability affects Xerox FreeFlow Core 7.0. Updating the affected product to Xerox FreeFlow Core 7.0.11 is highly recommended to address the issue.
CVE-2024-28995- Threat Actors Exploit SolarWinds, Targeting Sensitive Windows Files - On September 30, 2024, GreyNoise Labs reported that threat actors are exploiting CVE-2024-28995, a pathtraversal vulnerability in SolarWinds Serv-U. This flaw, disclosed on June 5, allows unauthorised access to sensitive files via manipulated URL requests, such as c:\windows\panther\unattend.xml.
Potential Threats
Phishing Campaign Targeting the US and UK Impersonates Royal Mail - Threat actors targeted organisations in the US and UK using phishing emails to impersonate the Royal Mail to deliver ransomware. According to a report by Proofpoint on October 2, 2024, the threat actors used the open-sourced Prince Ransomware available on GitHub, which was dedicated for educational purposes and has no known decryption feature or recovery mechanism.
Rackspace Suffers Data Breach - The breach, discovered on September 24, 2024, allowed the threat actor to gain unauthorised access to three of Rackspace's internal monitoring web servers and obtain customers’ account names, usernames, device information, IP addresses, and encrypted internal credentials. According to a report on September 30, 2024, by The Register, an unidentified threat actor exploited an unspecified zero-day remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in ScienceLogic SL1 platform.
Perfctl Malware Targets Linux in Cryptomining Campaign - Perfctl malware has been targeting Linux servers and workstations for at least three years, leveraging rootkits and high-level evasion techniques to remain undetected. According to a report by Aqua Nautilus’ October 3, 2024, Perfctl likely compromised thousands of Linux servers by exploiting misconfigurations and vulnerabilities, such as CVE2023-33246 (Apache RocketMQ) and CVE-2021-4034 (Polkit).
General News
Cloudflare Mitigates Record-Breaking 3.8Tbps DDoS Attack - On October 2, 2024, American internet infrastructure company Cloudflare reported that it had mitigated a record-breaking distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack, which peaked at 3.8 terabits per second (Tbps) with 2 billion packets per second (Pps). The campaign, which began in early September, targeted organisations in the financial services, internet, and telecommunications sectors.
Sellafield, UK’s largest nuclear site, fined £330,000 for cybersecurity failings - The company managing the Sellafield nuclear site in the United Kingdom has been fined £332,500 ($435,400) in a landmark prosecution after pleading guilty to three criminal charges over cybersecurity failings.
Experts warn of DDoS attacks using linux printing vulnerability - Researchers at technology firm Akamai said on Tuesday that distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks could be launched using four vulnerabilities affecting Common UNIX Printing System, also known as CUPS. The vulnerabilities, which allow attackers to run malicious code on a remote device, were discovered by Italian security researcher Simone Margaritelli and disclosed last week.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
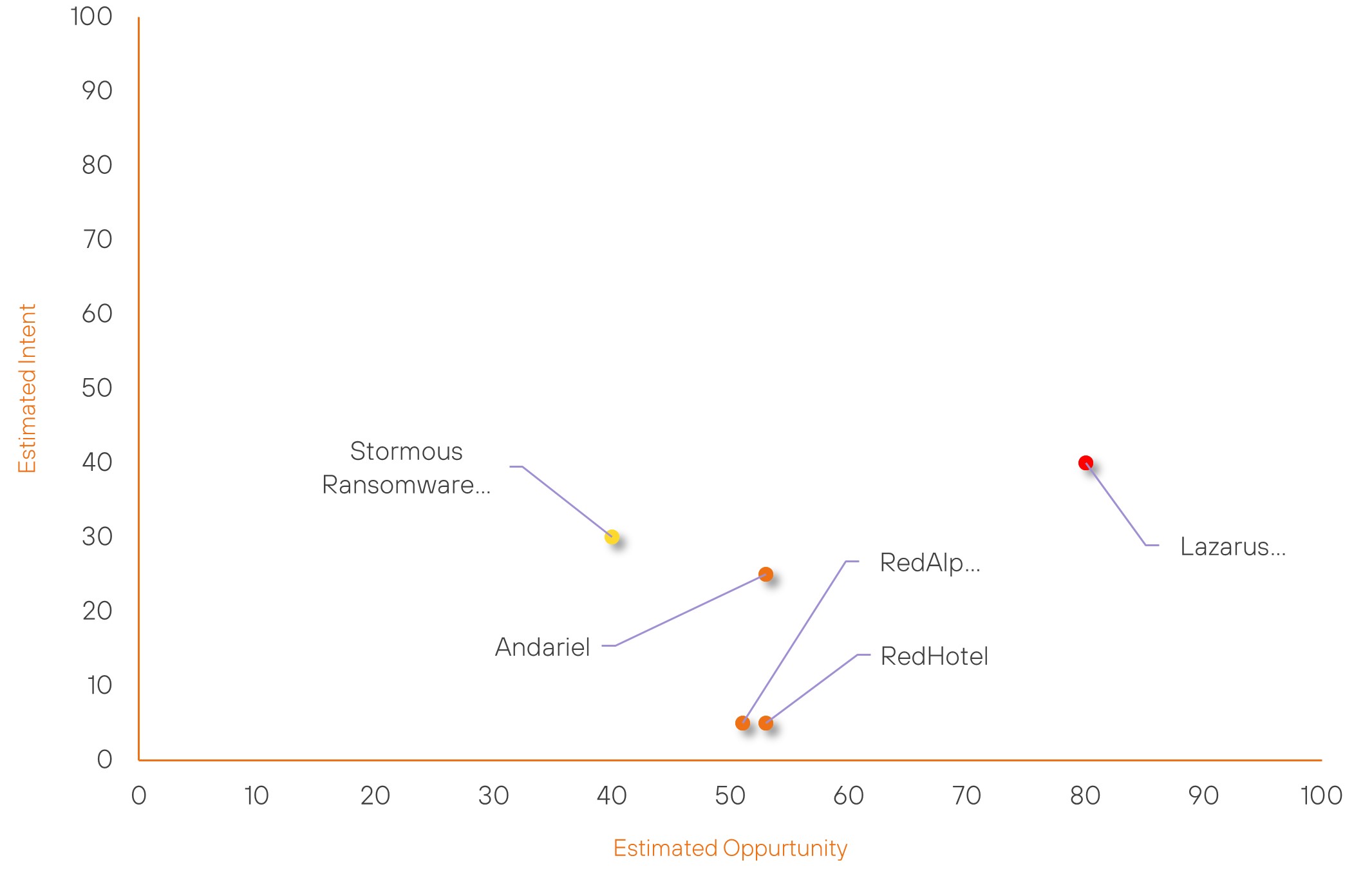
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lazarus Group | High | → | High | (80) | ↓ 1 | (40) | → 0 |
| RedHotel | New | → | Moderate | (53) | ↑ 53 | (5) | ↑ 5 |
| RedAlpha | New | → | Moderate | (51) | ↑ 51 | (5) | ↑ 5 |
| Andariel | Moderate | → | Moderate | (53) | ↑ 1 | (25) | → 0 |
| Stormous Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (40) | ↑ 40 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salt Typhoon | ▲ | Denial-ofService | ▲ | CVE-202432102 | ▲ | Internet Hosting | ▲ |
| Handala | ▲ | Trinity Ransomware | ▲ | CVE-202444193 | ▲ | Telecommunications | ▲ |
| Stormous Ransomware Group | ▲ | Cyberattack | ▲ | CVE-202443047 | ▲ | Publishing | ▲ |
| Majeed Brigade | ▲ | Domain Hijacking | ▲ | CVE-2024- 42415 | ▲ | Verizon | ▲ |
| CyberVolk Group | ▲ | Remote Code Execution | ▲ | CVE-202445519 | ▲ | Television | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Phishing Campaign Targeting Organisations in the US and UK Impersonates the Royal Mail to Deliver Prince Ransomware
Source: Insikt Group, Proofpoint | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: Email: tedra_yrigollen@proton[.]me
IOC: Email: indiracasciato@proton[.]me
IOC: Email: chitra_mcintire@proton[.]me
IOC: SHA256: e2a187babf980f024b94fa2cb4a93948d70c1e15bed1eccf975ab6c562754149
IOC: SHA256: 226b653e57484de58148b455b714dcb551a52eda5a3a6d8210095aab96d782df IOC: SHA256: ad1983a13a06919c9b8da04727ea3c210e9d19e0598c0811e4b8355b5a98589e
Threat actors targeted organisations in the US and UK using phishing emails impersonating the Royal Mail to deliver ransomware. According to a report by Proofpoint on October 2, 2024, the threat actors used the opensourced Prince Ransomware available on GitHub, which was dedicated for educational purposes and has no known decryption feature or recovery mechanism.
The infection chain began with threat actors sending messages from ProtonMail addresses, impersonating Royal Mail, via email and public contact forms. The emails contained a PDF attachment that linked to a Dropbox-hosted ZIP file. This ZIP file included a second password-protected ZIP and a text file with the password.
Inside the second ZIP was a malicious shortcut (LNK) file. When executed, the shortcut ran obfuscated JavaScript, which wrote multiple PowerShell scripts to the %temp% directory. These scripts bypassed Windows security features, created a scheduled task to run every twenty minutes, and ultimately decrypted and loaded a .NET assembly. This assembly was identified as the Prince ransomware, which encrypted files, changed their extensions, and displayed a ransom note.
Perfctl Malware Targets Linux in Cryptomining Campaign
Source: Insikt Group, Aqua Nautilus | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: IP: 211[.]234[.]111[.]116
IOC: IP: 46[.]101[.]139[.]173
IOC: IP: 104[.]183[.]100[.]189
IOC: IP: 198[.]211[.]126[.]180
IOC: MD5: 656e22c65bf7c04d87b5afbe52b8d800
IOC: MD5: 6e7230dbe35df5b46dcd08975a0cc87f
Perfctl malware has been targeting Linux servers and workstations for at least three years, leveraging rootkits and high-level evasion techniques to remain undetected. According to a report by Aqua Nautilus’ October 3, 2024, Perfctl likely compromised thousands of Linux servers by exploiting misconfigurations and vulnerabilities, such as CVE-2023-33246 (Apache RocketMQ) and CVE-2021-4034 (Polkit).
Once active, perfctl establishes communication over TOR with command-and-control servers, making traffic analysis difficult. It deploys rootkits (e.g., "libgcwrap.so") to intercept network traffic, modify authentication mechanisms, and replace legitimate system utilities, such as ldd, top, and lsof, to avoid detection. The primary objective of the malware is to conduct cryptomining for Monero, although Aqua Nautilus warns that it can support more damaging operations.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-29824 – Upgrade Ivanti EPM Core server to the latest version.
- CVE-2024-47555 – Upgrade to Xerox FreeFlow Core 7.0.11.
- CVE-2024-28995 – Install the provided Hotfix; this requires Serv-U 15.4.2.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
