Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
CVE-2024-23113 - CISA Adds Fortinet Vulnerability to KEV Catalogue - On October 9, 2024, the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added a critical-severity vulnerability affecting multiple Fortinet enterprise devices to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalogue. Fortinet recommends updating devices to the latest patched versions to mitigate the risk of exploitation.
Palo Alto Networks Issues Alert on Critical Vulnerabilities in Expedition Solution - Critical vulnerabilities have been identified in Palo Alto Networks' Expedition solution, which could expose PAN-OS firewall credentials. According to Palo Alto’s advisory on October 10, 2024, the CVE-2024-9463 allows unauthenticated threat actors to run OS commands as root, exposing usernames, passwords, device configurations, and API keys.
Critical Vulnerability in Visual Studio Allows Arbitrary Code Execution - A researcher discovered a critical vulnerability in Visual Studio, tracked as CVE-2024-30052, which allows arbitrary code execution when debugging dump files. According to a report by the security researcher Ynwarcs on October 4, 2024, the vulnerability was identified in August 2023 and patched in June 2024 with Visual Studio 17.8.11.
Potential Threats
Phishing Campaigns Exploiting Legitimate File Hosting Services - Microsoft has observed an increase in phishing campaigns that exploit legitimate file-hosting services, including OneDrive, SharePoint, and Dropbox. According to their October 8, 2024 report, these business email compromise (BEC) attacks target specific individuals and devices, aiming to conduct data exfiltration, financial fraud, and lateral movement. These campaigns also use restricted file access and view-only restrictions to bypass security measures.
Rhysida Ransomware Crawls into Systems with CleanUpLoader - Insikt Group identified a multi-tiered infrastructure used by the ransomware group Rhysida — in combination with Recorded Future Network Intelligence, this discovery enabled the identification of ransomware victims an average of 30 days before they appeared on public extortion sites.
Mamba 2FA Phishing-as-a-Service Targets Microsoft 365 - The Mamba 2FA Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) platform targets Microsoft 365 users by employing adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA), according to an analysis by Sekoia published on October 7, 2024. Priced at $250 per month, this platform enables threat actors to conduct phishing attacks that closely mimic legitimate Microsoft 365 login interfaces.
General News
Internet Archive Suffers Data Breach Exposing 31 Million Records - On October 9, 2024, BleepingComputer reported a security breach at the Internet Archive, resulting in unauthorised access to approximately 31 million user records from their authentication database. Users first learned of the breach through a JavaScript alert on the archive[.]org website. This notification also advised visitors to check the Have I Been Pwned (HIBP) service to see if their data was included.
Casio Suffers Operational Disruptions Following Network System Breach - On October 8, 2024, Casio Computer Co., Ltd., a prominent Japanese electronics company, disclosed that an unnamed threat actor infiltrated its network systems on October 5, 2024, leading to operational malfunctions that affected several services. The company is investigating the initial access method used by the threat actor and whether any sensitive personal or organisational data was compromised.
Recently-patched Firefox bug exploited against Tor browser users - The Tor anonymity network issued an emergency patch last week to address a recently-discovered security flaw that was being exploited against its users.The bug, tracked as CVE-2024-9680, allows attackers to execute malicious code within the browser’s content process — the environment where web content is loaded and rendered. The flaw was first patched by the Mozilla Foundation in its Firefox web browser last week.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
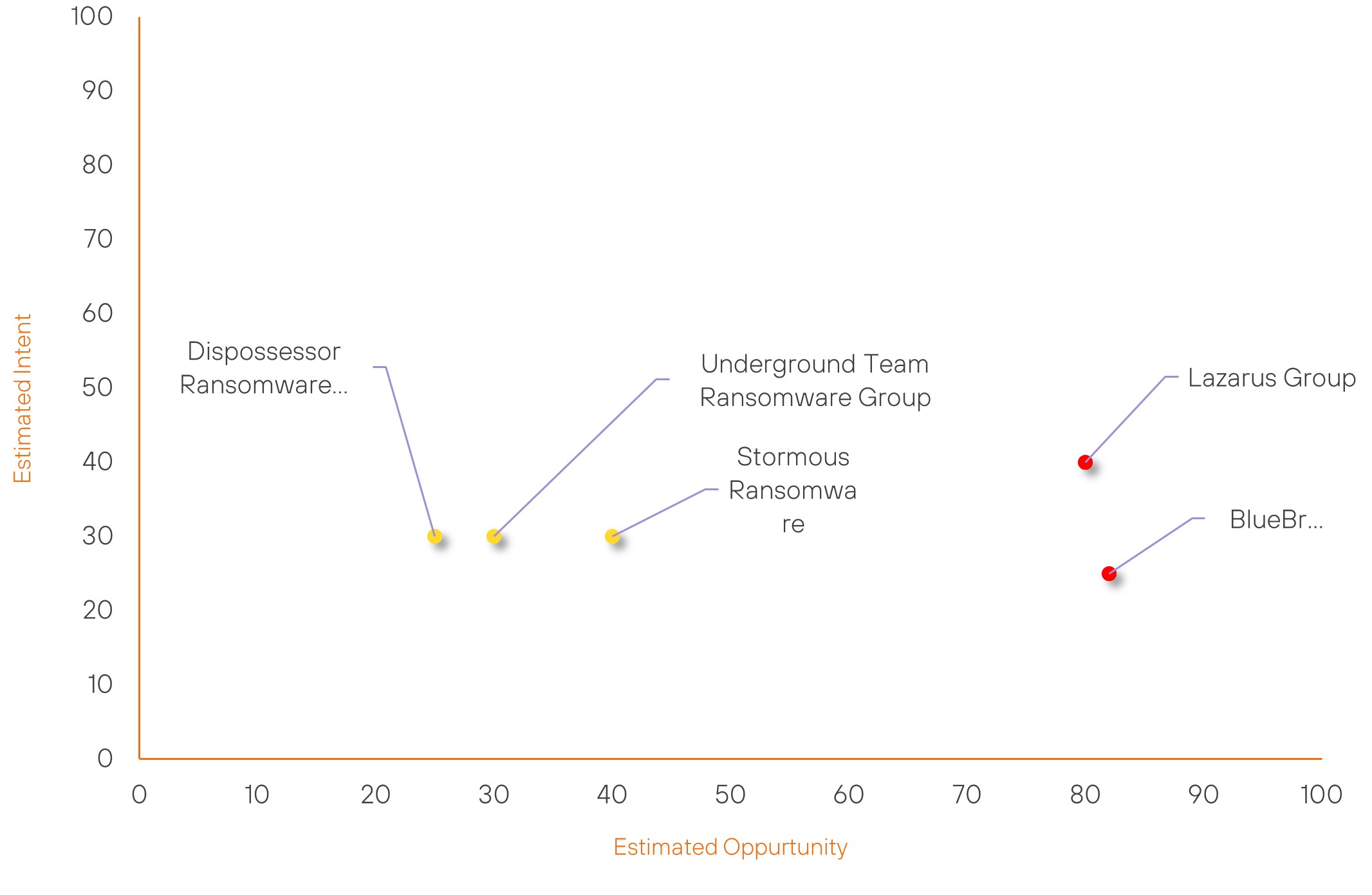
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stormous Ransomware | New | → | Basic | (40) | ↑ 40 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
| Lazarus Group | High | → | High | (80) | ↓ 2 | (40) | → 0 |
| BlueBravo | High | → | High | (82) | ↑ 1 | (25) | → 0 |
| Underground Team Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (30) | ↑ 30 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
| Dispossessor Ransomware Group | New | → | Basic | (25) | ↑ 25 | (30) | ↑ 30 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BlueBravo | ▲ | Dox | ▲ | CVE-2024-30088 | ▲ | Software | ▲ |
| Sarcoma Group | ▲ | Zero Day Exploit | ▲ | CVE-2024-40711 | ▲ | Interactive Entertainment | ▲ |
| LockBit Gang | ▲ | Phishing | ▲ | CVE-2024-43573 | ▲ | Internet Archive | ▲ |
| Lynx Ransomware Group | ▲ | Exploit Public-Facing Application | ▲ | CVE-2024-23113 | ▲ | Manufacturing | ▲ |
| Anonymous | ▲ | Privilege Escalation | ▲ | CVE-2024-43572 | ▲ | Consumer Electronics | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
New Mamba 2FA Phishing-as-a-Service Platform Targets Microsoft 365 in Adversary-in-the-Middle Attacks.
Source: Insikt Group, Sekoia | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: Domain: voltampereactive[.]com
IOC: Domain: twomancake[.]com
IOC: Domain: sithchibb[.]com
IOC: IP: 172[.]86[.]104[.]33
IOC: IP: 45[.]86[.]54[.]206
IOC: IP: 172[.]86[.]106[.]94
The Mamba 2FA Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) platform targets Microsoft 365 users by employing adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) attacks to bypass multi-factor authentication (MFA), according to an analysis by Sekoia published on October 7, 2024. Priced at $250 per month, this platform enables threat actors to conduct phishing attacks that closely mimic legitimate Microsoft 365 login interfaces. ANY.RUN first documented Mamba 2FA in June 2024 and has been operational since November 2023.
Mamba 2FA uses proxy servers provided by IPRoyal to conceal its relay servers' IP addresses, reducing its visibility to security defences. The platform also frequently rotates its phishing URLs and domain names to minimise the risk of being identified and blocked by security tools. The phishing pages are also designed with non-malicious appearing content that masks embedded malicious JavaScript.
Mamba 2FA uses phishing templates that resemble services' interfaces, such as OneDrive and SharePoint Online, replicating the branding of the targeted organisations. This platform captures credentials and session cookies, which it transmits to the threat actors via a Telegram bot. Furthermore, Mamba 2FA incorporates features that detect and bypass security sandboxes, redirecting analysis tools to ineffective pages. To mitigate these phishing threats, it is recommended that organisations implement security measures like hardware security keys and certificate-based authentication.
Rhysida Ransomware Crawls into Systems with CleanUpLoader.
Source: Insikt Group | Cyber Threat Analysis
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256: d40461331f4511c27611f6cba2af831aaa0789990c8387f6ec7bc0bf54b10961
IOC: SHA256: e60cab41b7602209c1660bc518b1f7b639ab45e60bbedf3b23757e4937c24fc4
IOC: SHA256: 4adfdd5d066fb1f880f02fdd0118095afdf60d644c5df79f43935cfc3b80640e
IOC: Domain: time-check-broker[.]com
IOC: Domain: basiconlineincome[.]com
IOC: Domain: registrar-servers[.]com
Insikt Group identified a multi-tiered infrastructure used by the ransomware group Rhysida — in combination with Recorded Future Network Intelligence, this discovery enabled identification of ransomware victims an average of 30 days before they appeared on public extortion sites. The first tier of infrastructure supports the initial access phase of the attack, consisting of typo-squatted domains, domains for search engine optimisation (SEO) poisoning, and payload servers. Subsequent tiers include CleanUpLoader C2 infrastructure for post-exploitation activities such as exfiltration, and a higher-tier infrastructure featuring an admin panel and a Zabbix monitoring server.
- Insikt Group uncovered Rhysida’s multi-tiered infrastructure, which consists of typo-squatted domains for SEO poisoning and payload servers for the infection process, CleanUpLoader C2 infrastructure for post-exploitation activities like exfiltration, and higher-tier infrastructure featuring an admin panel and a Zabbix monitoring server.
- CleanUpLoader, a backdoor primarily linked to Rhysida threat actors, is commonly delivered disguised as fake software installers for popular applications. It is often signed with valid digital certificates and includes multiple C2 domains for redundancy.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-23113 – Upgrade to the latest patched versions and migrate to fixed releases where necessary.
- CVE-2024-9463 – Customers must upgrade to Palo Alto Networks Expedition version 1.2.96 to patch this vulnerability.
- CVE-2024-30052 – Install the provided Security Update for Visual Studio.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
