Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
VMware Patches Critical SQL Injection Vulnerability in HCX Platform - On October 16, 2024, VMware addressed CVE-2024-38814, a high-severity SQL injection flaw in the HCX platform that could allow attackers to execute arbitrary queries and gain unauthorised data access. Immediate patching and activity reviews are recommended.
Kubernetes Patches Critical SSH Vulnerability, Affecting Kubernetes Image Builder - On October 14, 2024, Kubernetes fixed two vulnerabilities in its Image Builder tool: CVE-2024-9486, allowing root access via SSH using default credentials on Proxmox VMs, and CVE-2024-9594, enabling unauthorised modifications on VMs created with Nutanix, OVA, and QEMU. Users should update to version 0.1.38 or later to address this issue.
Quarkslab Discloses Four Vulnerabilities in Samsung Devices - On October 15, 2024, Quarkslab revealed vulnerabilities in the boot chain of several Samsung devices, including the Galaxy A225F. Key issues include CVE-2024-20832 (heap overflow), CVE-2024-20865 (authentication bypass), CVE-2024-20820 (read-out-of-bound), and CVE-2024-20021 (arbitrary memory mapping)., To date, no exploitations have been confirmed.
Potential Threats
Zendesk Email Spoofing Vulnerability Exposes Sensitive Support Tickets - A critical vulnerability in Zendesk, discovered by bug bounty hunter @hackermondev, allows attackers to exploit email spoofing to access sensitive support tickets for Fortune 500 companies. This flaw enables unauthorised access to internal systems by easily guessing ticket IDs, especially with Single Sign-On (SSO) configurations. It can also be exploited to gain access to a company’s internal Slack channels via Apple’s OAuth system.
Nidec Corporation Confirms Ransomware Attacks Followed by Data Breaches - A critical vulnerability in Zendesk, discovered by bug bounty hunter @hackermondev, allows attackers to exploit email spoofing to access sensitive support tickets for Fortune 500 companies. This flaw enables unauthorised access to internal systems by easily guessing ticket IDs, especially with Single Sign-On (SSO) configurations. It can also be exploited to gain access to a company’s internal Slack channels via Apple’s OAuth system.
Detecting Horus Protector with YARA - On October 8, 2024, SonicWall reported Horus Protector, a new malware distribution service advertised as fully undetectable (FUD). It delivers malware families like AgentTesla, Remcos, and NjRat through the Telegram group @Horus_Protector. The service uses multilayered propagation techniques, injecting malware into legitimate processes and employing persistence mechanisms to stay active while tracking antivirus detections for enhanced evasion.
General News
Cisco Confirms Security Incident After Hacker Offers to Sell Data - Cisco has confirmed a security incident after a hacker claimed to have stolen internal data, including sensitive employee information. The company is currently investigating the breach and has notified law enforcement to address the situation.
UK government inks five-year cloud and AI deal with Microsoft - The UK government has established a five-year partnership with Microsoft focused on cloud and artificial intelligence, aimed at enhancing public services and advancing digital transformation across various sectors. This initiative is part of the government's broader strategy to utilise cutting-edge technologies to boost efficiency and improve service delivery.
Internet Archive Breached Again Through Stolen Access Tokens - The Internet Archive has reported a security breach involving stolen access tokens, which allowed unauthorised access to its systems. This incident is the second breach within a year, raising concerns about the organisation's security measures.
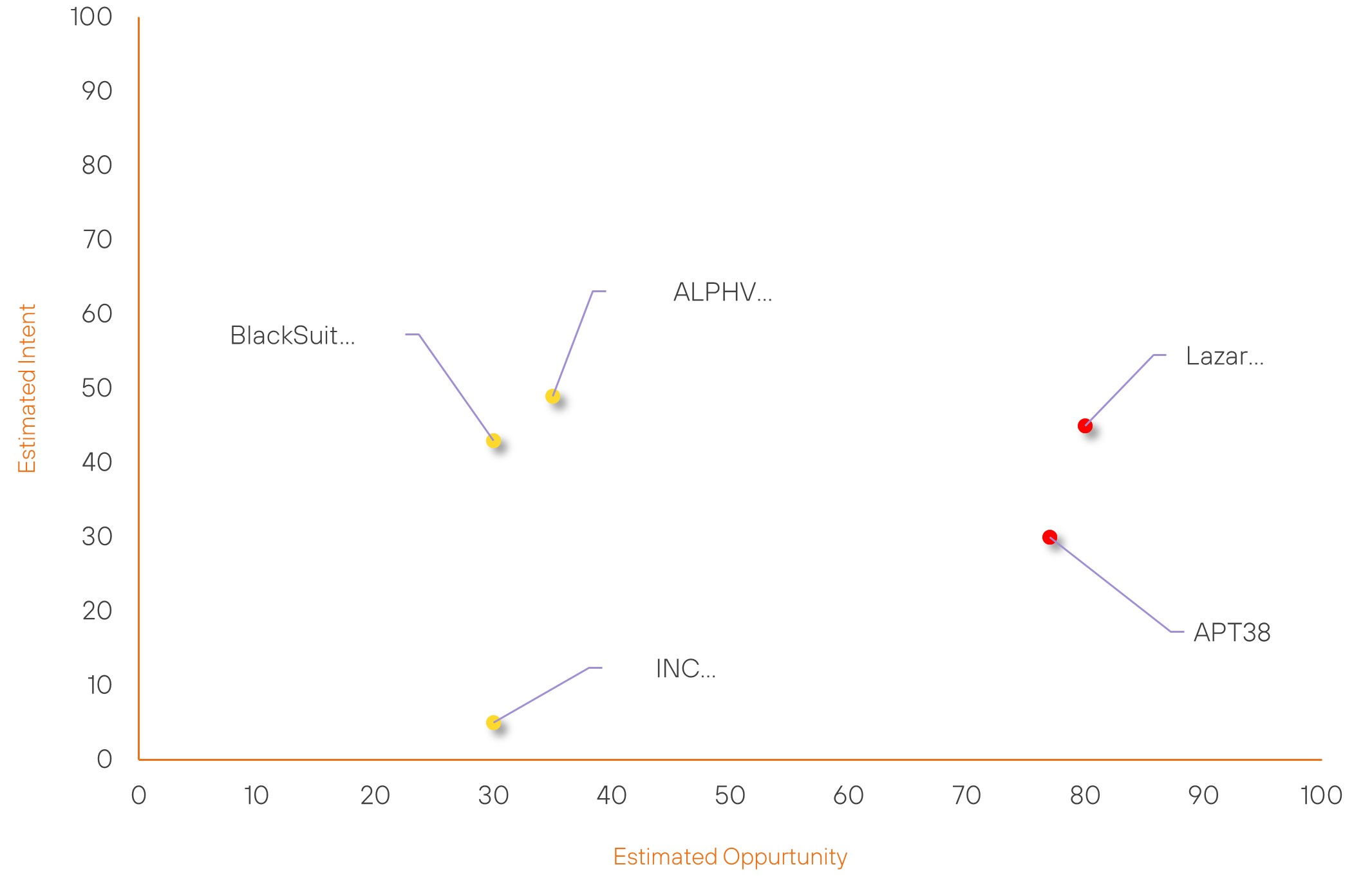
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lazarus Group | High | → | High | (80) | → 0 | (45) | ↑ 5 |
| APT38 | High | → | High | (77) | → 0 | (30) | ↑ 5 |
| INC RANSOM | Basic | → | Basic | (30) | → 0 | (5) | ↓ 21 |
| BlackSuit Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (30) | → 0 | (43) | ↑ 6 |
| ALPHV Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (35) | ↓ 5 | (49) | → 0 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USDoD | ▲ | Lockbit 3.0 | ▲ | CVE-2024-9264 | ▲ | Internet Archive | ▲ |
| RedGolf | ▲ | Babuk Ransomware | ▲ | CVE-2024-30090 | ▲ | Japan | ▲ |
| APT37 | ▲ | Phishing | ▲ | CVE-2024-37383 | ▲ | Transak Inc | ▲ |
| Anonymous | ▲ | DDoS | ▲ | CVE-2024-23113 | ▲ | Utilities | ▲ |
| Head Mare | ▲ | Disinformation | ▲ | CVE-2024-35250 | ▲ | Healthcare Providers | ▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Quarkslab Discloses Four Vulnerabilities in Samsung Devices
Source: Insikt Group, Quarkslab | Validated Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-20832 | CVVS Score: 7.1 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Medium – 30
CVE-2024-20865 | CVVS Score: 7.0 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Medium – 30
CVE-2024-20820 | CVVS Score: 4.6 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Medium – 25
CVE-2024-20021 | CVVS Score: 4.6 | Recorded Future Risk Score: Medium – 30
On October 15, 2024, Quarkslab published an analysis revealing multiple vulnerabilities in the boot chain of various Samsung devices, including the Galaxy A225F. Exploiting these vulnerabilities allows attackers to execute code in the bootloader, gain persistent root access, and leak sensitive data from the Secure World, such as Android Keystore keys.
Presented at BlackHat USA 2024, the research identifies two critical vulnerabilities in the Little Kernel:
- CVE-2024-20832: A heap overflow due to a custom JPEG parser that enables persistent code execution.
- CVE-2024-20865: An Odin authentication bypass that allows flashing arbitrary data to the device.
These vulnerabilities can be chained to bypass boot image verification and root the device. Additionally, two vulnerabilities in the Secure Monitor were discovered:
- CVE-2024-20820: A read out-of-bounds issue that leaks Secure Monitor memory.
- CVE-2024-20021: Allows mapping arbitrary physical memory to leak data.
Users are advised to apply software updates to mitigate these threats. More details and proof-of-concept exploits are available in the accompanying whitepaper and GitHub repository.
Detecting Horus Protector with YARA
Source: Insikt Group, SonicWall | TTP Instance | Hunting Package | YARA Rule
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: SHA256: a0966fffef49c8a67957c0e82ec1c44740a48c9638cbecfabf2a57a862114150
IOC: SHA256: 84deb128ce64d856ede811269d9962610c92ecc9d9fd4d07dde39a5de3a2f23d
IOC: SHA256: 1f30164da60635eb3b981fb302db2351aa57545ceb305b5db2e8344b3675d98c
IOC: IP ADDRESS: 144.91.79.54
On October 8, 2024, SonicWall reported on Horus Protector, a new malware distribution service claimed to be fully undetectable (FUD). It has been used to deliver malware families like AgentTesla, Remcos, and NjRat. Operated through the Telegram group @Horus_Protector, it offers subscription tiers ranging from $50 to $150 and collects unique hardware details for access management.
Horus Protector spreads malware using ZIP archives containing encoded Visual Basic (VBE) scripts and injects payloads into legitimate system processes, such as MSBuild.exe, to avoid detection. It communicates with a remote server at 144.91.79.54 and maintains persistence through Windows registry entries and scheduled tasks. The service also utilises kleenscan.com to evade antivirus detection.
Samples analysed by Insikt Group exhibited behaviours such as API hooking and reflective PE injection, and collecting system information, including geolocation data. The analysis also revealed connections to the command-and-control server and included the developer’s Telegram channel in the binaries. Insikt Group created a YARA rule to detect Horus Protector and provided indicators of compromise (IoCs) related to the samples.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2024-38814 – Upgrade to the latest patched versions to remediate this vulnerability
- CVE-2024-9486 and CVE-2024-9594 - Update the Kubernetes Image Builder to version 0.1.38 or later
- CVE-2024-20832 CVE-2024-20865, CVE-2024-20820 and CVE-2024-20021 - Update their devices with the latest firmware
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
