Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
Google Patches Six Security Vulnerabilities in Chrome - On September 17, 2024, Google updated Chrome to version 129.0.6668.58 across Windows, Mac, and Linux. This release addresses six security vulnerabilities discovered through external research and internal audits. Google advises users to update their browsers to mitigate potential risks. At the time of writing, there are no reports of these vulnerabilities being exploited in the wild.
CVE-2024-29847, PoC Exploit for Ivanti Endpoint Manager Released - Summoning Team security researchers have released a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2024-29847 on September 16, 2024. CVE-2024-29847 is a critical Ivanti Endpoint Manager (EPM) remote code execution (RCE). Ivanti released a patch for this vulnerability on September 10, 2024.
VMware Patches Critical and High-Severity Vulnerabilities in vCenter Server - On September 17, 2024, Broadcom released VMware Security Advisory VMSA-2024-0019. This advisory addresses critical and high-severity vulnerabilities in VMware vCenter Server, a management component of VMware vSphere and VMware Cloud Foundation.
Potential Threats
ServiceNow MisconKigurations Expose Sensitive Data in Over 1,000 Instances - Over a thousand ServiceNow instances have exposed sensitive corporate data due to conXiguration errors, security researcher Aaron Costello of AppOmni reported on September 17, 2024. These misconXigurations likely allowed unauthorised access to critical information, including personally identiXiable information (PII), system details, and access credentials.
Threat Actors Use Automatic Email Responses to Deliver Xmrig Miner - Unnamed threat actors distributed XMRig cryptocurrency miners using phishing links in email auto-replies of compromised accounts, according to a report by F.A.C.C.T. Cybersecurity Center on September 19, 2024. This malware delivery method is notable as it involves the victim initiating the communication, making the auto-reply appear less suspicious.
Malware Campaign to Steal Google Credentials via Kiosk Mode - Threat actors are using an AutoIt script that Amadey malware initially deploys to lock victims' browsers in kiosk mode to steal Google credentials. As reported by OALabs Research on September 11, 2024, this script searches for available browsers on the infected machine and forces one to launch the Google login page in full-screen mode.
General News
Dell Investigates Potential Data Breach Following Employee Data Leak - On September 20, 2024, American technology company Dell disclosed through BleepingComputer an ongoing investigation into a data breach allegedly exposing sensitive information of over 10,800 employees from the company and its partner organisations.
FBI says it recently dismantled a second major China-linked botnet - The FBI led an operation last week to disrupt a global botnet with connections to the Chinese government, much like its action against the Volt Typhoon hacking group earlier this year, bureau Director Christopher Way said Tuesday.
UK regulator stops LinkedIn from training AI models with British users’ content - LinkedIn recently began harnessing its users’ content and data to train artiXicial intelligence models, opting all platform participants into the program without formal notice — except for users in the United Kingdom and Europe.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
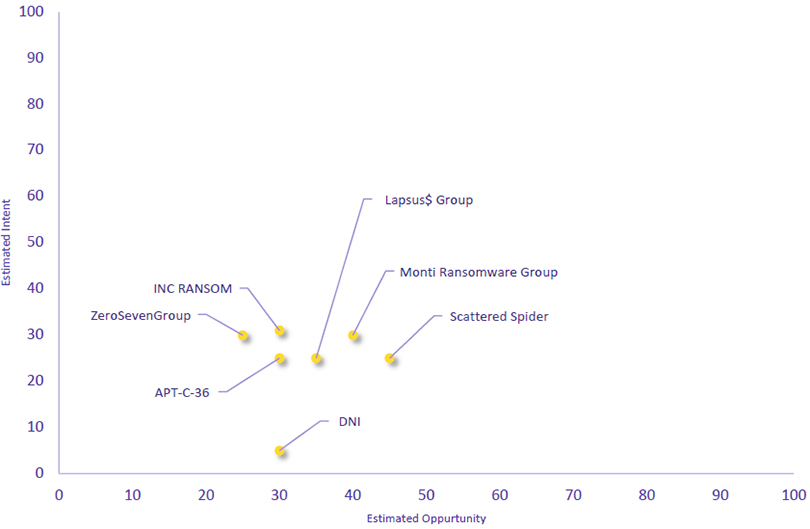
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group’s severity. These updates can be seen below.
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Change | Opportunity Change | Intent Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNI | New | → | Basic | (30) | ↑ 30 | (5) | ↑ 5 |
| Monti Ransomware Group | Basic | → | Basic | (40) | ↑ 10 | (30) | → 0 |
| Lapsus$ Group | Basic | → | Basic | (35) | ↑ 5 | (25) | → 0 |
| APT-C-36 | Basic | → | Basic | (35) | ↑ 5 | (25) | → 0 |
| ZeroSevenGroup | Basic | → | Basic | (25) | → 0 | (30) | ↑ 5 |
| Scattered Spider | Basic | → | Basic | (45) | ↓ 4 | (25) | → 0 |
| INC RANSOM | Basic | → | Basic | (30) | → 0 | (31) | ↓ 10 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren’t disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Twelve | ▲ | Agenda Ransomware |
▲ | CVE-2024-36401 | ▲ | DIN | ▲ |
| Pioneer Kitten | ▲ | Cobalt Strike | ▲ | CVE-2023-31315 | ▲ | European Union | ▲ |
| Blitz | ▲ | Spear Phishing | ▲ | CVE-2024-20017 | ▲ | Hong Kong | ▲ |
| LockBit Gang | ▲ | Wcry | ▲ | CVE-2024-43461 | ▲ | Rockstar Games | ▲ |
| NDT SEC | ▲ | Mirai | ▲ | CVE-2024-8190 | ▲ | Dell Technologies, Inc. |
▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
VMware Patches Critical and High-Severity Vulnerabilities in vCenter Server; No Active Exploitation Observed.
Source: Insikt Group, VMware | Vulnerability Intelligence
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
CVE-2024-38812 | CVVS Score: 9.8 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 79
CVE-2024-38813 | CVVS Score: 7.5 | Recorded Future Risk Score: High – 38
On September 17, 2024, Broadcom released VMware Security Advisory VMSA-2024-0019. This advisory addresses critical and high-severity vulnerabilities in VMware vCenter Server, a management component of VMware vSphere and VMware Cloud Foundation.
Broadcom says it has not found evidence that the CVE-2023-34048 RCE bug is currently exploited in attacks. Admins who are unable to immediately apply today's security updates should strictly control network perimeter access to vSphere management components and interfaces, including storage and network components, as an ofgicial workaround for this vulnerability is unavailable.
CVE-2024-38812: This critical vulnerability arises from a heap overglow in the implementation of the Distributed Computing Environment / Remote Procedure Call (DCERPC) protocol within VMware's vCenter Server. If exploited, this vulnerability could allow unauthenticated threat actors to perform remote code execution.
CVE-2024-38813: This high-severity vulnerability permits privilege escalation within VMware’s vCenter Server. It arises from improper handling of network packets. If exploited, a threat actor with network access could escalate their privileges to root by sending a designed network packet.
Amadey Deploys AutoIt Script in Malware Campaign to Steal Google Credentials via Kiosk Mode.
Source: Insikt Group, OALabs Research | Validated Intelligence Event
Intelligence Cards: Intelligence & Reports
IOC: 31[.]41[.]244[.]11
IOC: 185[.]215[.]113[.]103
IOC: SHA256: 53aeb2fd2ee3a30d29afce4d852e4b33e96b0c473240691d6d63796caa3016f2
IOC: SHA256: 78f4bcd5439f72e13af6e96ac3722fee9e5373dae844da088226158c9e81a078
IOC: SHA256: 0ec952da5d48ceb59202823d7549139eb024b55d93c2eaf98ca6fa99210b4608
IOC: SHA256: 99e3eaac03d77c6b24ebd5a17326ba051788d58f1f1d4aa6871310419a85d8af
IOC: SHA256: b119eb3e182224d5399b12f7f106ffd27a0f12dd418a64aa23425000adbc44de
A malware campaign uses the unusual method of locking users in their browser's kiosk mode to annoy them into entering their Google credentials, which are then stolen by information-stealing malware.
Threat actors are using an AutoIt script that Amadey malware initially deploys to lock victims' browsers in kiosk mode to steal Google credentials. As reported by OALabs Research on September 11, 2024, this script searches for available browsers on the infected machine and forces one to launch the Google login page in full-screen mode.
The script also disables the 'ESC' and 'F11' keys, preventing users from closing or minimising the browser. Furthermore, Amadey facilitates the deployment of StealC, an information stealer that exploits the credentials entered during the session.
Once the user enters their credentials, StealC malware immediately compromises the data by extracting it from the browser's credential store. This method combines forced user interaction with direct data extraction to capture login details efgiciently.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned above be fully patched and updated. We want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches should they apply:
- CVE-2024-38812, CVE-2024-38813 – Apply the latest security updates
- CVE-2024-29847– Apply the latest updates and “hot patches” for EPM 2024 and EPM 2022.
- Google Chrome – Ensure all versions of Chrome are updated to the latest release.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing the searching and hunting activities within your environment.
