Executive Summary -
Highlights of Cyber Threat Intelligence Digest
Vulnerabilities
SolarWinds Patches Remote Code Execution (RCE) Vulnerability CVE-2025-26399 Affecting Web Help Desk - SolarWinds has released a patch for a critical remote code execution vulnerability, CVE-2025-26399, found in Web Help Desk versions 12.8.7 and earlier. The flaw could allow unauthenticated attackers to run malicious commands on affected systems.
Although no active exploitation has been reported, security experts strongly advise organisations to apply the update without delay. Insikt Group recommends upgrading to Web Help Desk version 12.8.7 hotfix 1 to ensure protection against potential attacks.
Google Patches Four Chrome Vulnerabilities Including Actively Exploited CVE-2025-10585 V8 Type Confusion Vulnerability in Google Chrome - Google has patched four Chrome vulnerabilities, one of which, CVE-2025-10585, was already being actively exploited. This flaw, a type confusion issue in the V8 JavaScript engine, could enable attackers to execute arbitrary code. The other vulnerabilities include two use-after-free flaws in Dawn and WebRTC, and a heap buffer overflow in ANGLE, all of which could lead to remote code execution if exploited.
While exploitation of the remaining flaws has not been observed, security teams are urged to update Chrome promptly. The patched versions are 140.0.7339.185/.186 for Windows and Mac, and 140.0.7339.185 for Linux. Organisations should also enable automatic updates and closely monitor deployments to ensure patches are applied swiftly across all systems.
Threat Actors Exploit GeoServer Vulnerability (CVE-2024-36401) to Access US Federal Agency Network - On 23 September 2025, CISA confirmed that unknown threat actors exploited CVE-2024-36401, a remote code execution flaw in GeoServer, to breach a Federal Civilian Executive Branch agency. The vulnerability, disclosed in June 2024 and added to CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities list the following month, enabled attackers to compromise two GeoServers and persist inside the network for about three weeks before detection.
The attackers used Burp Suite to identify the flaw, then executed scripts, cron jobs and web shells to maintain access. They created accounts, scanned the network with fscan, and brute-forced credentials to move laterally to web and SQL servers, where they deployed tools such as China Chopper. Attempts were made to escalate privileges via the Dirty COW vulnerability (CVE-2016-5195). They also used .php shells, abused BITS jobs, and staged files to avoid detection, while relying on the Stowaway proxy tool for command-and-control traffic.
Potential Threats
Lockbit 5.0 Linux and ESXi RaaS Samples Analysed on MalwareBazaar - On 17 September 2025, Insikt Group published an analysis of the Lockbit 5.0 Windows version, a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) that emerged in September 2019. On 20 September 2025, a MalwareBazaar user submitted Lockbit 5.0 Linux and ESXi samples. Sandbox analysis flagged the samples as malicious, with the Linux version also demonstrating defence evasion and ransomware capabilities. Execution actions include retrieving system and kernel information, monitoring its own process, rotating Syslog files, and reloading rsyslog’s configuration, likely for detection avoidance or persistence. The ESXi sample retrieves the installed VMware version.
The Lockbit 5.0 Linux sample additionally renames itself, retrieves CPU attributes, encrypts files appending a random sixteen-character extension, and drops a ransom note, “ReadMeForDecrypt.txt,” in multiple directories. The note instructs victims to contact the actors via a Tor chat service and references Lockbit’s leak site. This analysis includes Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) from the examined samples.
US-Based Cybersecurity Company SonicWall Confirms Cloud Backup Breach After Targeted Brute-Force Attack Exposes Firewall Configurations - On 18 September 2025, SonicWall disclosed a security incident in which threat actors accessed firewall configuration backup files stored in MySonicWall cloud accounts. Attackers used brute-force techniques against the cloud backup API and obtained preference files for fewer than 5% of deployed firewalls.
Although the files were encrypted, they contained sensitive information such as authentication tokens, shared secrets, and device settings that could allow further exploitation. SonicWall notified affected customers through account banners and stated there is no evidence the files were leaked online. The company also confirmed the incident was unrelated to ransomware.
Iranian State-Sponsored Threat Group Nimbus Manticore Targets European Defense, Telecom, and Aerospace Sectors Using MiniJunk and MiniBrowse Malware - On September 22, 2025, Checkpoint reported that an Iranian state-sponsored threat group, Nimbus Manticore, has been targeting Western European defense, telecommunications, and aviation industries in a long-running campaign. Nimbus Manticore used recruiter-themed spearphishing to deliver the MiniJunk backdoor and MiniBrowse stealer.
The infection chain begins with a recruiter-themed spearphishing link that directs victims to a fake career portal. After authenticating with pre-shared credentials, victims download a malicious archive and run a legitimate Setup.exe, which sideloads userenv.dll. Setup.exe then launches SenseSampleUploader.exe.
General News
Major European airports work to restore services after cyberattack on check-in systems - Europe’s busiest airports are still facing disruptions after a suspected ransomware attack on Collins Aerospace, a U.S. aviation technology provider, which affected its vMUSE self-service check-in software. The outage, starting Friday night, impacted airports in London, Brussels, Berlin and Dublin, causing long queues, flight delays, and cancellations. ENISA confirmed the incident was a “third-party ransomware” attack, though the ransomware type and threat actor remain undisclosed.
Brussels Airport cancelled nearly half of Monday’s departures, while Dublin and Heathrow continued partial operations with manual check-in and baggage processing. Berlin saw some improvement, but delays persisted. Collins Aerospace and parent company RTX said the impact was limited to electronic check-in and baggage drop, with manual systems providing a workaround. The aviation sector has faced multiple cyber incidents recently, including attacks on Russian airports and a July breach of Qantas, with U.S. authorities warning of threats from groups such as Scattered Spider.
Jaguar Land Rover extends shutdown again following cyberattack - Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) has extended the shutdown of its global operations until at least next month following a cyberattack, halting all vehicle and parts production since early September. The company is working with cybersecurity experts, the NCSC and law enforcement to safely restart operations. The shutdown directly affects over 30,000 employees, with thousands of agency and temporary workers sent home or on reduced pay, while unions have called for a furlough scheme to support staff.
The cyberattack is causing major supply-chain disruptions, impacting around 150,000 associated jobs and causing significant financial losses, estimated at £50-70 million per day. Government officials, including the business secretary and minister for industry, have engaged with JLR and its suppliers to assess support measures, though no direct taxpayer funding is planned. Analysts warn the incident represents a broader economic security concern, with supplier shares, such as Autins, already plummeting due to the disruption.
GitHub tightens npm security with mandatory 2FA, access tokens - GitHub is introducing new security measures to defend against supply-chain attacks that recently compromised thousands of accounts and private repositories, causing significant data loss and remediation costs. Recent incidents include the “s1ngularity” attack in August, the “GhostAction” campaign in early September, and the worm-like “Shai-Hulud” attack. To reduce risks, GitHub will gradually enforce two-factor authentication (2FA) for local publishing, adopt short-lived granular tokens, expand trusted publishing, deprecate classic tokens and TOTP 2FA, and restrict publishing access by default. Developers, particularly NPM maintainers, are urged to switch to trusted publishing, enable 2FA, and use WebAuth instead of TOTP.
Ruby Central has also announced tighter governance over the RubyGems package manager following similar attacks, including campaigns distributing 60 malicious gems and typosquatting popular projects. Until new policies are finalised, only Ruby Central staff will hold admin access, with a future shift planned towards a transparent, community-led model. Both platforms emphasise that supply-chain security is a collective responsibility, and developers are expected to adopt the enhanced protections to safeguard their ecosystems.
Threat Actor Weekly Graph
Over the past 7 days, we have been tracking the following intent and opportunity changes within our Threat Actor Landscape.
Intent represents the potential targets of a group. When a group is observed attacking a different organisation or entity, their intent will increase.
Opportunity represents the various methods and technologies these groups may use. For example, if a group started using a new attack vector, such as a new kind of ransomware, their opportunity would increase.
Both intent and opportunity are scored out of 100 and are responsible for scoring the group's severity. These updates can be seen below.
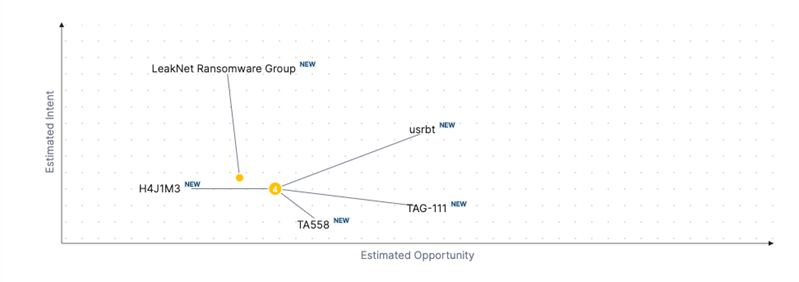
| ● Limited Severity | ● Basic Severity | ● Moderate Severity | ● High Severity |
| Threat Actor | Severity Increase | Opportunity | Intent | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| usrbt | NEW | → | ● Basic | NEW | → | ● 30 | NEW | → | ● 26 |
| H4J1M3 | NEW | → | ● Basic | NEW | → | ● 30 | NEW | → | ● 25 |
| LeakNet Ransomware Group | NEW | → | ● Basic | NEW | → | ● 25 | NEW | → | ● 30 |
| TAG-111 | NEW | → | ● Basic | NEW | → | ● 30 | NEW | → | ● 25 |
| TA558 | NEW | → | ● Basic | NEW | → | ● 30 | NEW | → | ● 25 |
Global Trends Powered by Recorded Future
Within each category, we have provided the current top five globally trending items. Each item is linked to how actively trending it is and is marked with a small symbol.
The spikes in references are calculated over 60 days and are normalised to ensure they aren't disproportionate when compared to bigger entities that will naturally have more baseline mentions.
▲- Spike – This indicates a large increase in reporting volume and a high diversity in the event descriptions,
▲- Rise – This indicates a small increase in reporting volume with little diversity in the descriptions.
| Attackers | Methods | Vulnerabilities | Targets | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lapsus$ Group | ▲ |
Exploit |
▲ | CVE-2025-51591 | ▲ |
Collins Aerospace |
▲ |
|
KillSecurity Ransomware Group |
▲ |
BadIIS |
▲ | CVE-2025-10585 | ▲ |
United Technologies |
▲ |
|
Anonymous |
▲ |
Ransomware |
▲ | CVE-2025-36401 | ▲ |
Brussels |
▲ |
|
Hobi |
▲ |
DDos |
▲ | CVE-2025-59689 | ▲ |
Berlin |
▲ |
|
Lab Dookhtegan |
▲ |
Supply Chain Attack |
▲ |
CVE-2025-48061 |
▲ |
Gambling and Casinos |
▲ |
Prominent Information Security Events
Iranian State-Sponsored Threat Group Nimbus Manticore Targets European Defense, Telecom, and Aerospace Sectors Using MiniJunk and MiniBrowse Malware
Source: Insikt Group | Validated Intelligence Event
IOC: SHA256 Hash - bc9f2abce42141329b2ecd0bf5d63e329a657a0d7f33ccdf78b87cf4e172fbd1
IOC: SHA256 Hash - 954de96c7fcc84fb062ca1e68831ae5745cf091ef5fb2cb2622edf2358e749e0
IOC: SHA256 Hash - 9ec7899729aac48481272d4b305cefffa7799dcdad88d02278ee14315a0a8cc1
On September 22, 2025, Checkpoint reported that an Iranian state-sponsored threat group, Nimbus Manticore, has been targeting Western European defense, telecommunications, and aviation industries in a long-running campaign. Nimbus Manticore used recruiter-themed spearphishing to deliver the MiniJunk backdoor and MiniBrowse stealer.
The infection chain begins with a recruiter-themed spearphishing link that directs victims to a fake career portal. After authenticating with pre-shared credentials, victims download a malicious archive and run a legitimate Setup.exe, which sideloads userenv.dll. Setup.exe then launches SenseSampleUploader.exe.
Nimbus Manticore then copies Setup.exe to %AppData%\Local\Microsoft\MigAutoPlay\ as MigAutoPlay.exe, places userenv.dll, creates a scheduled task for persistence, and executes MigAutoPlay.exe to load MiniJunk. MiniJunk collects host identifiers, executes command-and-control (C2) commands for file I/O, process creation, DLL loading, and chunked exfiltration, while the MiniBrowse component, later deployed by Nimbus Manticore, steals browser credentials and sends them to rotating HTTPS C2 servers.
The campaign leveraged Cloudflare fronting and Azure App Service for resilient C2, signed and inflated binaries, and applied heavy compiler-level obfuscation to evade detection.
Lockbit 5.0 Linux and ESXi RaaS Samples Analysed on MalwareBazaar
Source: Insikt Group | TTP Instance
IOC: SHA 256 Hash - 4dc06ecee904b9165fa699b026045c1b6408cc7061df3d2a7bc2b7b4f0879f4d
IOC: SHA 256 Hash - 90b06f07eb75045ea3d4ba6577afc9b58078eafeb2cdd417e2a88d7ccf0c0273
On 17 September 2025, Insikt Group published a TTP Instance detailing an analysis of the Lockbit 5.0 Windows version. Lockbit is a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) that first emerged in September 2019 and has since evolved to target multiple platforms. On 20 September 2025, a MalwareBazaar user submitted samples of the Lockbit 5.0 Linux and ESXi versions.
Sandbox analysis detected the samples as malicious due to their discovery capabilities. The Linux version additionally demonstrated defence evasion and ransomware behaviours, matching the sandbox rule for detecting the Lockbit ransomware family. Upon execution, the samples perform several actions on a victim’s machine, including retrieving runtime system information from the /proc virtual filesystem, monitoring their own processes to prevent debugging, and retrieving the kernel version using the “uname” system call. The Linux version also rotates log files for the Syslog service and reloads rsyslog’s configuration, likely to evade detection, maintain persistence, or support privilege escalation. The ESXi sample executes a shell command to identify the installed VMware version.
The Lockbit 5.0 Linux sample also renames itself, retrieves CPU attributes, encrypts the victim’s files with a random sixteen-character extension, and drops a ransom note named “ReadMeForDecrypt.txt” in multiple directories. The note instructs victims to contact the threat actors through a Tor-based chat support service and references Lockbit’s leak site. This analysis includes Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) associated with the examined Lockbit 5.0 samples, providing valuable information for defensive measures and detection efforts.
Remediation Actions
Following the information provided above, we recommend that the technologies mentioned be fully patched and updated. We also want to highlight and recommend applying the following patches where applicable:
- CVE-2025-26399: To prevent threat actors from exploiting CVE-2025-26399, we recommend upgrading to Web Help Desk version 12.8.7 hotfix 1 to ensure protection against potential attacks.
- CVE-2025-10585: We recommend organisations apply the latest Google Chrome updates, as well as enabling automatic updates and closely monitoring deployments to ensure patches are applied promptly across their environments.
- CVE-2024-36401: We recommend organisations apply the latest patch, 2.25.2, to ensure this vulnerability has been remediated successfully.
If you are currently an Acumen Cyber Vulnerability Management customer, we will be proactively performing related searching and hunting activities within your environment.
